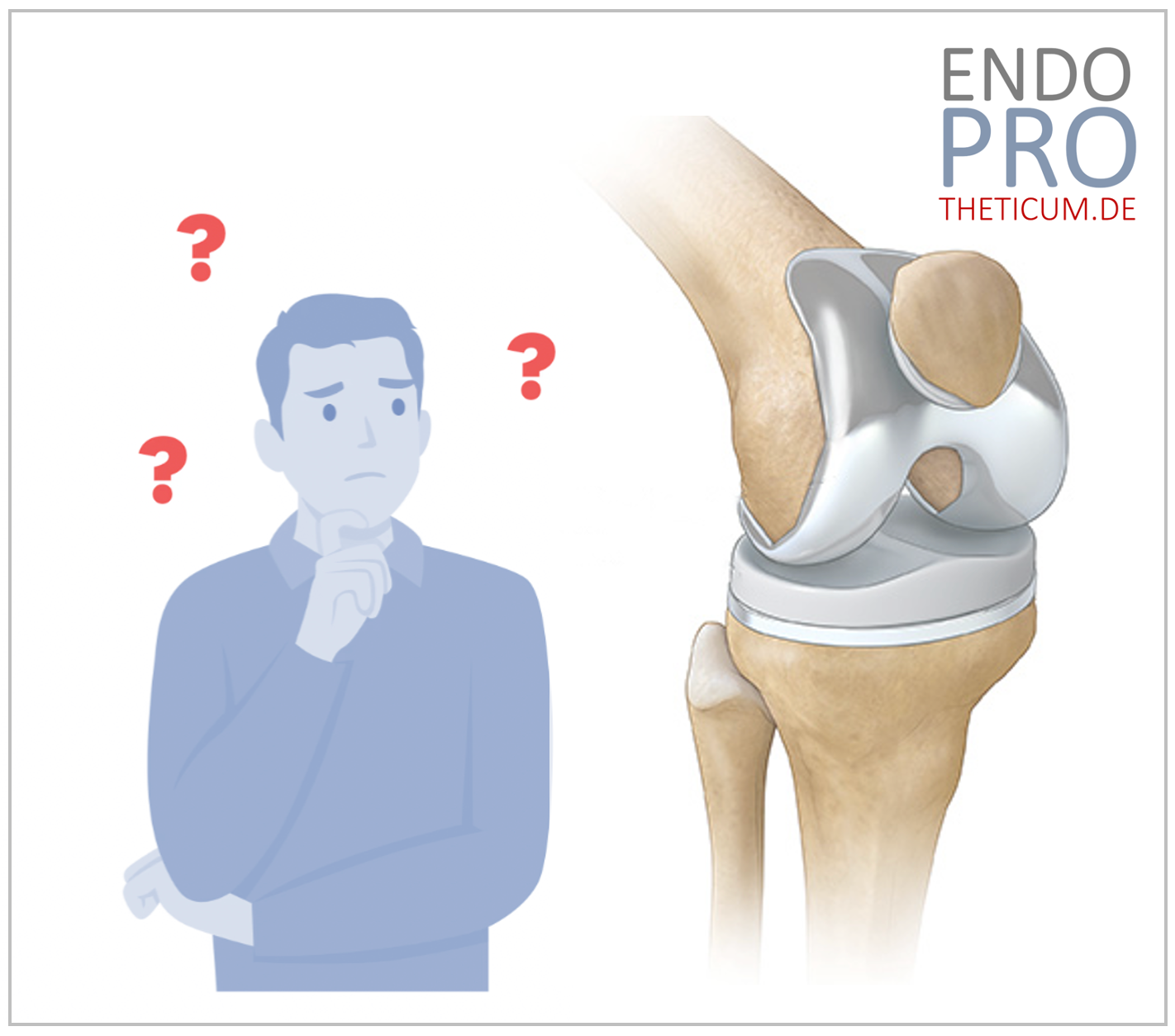
Is robotics the savior in knee replacement surgery?
What does robotics offer in knee endoprosthetics today?
Knee replacement surgery has made enormous progress in recent decades. The introduction of robotics and computer-assisted systems has revolutionized the way knee replacement operations are performed. But is robotics truly the savior in knee replacement surgery? In this blog, we will examine the role of robotics in knee replacement surgery in detail, highlighting its advantages and challenges, and answering the question of whether it can truly be considered a panacea.
1. What is robotics in knee arthroplasty?
Definition and Functioning
Robotics in knee arthroplasty refers to the use of robotic arms and computer-assisted systems to support the placement and alignment of knee prostheses. These technologies enable more precise planning and execution of the operation, which can lead to better outcomes.
Historical development
The first steps towards robotics in orthopedics were taken in the 1980s, but it is only in the last two decades that the technology has made significant progress. Today, systems such as MAKO, ROSA, and NAVIO are leaders in this field and are used in hospitals worldwide.
2. Potential advantages of robotics in knee arthroplasty
Precision and accuracy
One of the greatest advantages of robotics in knee arthroplasty is, theoretically, improved precision. Robot-assisted systems can make more precise cuts and placements, which should lead to better alignment of the prosthesis and greater durability.
Individualized planning
Using 3D imaging and planning software, surgeons can create individualized surgical plans tailored to each patient's specific anatomical characteristics. This is intended to increase the likelihood of a successful outcome.
Error reduction
Robotics is intended to minimize human errors that can occur during surgery. This is particularly important in complex operations, where small deviations can have major consequences.
Faster recovery times
Patients undergoing robot-assisted knee replacement could theoretically experience shorter recovery times and regain mobility more quickly. This would be attributed to the more precise placement of the prosthesis.
Better long-term results
Thanks to improved precision and individualized planning, patients with robot-assisted knee replacements could theoretically experience better long-term results, less pain, and a higher quality of life.
The theoretical advantages of robotics are currently countered by several disadvantages and open questions.
3. Challenges and risks of robotics in knee arthroplasty
High costs
One of the biggest challenges in implementing robotics in knee arthroplasty is the high cost. Acquiring and maintaining robotic devices is expensive, and these costs are often passed on to patients.
learning curve and training
Surgeons must complete specialized training to use robot-assisted systems safely and effectively. This can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, and requires ongoing professional development.
Technical failures
As with any technology, robot-assisted systems also carry the risk of technical failure. Such a failure during an operation can have serious consequences and therefore necessitates backup plans and manual intervention options. Surgeons should be able to achieve excellent results even without a robot.
Not suitable for all patients
Not all patients are suitable candidates for robot-assisted knee replacement. Factors such as the extent of joint damage, bone quality, and other health conditions must be taken into account.
4. Clinical studies and research results
comparative studies
Several clinical studies have compared the outcomes of robot-assisted knee replacements with those of traditional methods. These studies have so far shown that robot-assisted procedures do not clearly lead to better prosthesis alignment and, in no case, to better functional outcomes.
Long-term studies
Long-term studies are not yet available to assess the actual durability and long-term benefits of robot-assisted knee replacement. Early results are not yet clearly convincing, and further research is needed to draw definitive conclusions.
6. The future of robotics in knee arthroplasty
Further development of the technology
Robotics technology is constantly evolving. Future innovations could enable even more precise and less invasive procedures. It remains to be seen whether this will actually lead to better results that justify the effort.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into robot-assisted systems could further improve preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation by providing real-time data and analysis.
Extension to other joints
While robotics is already widespread in knee replacement surgery, similar technologies could be used more frequently in the future for other joints, such as the hip or shoulder.
7. Conclusion: Is robotics the savior in knee endoprosthetics?
In summary, robotics in knee arthroplasty could theoretically offer numerous advantages, including improved precision, more individualized planning, and better long-term outcomes, but these have not yet been proven. Despite extremely high costs and technical complexity, current research and clinical experience do not yet demonstrate a decisive advantage. In the future, robotics could have the potential to fundamentally change the way knee replacement surgery is performed. However, whether it can be considered a panacea depends on the further development of the technology, its availability and accessibility for patients, and the long-term results.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .