Trochanteric bursitis after hip replacement: causes, symptoms and treatment
Mild complication after total hip replacement: trochanteric bursitis (bursitis)
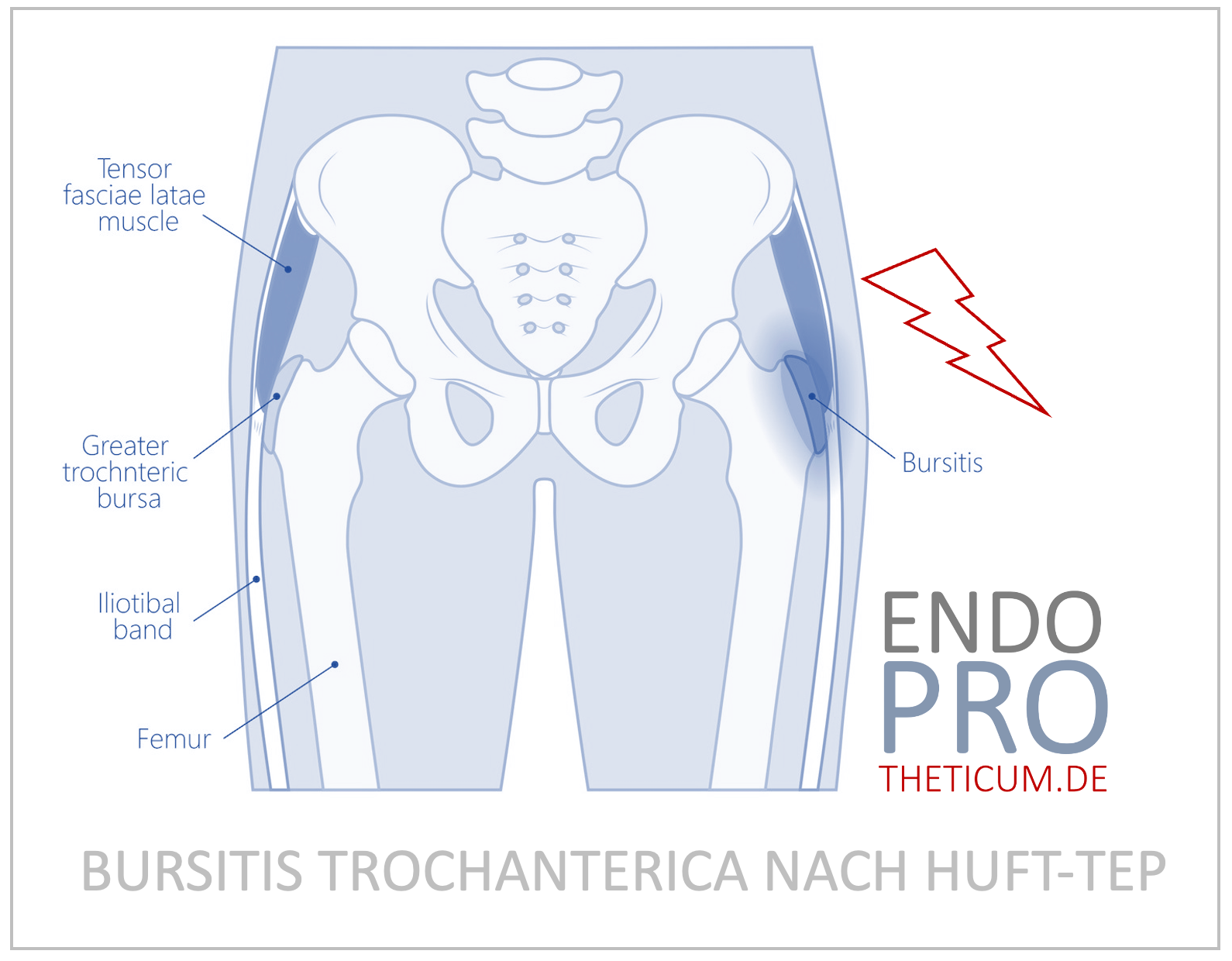
Trochanteric bursitis , also known as hip bursitis , is a painful condition often associated with hip joint replacement. The bursa on the greater trochanter plays an important role in reducing friction between muscles, tendons and bones. After hip replacement implantation, biomechanical changes can put stress on this area, causing temporary inflammation.
Hip prosthesis is a proven method for treating coxarthrosis and other serious joint diseases. However, post-operative complications such as trochanteric bursitis can occur, delaying recovery and affecting the quality of life of those affected. This article details the causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Frequency and significance of trochanteric bursitis after hip replacement
Statistics: Studies show that trochanteric bursitis affects approximately 4-10% of patients who receive hip replacements. It is therefore one of the most common causes of pain after a successful operation.
Significance: The disease has serious effects on the mobility of patients. Pain when lying on the affected side, climbing stairs or during everyday activities can significantly reduce the quality of life. In addition, chronic inflammation can lead to long-term symptoms.
Causes and risk factors
- Mechanical irritation: After the insertion of a hip prosthesis, changes in biomechanics or misalignments can lead to increased stress on the bursa.
- Muscle Imbalances: Weaknesses or imbalances in the hip muscles can increase stress on the greater trochanter and promote bursitis.
- Postoperative complications: In rare cases, infection or inadequate healing after surgery can lead to inflammation of the bursa.
Biomechanical changes after prosthesis implantation: After a hip prosthesis, the force transmission to the surrounding soft tissues changes. These mechanical stresses can irritate the bursa.
Prosthesis position: An often overlooked factor is the placement of the prosthesis. Incorrect angle of the prosthetic shaft or socket can cause excessive stress on the trochanter area.
Other risk factors:
- Obesity: Higher body weight increases the stress on the hip region.
- Activity: Sporting activities with high stress on the hips can inflame the bursa.
- Soft tissue problems: Shortened or inflamed tendons, especially of the iliotibial band, can worsen the symptoms.
Symptoms of trochanteric bursitis
Local pain: Pain typically occurs over the greater trochanter. These are intensified by pressure, e.g. B. when lying on your side or during certain movements.
Restrictions on movement: Patients often report restrictions when climbing stairs or getting up from a sitting position.
Differentiation from other diseases: Trochanteric bursitis must be differentiated from lumbosciatica, piriformis syndrome or problems with the hip prosthesis itself. Imaging diagnostic procedures help here.
diagnosis
Clinical examination: An experienced orthopedist can make a suspected diagnosis using targeted pressure tests and movement checks.
Imaging procedures:
- Ultrasound: Depiction of inflammatory processes.
- MRI: Exact localization of the inflammation.
- X-ray: Rule out prosthesis loosening or misalignment.
Differential diagnoses: Conditions such as tendonitis or insertional tendinopathy can cause similar symptoms.
Treatment options for trochanteric bursitis: Conservative approaches
Drug therapy:
- NSAIDs: pain and inflammation relief.
- Cortisone injections: targeted treatment of inflammation.
Shockwave therapy: Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive method in which high-energy sound waves are applied specifically to the affected area. It can promote healing, relieve pain and improve blood circulation in tissues. This form of therapy is particularly suitable for patients with chronic complaints that do not respond adequately to other conservative measures.
Physiotherapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises reduce the strain on the bursa.
Shoes and aids: Orthopedic insoles can compensate for incorrect loading.
Minimally invasive and surgical treatments (rarely recommended)
When is an operation necessary? In the case of chronic complaints or a lack of response to conservative therapies.
Arthroscopic procedures: minimally invasive removal of the inflamed bursa.
Open operations: correction of misalignments or relief of neighboring structures.
Significance of prosthesis positioning in the development of trochanteric bursitis
Biomechanics of the prosthesis: Correct implantation avoids incorrect loading, which can lead to trochanteric bursitis.
Preventive measures: Modern navigation systems and patient-specific prostheses contribute to better positioning.
Prevention of trochanteric bursitis
Physiological movement patterns: Targeted movement therapy before and after surgery.
Individual load control: Avoiding overuse by gradually increasing activity.
Optimized rehabilitation: Use of special rehabilitation programs that are tailored to prosthesis care.
Frequently asked patient questions
Can trochanteric bursitis be permanently cured? Yes, with targeted therapy the chances of recovery are high.
How long does the therapy last? Typically 1-3 months, depending on severity.
Summary
Trochanteric bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa above the greater trochanter of the thigh bone. This bursa serves as a buffer between bones and tendons to minimize friction. In some cases, such inflammation can occur after a hip replacement
Trochanteric bursitis following hip replacement is a treatable complication. Early diagnosis and individually tailored therapy are crucial to relieve pain and restore hip function.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .