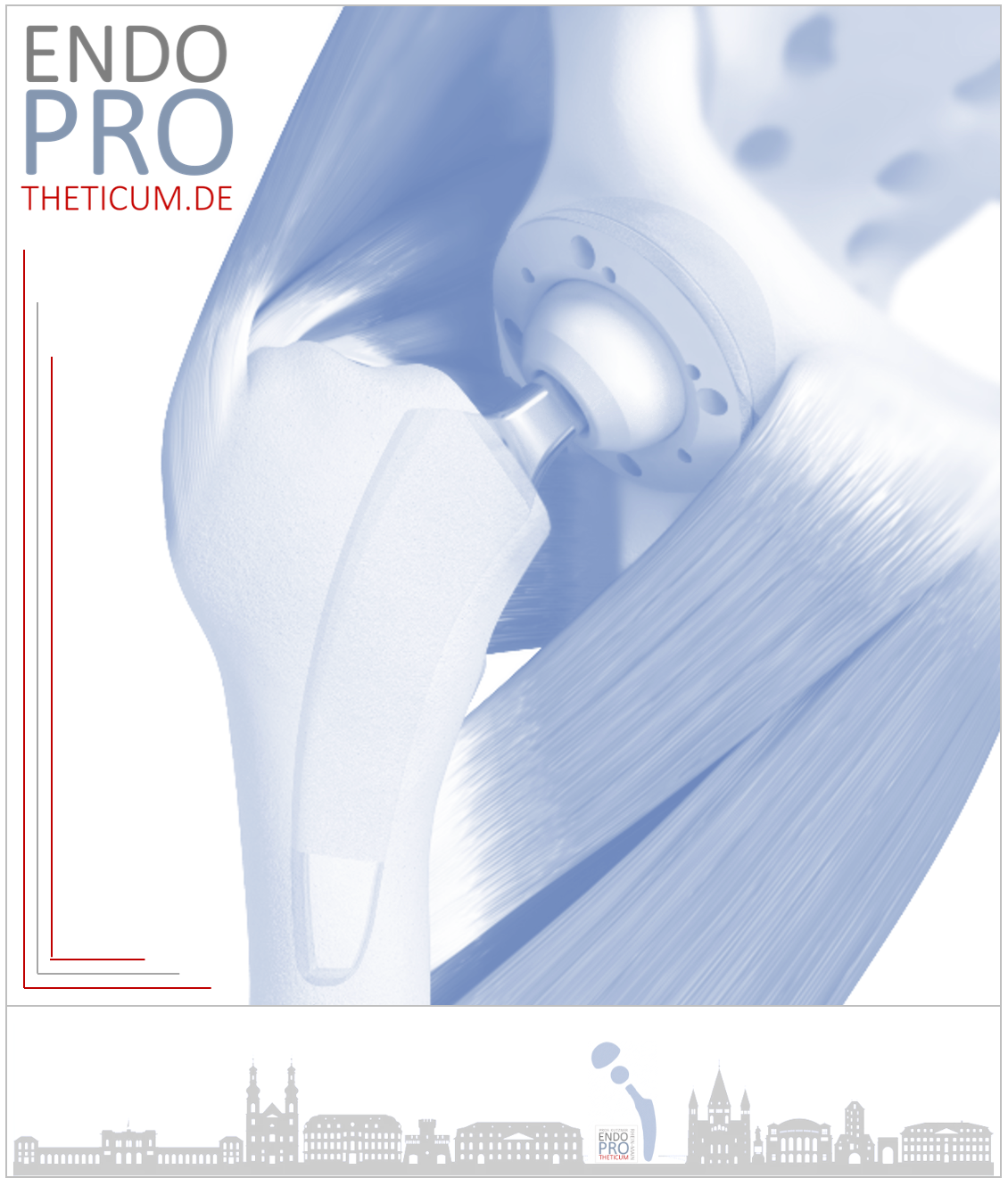
Short-Stem Total Hip Replacement: The Future of Hip Arthroplasty Surgery
Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty: Advantages, Recovery & Top Implants Explained

When hip pain becomes unbearable and everyday activities feel like an uphill battle, a total hip replacement can be life-changing. But not all hip replacements are the same — and in recent years, short-stem total hip arthroplasty has emerged as a groundbreaking alternative to traditional hip implants.
Whether you're an active individual looking to preserve mobility or a younger patient seeking a long-lasting solution, short-stem implants offer faster recovery, improved joint mechanics, and better bone preservation — making them an increasingly popular choice among both patients and surgeons.
But what exactly makes a short-stem hip replacement different from the traditional method? And which short-stem implant is suitable for you?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know — from the principles behind short-stem technology to comparative analyses of leading implants — helping you make an informed, confident decision about your hip health.
Let's explore why short-stem total hip arthroplasty is reshaping the future of hip replacements — and how it could transform your quality of life.
1. Introduction
Total hip arthroplasty (THA), commonly known as hip replacement surgery, has been a transformative procedure in orthopedic medicine, offering relief and improved mobility to countless individuals suffering from hip joint disorders. In recent years, the advent of short-stem implants has introduced a new dimension to hip replacement options, aiming to preserve more bone and potentially offer better outcomes for certain patient populations. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of short-stem total hip arthroplasty, exploring its benefits, surgical techniques, patient selection criteria, and more.
2. Anatomy of the Hip Joint
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket synovial joint, comprising the femoral head (the ball) and the acetabulum of the pelvis (the socket). This joint structure allows for a wide range of motion, enabling activities such as walking, running, and sitting. The joint's stability is maintained by a combination of ligaments, tendons, and muscles, all working in harmony to facilitate movement and bear the body's weight.
3. Understanding Hip Arthritis
Arthritis, especially osteoarthritis, is a major cause of hip pain and disability. This degenerative condition is the result of gradual wear and tear on the cartilage that cushions the hip joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Other forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can also affect the hip joint, causing inflammation and joint damage.
4. Advances in Hip Replacement Surgery
The journey of hip replacement surgery began in the early 20th century, with significant advancements over the decades. Traditional hip replacements involved longer stems inserted deep into the femur for stability. While effective, these designs could lead to complications such as bone loss and stress shielding. The development of short-stem implants emerged as a solution to these challenges, offering a bone-preserving alternative that aligns with the body's natural biomechanics.
5. What is Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty?
Short-stem total hip arthroplasty involves the use of a femoral implant with a reduced stem length compared to traditional designs. These implants are designed to fit into the proximal femur, preserving more of the patient's natural bone and potentially offering a more physiological load distribution. This approach aims to reduce the risk of complications associated with longer stems and improve patient outcomes.
6. Indications for Short-Stem Hip Replacement
Short-stem hip replacements are particularly suitable for younger, active patients with good bone quality. They are also considered for patients requiring revision surgeries where bone preservation is crucial. However, patient selection is critical, and factors such as bone density, anatomy, and overall health play a significant role in determining the appropriateness of this implant type.
7. Advantages of Short-Stem Implants
The benefits of short-stem implants include:
- Bone Preservation: By conserving more of the femoral bone, these implants facilitate easier future revisions if necessary.
- Improved Biomechanics: Short-stem designs aim to mimic the natural biomechanics of the hip, potentially leading to better functional outcomes.
- Reduced Stress Shielding: The design promotes a more natural load distribution, minimizing the risk of bone resorption associated with stress shielding.
8. Surgical Techniques in Short-Stem Hip Arthroplasty
The surgical approach for short-stem hip arthroplasty requires meticulous planning and execution. Surgeons must be familiar with the specific implant system and its instrumentation. The procedure involves precise bone preparation to ensure optimal implant fit and stability. Minimally invasive techniques may be used to reduce soft tissue damage and promote faster recovery.
9. Postoperative Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation is a crucial component of successful hip replacement surgery. Patients usually start weight-bearing activities shortly after surgery, with a structured physiotherapy program to restore strength, flexibility, and function. Adherence to rehabilitation protocols is essential to achieve the best possible outcomes.
10. Potential Complications and Their Management
While short-stem hip arthroplasty offers numerous benefits, potential complications can occur:
- Implant Loosening: Proper surgical technique and patient selection are vital to minimize this risk.
- Breaks: Fractures during surgery can occur, particularly in patients with poor bone quality.
- Infection: Strict aseptic techniques and perioperative antibiotics are employed to reduce infection rates.
11. Long-Term Results and Success Rates
Research has demonstrated encouraging outcomes with short-stem implants, featuring high survival rates and satisfactory functional results. Nevertheless, long-term data is still being gathered, and ongoing research is crucial to fully comprehend the durability and performance of these implants over time.
12. Comparing Short-Stem with Conventional Hip Replacements
When comparing short-stem to traditional hip replacements, key factors to consider include:
- Bone Conservation: Short-stem implants offer superior bone preservation.
- Patient Characteristics: Younger, active patients may benefit more from short-stem designs.
- Revision Surgery: Bone preservation with short-stem implants can facilitate easier revision procedures if needed.
13. Patient Selection Criteria (continued)
- Younger Patients: Typically under 60 years old, who are more likely to require revision surgery later in life, benefit from the bone-preserving nature of short-stem implants.
- Active Individuals
- Good Bone Density: Patients with healthy, dense bone in the proximal femur are ideal candidates, as this ensures optimal stability and reduces the risk of implant loosening or subsidence.
- Patients Seeking Quicker Recovery: Short-stem implants, often placed using minimally invasive techniques, are associated with faster recovery times, making them appealing to those who prioritize a speedy return to daily activities.
However, short-stem implants may not be suitable for patients with severe osteoporosis, complex deformities, or significant bone loss. In such cases, traditional long-stem implants may provide more reliable fixation.
14. Advancements and Future Directions in Hip Arthroplasty
Short-stem total hip arthroplasty represents a significant advancement in joint replacement technology — but innovations continue to evolve to improve outcomes further.
- 3D Printing and Custom Implants: Advances in 3D printing are enabling the creation of custom-designed short-stem implants tailored to each patient's unique anatomy. This customization may improve stability, reduce wear, and enhance durability.
- Biocompatible Coatings: New surface coatings, such as hydroxyapatite or porous titanium, promote better bone integration and enhance the implant's longevity.
- Smart Implants: Emerging technologies may incorporate sensors within the implant to monitor load distribution, alignment, and early signs of loosening or wear, enabling proactive management of complications.
- Minimally Invasive Robot-Assisted Surgery: The use of robotic systems is becoming more common in orthopedic surgery. These systems improve accuracy in implant placement, which is particularly helpful for short-stem procedures where precise positioning is crucial for stability.
- Tissue-Sparing Techniques: Future surgical approaches may further minimize soft tissue disruption, accelerating recovery while maintaining long-term stability and function.
15. Conclusion
Short-stem total hip arthroplasty is transforming hip replacement surgery. By focusing on bone preservation, enhancing biomechanics, and facilitating quicker recovery, this innovative method is especially suitable for younger, active patients and those seeking a more natural joint sensation.
While long-term studies are ongoing, current data suggests that short-stem implants offer comparable — if not superior — outcomes to traditional long-stem designs. However, patient selection remains critical to ensure optimal results.
With advancements in implant materials, surgical techniques, and emerging technologies like 3D printing and robotic assistance, the future of short-stem total hip arthroplasty looks promising. For patients considering hip replacement, consulting with an experienced orthopedic surgeon who specializes in this technique is essential to determine whether a short-stem implant is the right choice for their individual needs.
Whether you're an active adult seeking faster recovery or a younger patient prioritizing bone preservation for future revisions, short-stem total hip arthroplasty offers a promising path to restored mobility, pain relief, and a better quality of life.
Comparison of Leading Short-Stem Implants
Short-stem implants are not one-size-fits-all. Below is a detailed comparison of the most widely used and clinically studied models:
16.1. Optimys (Mathys)
- Design Characteristics:
- Anatomically adapted stem with a lateral curvature that mimics natural femoral anatomy.
- Collarless design to allow for metaphyseal anchoring and physiological load transfer.
- Material: Titanium alloy featuring a roughened surface to enhance bone integration.
- Advantages:
- Bone-preserving proximal fixation minimizing the risk of thigh pain.
- Excellent rotational stability is achieved due to an optimized design that fits tightly in the metaphysis.
- Reduced risk of stress shielding due to anatomical load distribution.
- Clinical Outcome: Studies report high primary stability and low rates of migration. It’s the most successful short-stem in terms of revision rates.
- Ideal Candidate: Young, active adults with good bone density.
16.2. MiniHip (Corin) Implant
- Design Characteristics:
- Designed to preserve more of the femoral neck than other short-stem options, promoting natural biomechanics.
- Short, straight design facilitating easier insertion via minimally invasive approaches.
- Material: Titanium alloy with a hydroxyapatite coating to enhance bone integration.
- Advantages:
- Improved stability due to greater preservation of the femoral neck.
- Facilitates improved leg length and offset restoration, resulting in more natural hip mechanics.
- Excellent outcomes in patients with mildly abnormal proximal femur anatomy.
- Clinical Outcome: Long-term studies show promising survivorship, with bone remodeling patterns similar to natural hip biomechanics.
- Ideal Candidate
16.3. Metha (Aesculap)
- Design Characteristics:
- Tapered stem for enhanced metaphyseal fixation.
- Material: Titanium alloy with a roughened surface for long-term fixation.
- Advantages:
- Excellent primary stability encouraging early weight-bearing.
- Allows for individual anatomical reconstruction, suitable for complex hip shapes.
- Clinical Outcome: Reported to demonstrate excellent survivorship with low rates of loosening, even in complex anatomical situations.
- Ideal Candidate: Patients with superior bone quality to ensure effective metaphyseal fixation.
16.4. Nanos (Smith & Nephew)
- Design Characteristics:
- Short, curved stem with metaphyseal fixation and reduced distal stress.
- Collarless design for enhanced proximal load transfer.
- Material: Titanium alloy with a porous surface for enhanced bone bonding.
- Advantages:
- Preserves maximum bone stock, making it ideal for future revisions.
- High primary stability, even with less invasive surgical techniques.
- Low incidence of thigh pain, common in longer stems.
- Clinical Outcome: Proven long-term durability and excellent rotational stability, even in younger and active individuals.
- Ideal Candidate: Younger patients who may need future revisions or those seeking quicker recovery with minimally invasive techniques.
16.5. Fitmore (Zimmer Biomet)
- Design Characteristics:
- Unique modular stem design optimized for proximal fill to enhance stability.
- A progressive curvature adapts to different femoral morphologies.
- Material: Titanium alloy with a porous coating for faster bone ingrowth.
- Advantages:
- Versatile design suitable for various femoral anatomies and sizes.
- Supports minimally invasive surgical techniques.
- Maintains natural femoral loading to prevent stress shielding.
- Clinical Outcome: Demonstrated excellent clinical outcomes with low rates of loosening and subsidence.
- Ideal Candidate: Patients with varying femoral anatomies, particularly those requiring customization for leg length or offset.
Final Considerations for Selecting a Short-Stem Implant
Each short-stem implant design offers unique benefits suited to different patient profiles.
- For young, active patients prioritizing bone preservation and future revision options, Nanos and MiniHip stand out.
- For patients with anatomical abnormalities, Metha and Fitmore provide more customization and adaptability.
- For straightforward primary hip replacements with a focus on early weight-bearing and faster recovery, Optimys provides robust stability and load distribution.
Ultimately, the most suitable short-stem implant is determined by a combination of the patient's anatomy, the surgeon's experience, and long-term treatment objectives.
Patient Decision Guide: Selecting the Appropriate Short-Stem Implant
When patients are informed they require a hip replacement, the numerous implant options can be overwhelming. This section provides a step-by-step breakdown to help patients and caregivers make informed decisions in consultation with their surgeon.
19.1. Step 1: Understand Your Personal Needs
Before exploring implant brands, it's crucial to assess your needs for hip replacement. Ask yourself:
- How active should I be after surgery?
- If you are active in sports, hiking, or dancing, implants designed for high stability (e.g., Nanos, MiniHip) may be the most suitable option for you.
- How significant is bone preservation for me?
- Younger patients who may need a revision in the future should consider bone-preserving designs like Nanos or MiniHip.
- Do I have any distinct anatomical characteristics?
- Patients with anatomical variations may benefit from adjustable modular implants like Metha or Fitmore.
19.2. Step 2: Consult with Your Orthopedic Surgeon
Bring your questions to the consultation. Here's what to ask:
- Which short-stem implants do you use most often, and why?
- What are the pros and cons of each implant for my specific case?
- How does my bone quality and hip anatomy affect the choice?
- What are the long-term outcomes for this implant in patients like me?
19.3. Step 3: Evaluate Your Long-Term Objectives
A hip replacement is designed to last 15–25 years or more. Think about:
- Future revision surgery: Short-stem implants aid in preserving bone, making future revisions more manageable.
- Return to activity: If you want to return to strength training, cycling, or other low-impact sports, ensure your implant supports those goals.
- Lifestyle factors: For instance, frequent travelers may prefer an implant with quicker recovery potential.
Post-Surgery Rehabilitation Guide: Regaining Mobility After Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty
The journey doesn’t end after surgery — rehabilitation is where the real transformation happens. A successful recovery helps ensure the implant stays stable, functional, and pain-free for years to come.
20.1. Phase 1: Early Recovery (0–6 Weeks)
Objective: Protect the implant and restore basic mobility.
- Weight-bearing: Most short-stem implants allow immediate weight-bearing, but follow your surgeon’s guidance.
- Exercises: Gentle ankle movements, leg slides, and seated knee extensions can help prevent stiffness and reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Walking: Begin with a walker or crutches, then gradually transition to a cane as your strength and mobility improve.
✅ Pro tip: Avoid deep bending,usin twisting, or crossing your legs to prevent dislocation during the first 2 weeks.
20.2. Phase 2: Strength and Mobility (6–12 Weeks)
Goal: Enhance hip stability and flexibility.
- Exercises: Include seated leg raises, light squats, and side leg lifts to enhance hip strength.
- Balance training: Standing on one leg (with support) enhances stability.
- Walking progression: Increase daily walking distances, aiming for 20–30 minutes per day.
✅ Pro tip: Swimming and stationary cycling are excellent low-impact alternatives to maintain cardiovascular fitness.
20.3. Phase 3: Return to Activity (3–6 Months)
Goal: Restore full functionality and resume light activities.
- Strength training: Focus on compound exercises like squats and lunges — but avoid heavy weights to minimize implant stress.
- Cardiovascular exercise: Walking, swimming, and cycling remain ideal. Avoid running or jumping sports to prevent implant wear.
- Stretching: Incorporate gentle stretches for the hip flexors, glutes, and hamstrings to prevent stiffness.
✅ Tip: Pay attention to your body. Mild soreness is normal, but sharp pain isn't — consult your surgeon if needed.
20.4. Long-Term Care (6 Months and Beyond)
Objective: Maintain muscular strength, prevent potential complications, and enjoy your new hip joint.
- Strength training: Continue with light weight training, focusing on controlled movements and proper form.
- Cardiovascular exercise: Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are recommended for long-term health.
- Lifestyle modifications: Keep a healthy weight to reduce unnecessary stress on the implant.
✅ Pro tip: Regular follow-ups are essential. X-rays monitor implant stability and check for loosening or wear.
Frequently Asked Questions from Patients about Short-Stem Implants
To wrap things up, let's tackle a few common questions:
Q: Can I still play sports with a short-stem implant?
A: Yes — but low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and strength training are safest. High-impact sports like running or tennis may accelerate implant wear.
Q: How long do short-stem implants last?
A: Studies show excellent durability, often matching or exceeding traditional longer stems. Many short-stem implants demonstrate
95%+ survivorship at 10–15 years.
Q: Is a short-stem implant better for younger patients?
A: Typically, yes! Short-stem implants preserve more bone, making future revisions easier — an important consideration for younger, active patients.
Q: Are there any disadvantages to short-stem implants?
A: While the benefits are significant, short-stem implants might not be ideal for patients with severe osteoporosis or unusual hip anatomy. Your surgeon will determine the best course of treatment for you.
Final Thoughts: A New Era for Hip Replacement
Short-stem total hip arthroplasty represents a revolution in hip replacement surgery. From faster recovery to improved biomechanics and bone preservation, short-stem implants are transforming patient outcomes — particularly for younger, active adults.
By understanding the various designs, weighing the advantages and disadvantages, and following a dedicated rehabilitation program, patients can feel confident they're making the best decision for their health and future mobility.
Take the Next Step: Is Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty Right for You?
Hip pain shouldn’t control your life — and with modern advancements like short-stem total hip arthroplasty, it doesn’t have to. These innovative implants offer faster recovery, better bone preservation, and a more natural feel compared to traditional long-stem designs.
Whether you're an active adult eager to maintain mobility, a younger patient looking to preserve bone for future revisions, or someone seeking a smoother, faster recovery — short-stem technology could be the ideal solution for your needs.
👉 Your next step?
- Consult your orthopedic surgeon about short-stem implants and whether they're suitable for your specific condition.
- Ask specific questions about implant brands, surgical techniques, and expected outcomes.
- Seek a second opinion if you're uncertain — particularly if your lifestyle or age makes preserving bone stock crucial.
The future of hip replacement is here — and it's lighter, stronger, and more patient-focused than ever before. Take charge of your hip health today — because you deserve a pain-free, active future.
Make an Appointment?
You can easily make an appointment both by phoneand online .