Artificial joint in young people - when is it too early for a joint replacement?
Artificial joint replacement at a young age - exception or new reality?

Just a few decades ago, artificial joint replacement a medical procedure reserved exclusively for older people – typically those over 65 suffering from advanced osteoarthritis. However, this view has changed dramatically. Increasingly, younger patients , meaning people under 55 or even under 40, are opting for hip replacement , knee replacement , or partial knee replacement because the pain, limited mobility, and restrictions in daily life leave them with no other options.
In an active society where physical mobility, sports, employment, and quality of life are central values, the demand for permanent joint replacement is growing louder, even at a younger age . Many people ask themselves: When is the right time? And when is it too early? This blog provides well-founded, up-to-date, and easily understandable answers to these questions.
Chapter 1: Definition – What is an artificial joint?
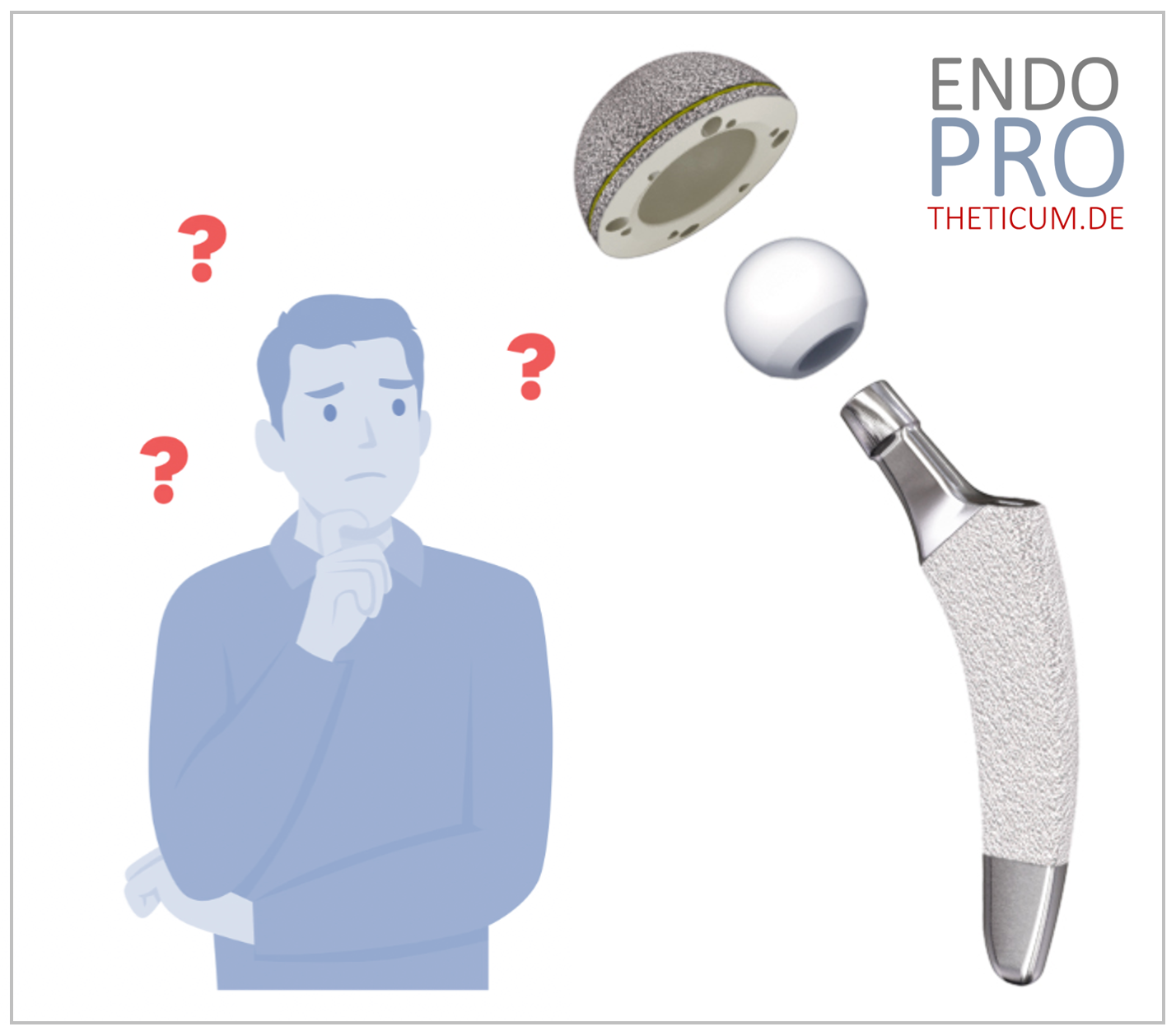
An artificial joint , also an endoprosthesis , permanently replaces the function of a diseased natural joint. It is usually made of metal alloys, ceramic, or highly cross-linked plastic (polyethylene) and is firmly anchored in the bone – either cementless (press-fit), cemented, or a hybrid method.
The most frequently used endoprostheses in Germany are:
- Total hip replacement (THR)
- The total knee endoprosthesis (TEP)
- Partial joint replacement , e.g., unicompartmental knee replacement for isolated osteoarthritis of one knee compartment
The goal of joint replacement is to relieve pain, restore joint function and improve quality of life in the long term – regardless of age.
Structure of an endoprosthesis
The basic construction can be well explained using the example of a hip replacement:
- Hip socket: Inserted into the pelvis, often made of titanium, sometimes with a ceramic insert
- Hip stem: Anchored in the femur, supports the head
- Head component: Made of ceramic or metal, it slides in the pan.
Knee replacements as follows:
- Monocondylar prosthesis (unicompartmental prosthesis) – replaces only one part of the joint
- Bicondylar prosthesis (knee replacement) – replaces the entire joint (usually femorotibial on both sides)
- Patellofemoral prosthesis – only for the kneecap joint, rare
Chapter 2: Who is considered "young" in the context of joint replacement?
In endoprosthetics, the term "young" is not a fixed age limit, but a relative concept. The following classifications are generally used in medical literature and clinical practice:
- < 40 years – very young
- 40–55 years – young
- 55–65 years – middle age
- > 65 years – classic joint replacement area
An artificial joint is viewed as particularly critical in people under 50 – not because it is technically impossible, but because in this age group the risk of premature loosening , later surgery and higher mechanical loads is particularly high.
However, there are exceptions: Those who suffer from chronic pain, can no longer cope with everyday life, and have exhausted conservative therapies – may receive a hip or knee replacement , provided the indication is correct.
Chapter 3: Figures & Trends – Why more and more young people are receiving artificial joints
The number of artificial joint in Germany has been rising steadily for years – and the increase is particularly noticeable among younger patients under 60 , and sometimes even under 40 are opting for a hip replacement , knee replacement , or partial knee replacement .
Current statistics: Knee and hip replacements by age group
According to the German Medical Technology Association (BVMed) and the German Endoprosthesis Registry (EPRD), the following is evident:
- Approximately 450,000 joint replacement surgeries are performed annually in Germany
- Of these, over 240,000 are hip replacements and over 190,000 are knee replacements.
- The proportion of patients under 60 years of age is steadily increasing – for hip replacements it is already over 15 %
- In the case of knee replacements, patients under 65 years of age even make around a third of the cases.
In the USA, a particularly significant trend became visible: Between 2000 and 2017, the number of knee replacements in 45- to 64-year-olds increased by 188% , and hip replacements by 123% – and this trend is similar in Europe.
Why this increase?
Several factors explain why more and more young people are opting for joint replacement :
- More active lifestyle:
Many people today remain physically active for longer – jogging, tennis, mountain hiking or CrossFit lead to higher stress and therefore also earlier joint wear and tear. - Earlier diagnosis:
Thanks to MRI, arthroscopy and improved imaging, joint damage is now detected and documented earlier. - Growing expectations for quality of life:
Young patients are not willing to live with pain and functional limitations for decades. The desire for an unrestricted lifestyle is greater than ever. - Improved implants and techniques:
Modern prostheses last significantly longer today. Studies show survival rates of over 90% after 20 years – making them more attractive for younger patient groups as well. - Specialization of centers:
Highly specialized endoprosthetics centers such as the ENDOPROTHETICUM Mainz enable even complex treatment at a young age with individually adapted implants.
Typical scenarios
A physically active 42-year-old man has been suffering for years from post-traumatic knee osteoarthritis following an accident in his youth. Conservative treatments no longer provide relief. A partial knee replacement offers him the possibility of living largely pain-free again – without having to give up sports. The decision wasn't easy, but for him it's the right step.
Anna, 34 years old, employed, athletically active, and mother of a young child, has suffered from bilateral hip dysplasia . Despite previous joint-preserving surgeries and years of conservative therapy (physiotherapy, injections, pain medication), her condition deteriorated significantly: the pain increased, her mobility decreased, and her limping became noticeable. After only a few minutes of walking, she had to stop, and nighttime pain disrupted her sleep. Jogging, yoga, or prolonged sitting were hardly possible anymore. It was also a very difficult decision, but a short-stem hip has brought the patient back to life.
Chapter 4: When is joint replacement medically advisable at a young age?
The decision to have an artificial joint at a young age always involves weighing medical necessity , individual circumstances , and the long-term consequences of surgery. While age was almost automatically considered a contraindication in the past, modern orthopedic guidelines now consider the degree of suffering and functional capacity as decisive factors for the indication.
Important criteria for determining the indication for treatment in young people
Joint replacement – be it a total hip replacement , total knee replacement , or partial knee replacement – can be medically advisable for younger patients if:
- Conservative therapy has been exhausted:
Physiotherapy, painkillers, injections (e.g. hyaluronic acid, cortisone), orthoses, weight reduction and other measures have been used for at least 6 months – without lasting success. - There are severe limitations in everyday life:
The joint causes such severe pain that everyday movements such as walking, climbing stairs or sitting are no longer possible – or only with medication. - Painful resting pain occurs:
Pain that also occurs at night or during periods of rest is considered a serious warning sign of a serious joint pathology. - Imaging shows advanced destruction:
X-ray or MRI images show pronounced osteoarthritis (stage III–IV according to Kellgren and Lawrence), joint deformities or axial deviations. - The quality of life suffers massively:
Social, family or professional life is significantly restricted by the damaged joint.
Typical underlying diseases that necessitate an endoprosthesis at a young age
The cause of premature joint wear is often not age-related , but lies in certain pre-existing conditions. These include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune diseases
- Congenital malformations (e.g. hip dysplasia)
- Perthes disease or epiphyseal separation in childhood
- Aseptic bone necrosis (e.g., AVN of the femoral head due to cortisone therapy or alcohol abuse)
- Post-traumatic osteoarthritis following accidents or sports injuries
- Early meniscus or cartilage surgeries that lead to instability
- Incorrect loading due to axial deviations (e.g. X-leg or O-leg)
- Chronic joint infections
the medical necessity partial joint replacement such as a unicompartmental knee replacement even in 30- to 40-year-olds
Beware of misdiagnoses or hasty decisions!
Especially in young patients, there is a risk of prematurely making a diagnosis or misjudging the cause of the pain. It is essential to consider the following points:
- Not every pain means osteoarthritis – soft tissue problems , such as patellar tendinitis , runner's knee , trochanteric bursitis or sacroiliac joint blockages , can also cause severe discomfort.
- A thorough clinical examination is essential. Clinical correlation with imaging findings must always be present.
- Patients should always a second opinion from a specialized center such as the ENDOPROTHETICUM in Mainz before having an endoprosthesis implanted.
Joint replacement at a young age is not a mistake – if the indication is correct . For many patients, it can even be a turning point towards greater quality of life, mobility, and future prospects. Crucially, however, it requires careful consideration , specialized diagnostics , and treatment by experienced endoprosthetics experts .
Chapter 5: Which prosthesis is the right one for a young person?
Choosing the right implant is particularly critical for younger patients. While long-term pain relief and rapid rehabilitation are often paramount for older people, younger patients also need to consider aspects such as durability, activity level, bone preservation, and revision options .
The goal must be to preserve the natural joint for as long as possible , and if replacement is unavoidable, as tissue-sparing and modular . This requires precise individual assessment of the indications , sound experience, and modern implant technology.
Total joint replacement vs. partial joint replacement – When is which option appropriate?
1. Total endoprosthesis (knee replacement, hip replacement)
- Complete joint replacement
- In hip surgery: replacement of the femoral head and the acetabulum
- In the case of the knee: replacement of the femoral and tibia joint surfaces
- Advantages: long lifespan, proven technology, also suitable for advanced osteoarthritis
- Disadvantages: increased bone loss, possible limitations during very strenuous physical activity
Suitable for:
Younger patients with multiple joint compartment osteoarthritis (e.g., femoropatellar and medial gonarthrosis simultaneously) or in cases of rheumatic diseases
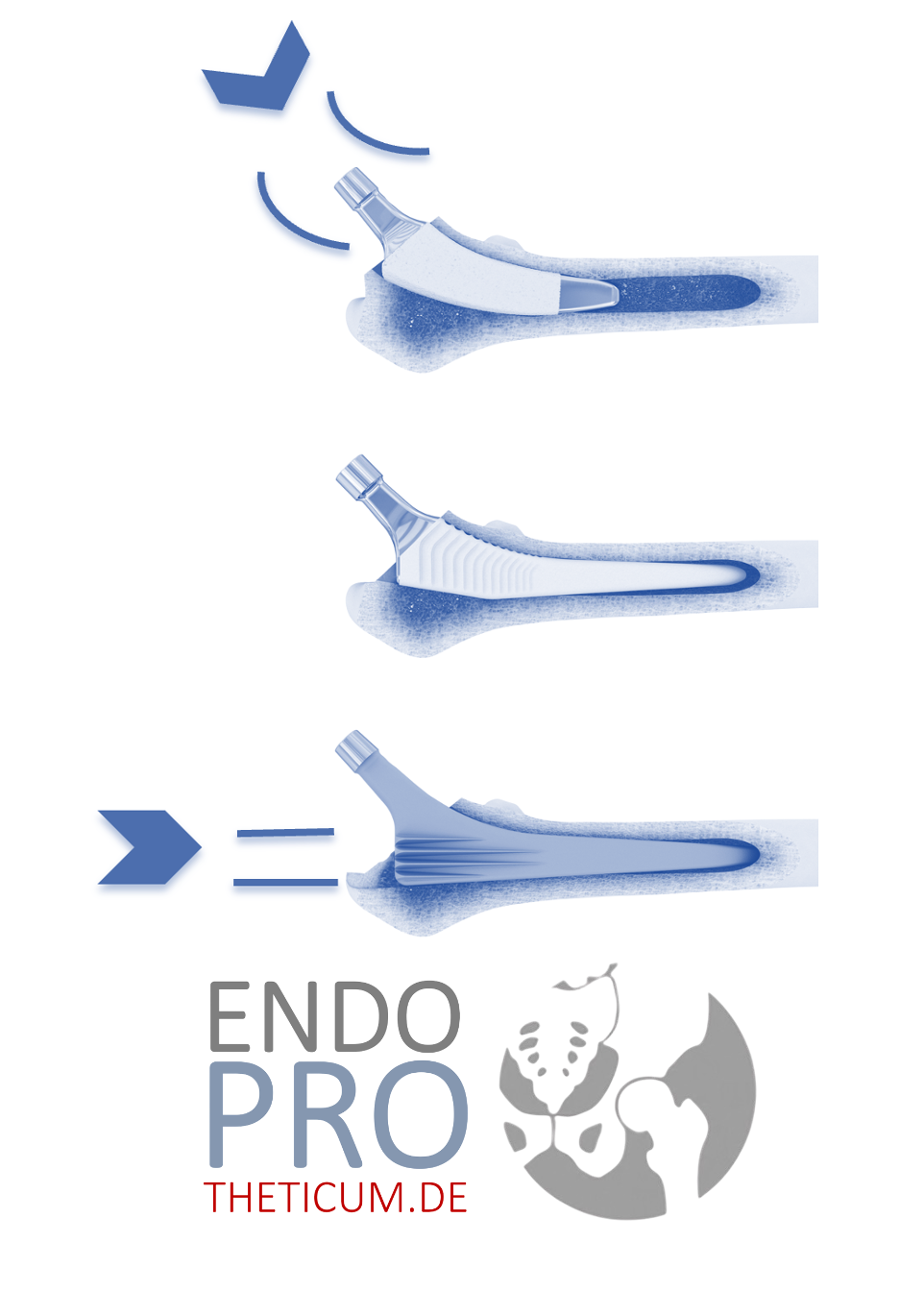
2. The unicompartmental knee replacement (sliding prosthesis)
- Replacement of only the medial or lateral joint component in the knee
- The healthy bone, ligaments, and cartilage in the rest of the joint are preserved
- Advantages: Gentle on bones and soft tissues, faster rehabilitation potential, more natural movement patterns
- Disadvantages: Not suitable for inflammatory diseases or advanced osteoarthritis in multiple joint components
Suitable for:
Younger patients with isolated medial or lateral gonarthrosis – often as a result of malalignment or meniscus loss
3. Patellofemoral joint replacement
- Special form of partial prosthesis for isolated osteoarthritis of the kneecap
- Often occurs in cases of dysplasia or patellar malalignment at a young age
Hip replacements: cementless, short stem or surface replacement?
a) Cementless hip replacement
- Standard practice among younger people today
- Enables good integration of the prosthesis into the bone (so-called "press-fit" technique)
- Especially suitable for patients with good bone quality
- Advantages: better future revision options
b) Short stem prosthesis
- Specifically designed for younger patients
- Saves bone mass in the femoral neck
- Improved proprioceptive sense and biomechanically more favorable
- Especially suitable for hip dysplasia or after Perthes disease
c) Surface replacement (resurfacing)
- Rarely, but indicated in special cases (especially in young athletic men with good bone quality)
- Advantage: maximum bone preservation
- Disadvantage: Metal-to-metal contact and potential abrasion problems
Factors influencing the choice of prostheses at a young age
- Bone substance and bone quality
- Axle ratios and misalignments
- Type of disease (e.g., degenerative vs. inflammatory)
- Professional requirements
- Sporting ambitions
- Body weight and mobility
- Individual anatomy (e.g., in cases of dysplasia or leg length discrepancies)
Why choosing the right implant is crucial
Especially in younger patients, the likelihood of needing revision surgery later in life significantly increased. Therefore, individualized, forward-looking planning is crucial. In specialized centers like the ENDOPROTHETICUM in Mainz, not only is the appropriate prosthesis selected, but the surgical technique and long-term strategy are also individually tailored.
Chapter 6: What young patients need to know after surgery
An artificial joint at a young age represents a significant life change – but also a great opportunity for a new lease on life, freedom from pain, and increased mobility. However, for the implant to last as long as possible what happens after the operation is crucial . Young patients often have different lifestyle requirements than older people – and that's precisely what makes comprehensive aftercare so important.
The first phase after surgery: rehabilitation and mobilization
Following hip replacement , knee replacement , or partial knee replacement, rehabilitation usually begins on the day of surgery or the following day. At the curaparc-clinic in Mainz, under the direction of Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner, particular emphasis is placed on rapid, structured mobilization – tailored to the individual patient's capacity and the type of prosthesis.
Typical sequence of events:
- Day 1: initial mobilization with physiotherapy, first steps with crutches, full weight-bearing usually allowed from the start
- Weeks 1–2: Training of mobility, coordination, gait pattern
- Weeks 3–6: Increasing workload, building muscle strength
- Weeks 6–12: Transition to normality, return to everyday life
The goal is to regain mobility as soon as possible without overloading the implant. Finding the right balance is crucial – as is close coordination between the surgeon, physiotherapist, and rehabilitation team.
Special requirements of young patients with artificial joints
Unlike seniors, many young people want to go back to their old ways after surgery:
- to do sports
- be professionally active
- Looking after or lifting children
- Going on vacation , traveling, or driving a car
- Some even competitive sports or physically demanding activities (e.g. crafts, agriculture).
Therefore, differentiated aftercare is crucial. The following sporting activities are usually possible after 3–6 days.
Individual sports clearance must always be issued by the treating center.
Strategies for prosthesis durability
Even though modern hip and knee replacements now achieve a lifespan of 15 to 25 years , younger patients are almost always at increased risk of early loosening , abrasion or wear and tear – simply due to their more active lifestyle.
Tips for long-term prosthesis function:
- Avoiding excess weight:
Every kilogram of body weight exerts a force 3–5 times greater on the joint.
Goal: Keep BMI below 30. - Correct gait pattern:
Avoid incorrect loading through protective posture; use insoles or orthoses if necessary. - high-performance sports:
Avoid impact loads (e.g., jumps, rapid changes of direction). - Physiotherapy for proprioception and stability:
Especially important in the case of total knee replacement or unicompartmental knee replacement to stabilize the ligamentous apparatus. - No more need for long-term pain medication – but get any new pain checked out quickly!
What about work-related stress?
Many young patients are in the prime of their careers. For physically demanding jobs (e.g., nursing, construction, catering), a return to work may be possible after 2–4 months – sometimes requiring adjustments or retraining.
After joint replacement surgery, the success of the operation is only half the battle. Especially at a young age, aftercare crucial for long-term success. Those who follow the recommendations, remain active – but don't overdo it – can lead a long, fulfilling, and pain-free life with an artificial joint. Personalized aftercare is key to maximum durability and quality of life.
What distinguishes the ENDOPROTHETICUM?
✅ Specialization in modern endoprosthetics for young people
Unlike many other facilities, the ENDOPROTHETICUM is not a general hospital , but a highly specialized center for joint replacement. It places particular emphasis on complex cases, revision surgeries , and the care of young patients for whom other clinics hesitate or prematurely recommend total joint replacement.
✅ Individual implant selection instead of a "one-size-fits-all" approach
Thanks to the extensive experience of Prof. Kutzner and his team, modern, joint-preserving procedures such as partial knee replacement, patellofemoral replacement, or short-stem implants routinely offered. Surgery is never performed "blindly"—but rather based on:
- Body structure and anatomy
- Occupational and sporting stress
- Bone quality
- Type and extent of osteoarthritis
- Long-term perspective
✅ Use of state-of-the-art technologies
- Digital surgical planning with 3D imaging
- Tissue-sparing minimally invasive techniques
- Special anesthesia techniques for maximum tolerability and rapid mobilization
✅ Personal support from Prof. Dr. Kutzner himself
Many patients appreciate that the diagnostics, consultation, surgery, and aftercare are not overseen by rotating resident physicians , but are personally supervised by Prof. Kutzner . This fosters trust, security, and high quality.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .