Total knee with a robot: Why this will be normal in the future
Robots in the implantation of a knee prosthesis (TKA) are developing!
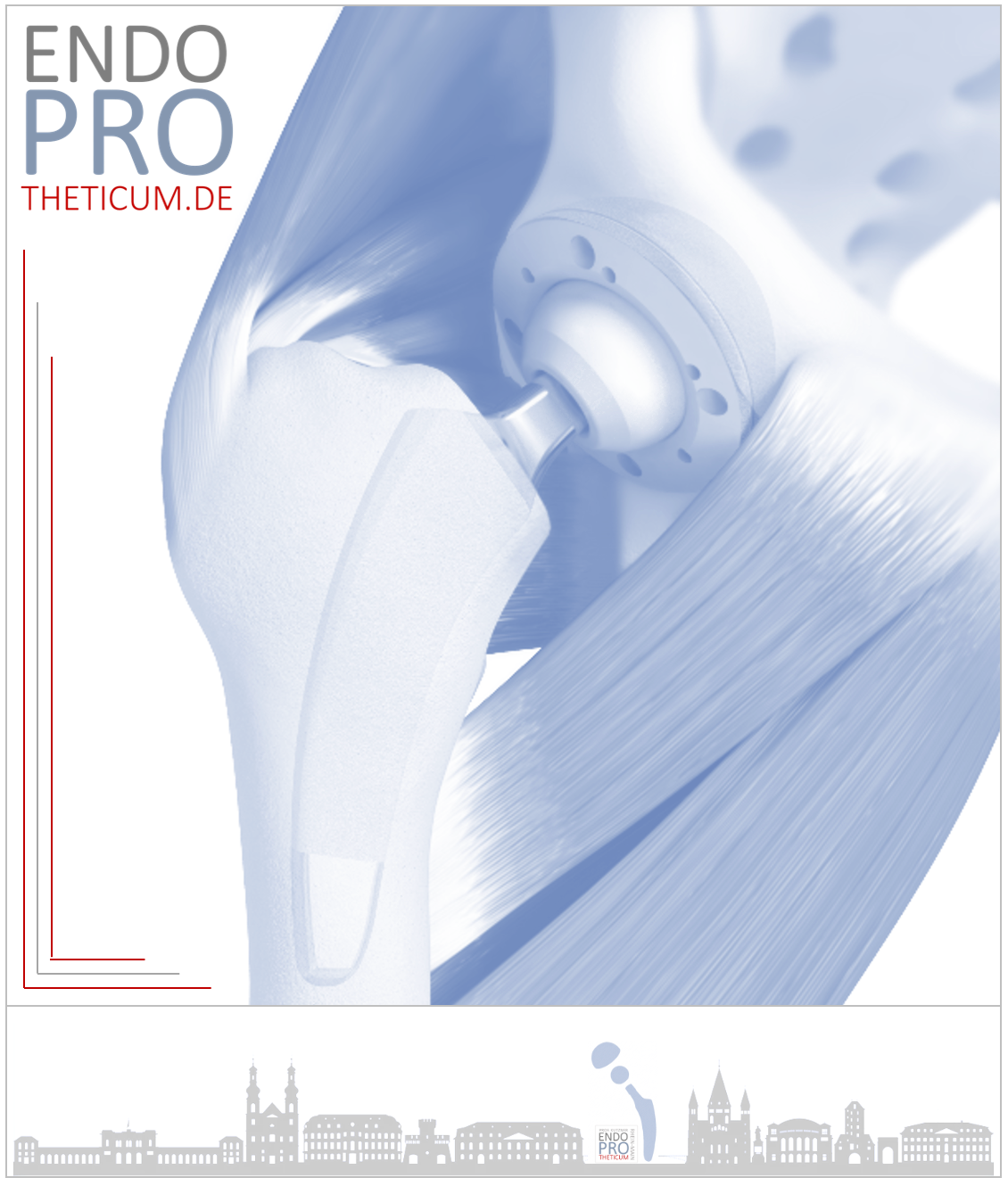
Total knee replacement (TKR) has undergone continuous development over the past few decades. One of the latest innovations is the use of robotic systems in knee replacement surgery. Robot-assisted surgery promises more precise prosthesis placement, faster rehabilitation, and longer implant lifespan. But why will this technology become the standard method in the future? In this comprehensive article, we examine the most important aspects of robot-assisted TKR, analyze current developments, and demonstrate why robots represent the future of knee replacement surgery.
1. Basics of total knee replacement
Total knee replacement is a proven method for treating serious knee joint diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic knee injuries. The damaged joint is replaced with an artificial prosthesis to relieve pain and improve the patient's mobility.
1.1 When is a total knee replacement necessary?
- Advanced knee osteoarthritis with severe pain
- Movement restrictions that make everyday life difficult
- Knee joint misalignment
- Failure of conservative therapies (physiotherapy, painkillers, injections)
1.2 Procedure of a knee replacement operation
- Preparation: Imaging procedures for precise planning
- Removal of damaged articular cartilage
- Adaptation of bone structure
- Knee replacement surgery
- Fixation and control of stability
2. The role of robotics in knee surgery
2.1 What is a robot-assisted knee replacement?
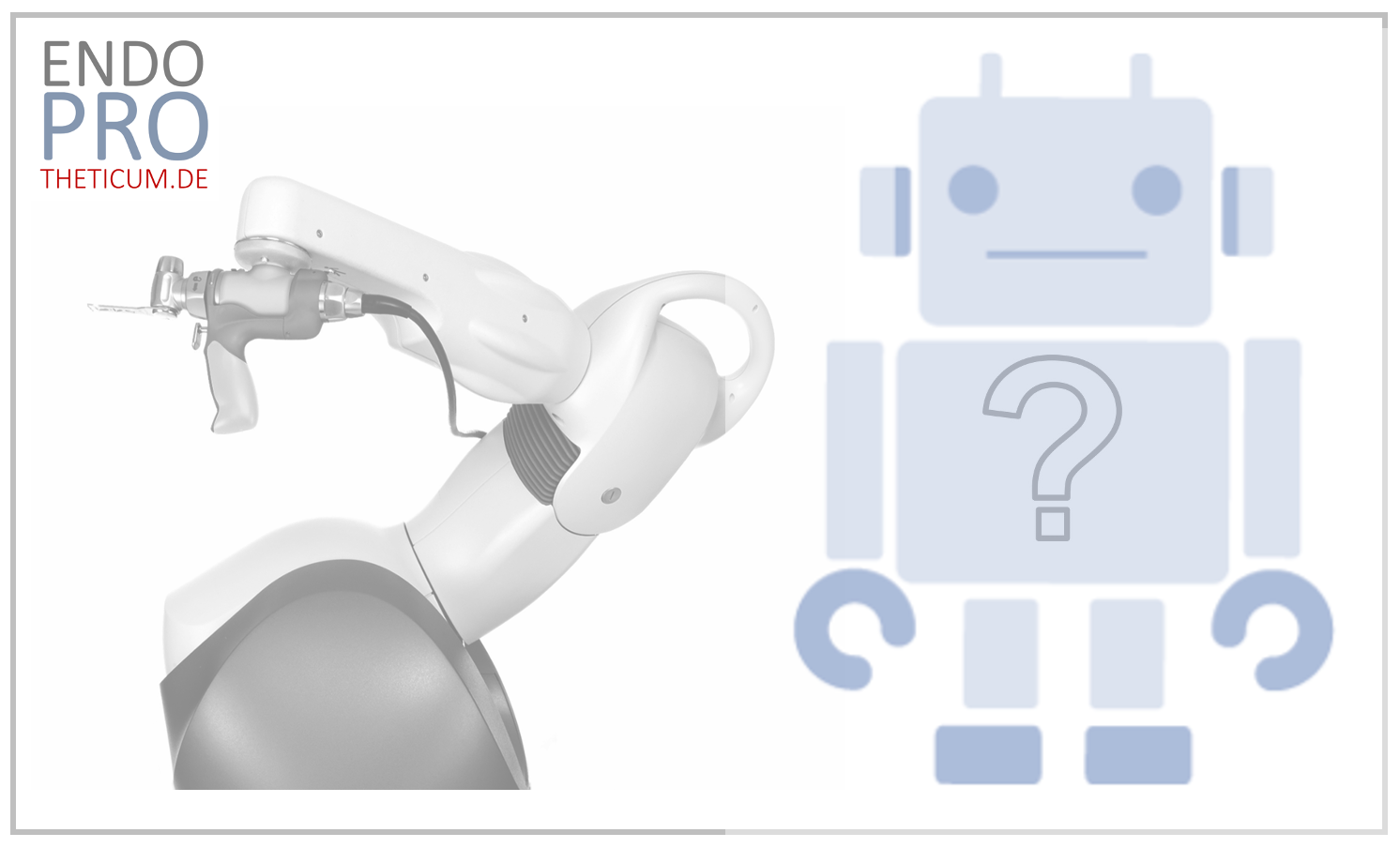
Robot-assisted total knee replacement uses computer-aided systems to perform the operation with the highest precision. A robotic system is employed to assist the surgeon in optimally positioning the implant. This potentially reduces the risk of human error and improves the long-term outcomes of the surgery.
2.2 Which robots are used today?
- MAKO Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery: This system supports the surgeon with data from a preoperative CT scan and real-time feedback during the operation.
- NAVIO Surgical System: A robotic platform that does not require prior CT scans and uses intraoperative imaging.
- ROSA Knee System: Developed by Zimmer Biomet, this system combines artificial intelligence with surgical precision.
- CORI Surgical System: A compact, portable robotic solution for minimally invasive total knee replacement.
- MISSO Robotic System: The first system with fully automated bone preparation from the company Meril. This system also uses CT data, making it an image-guided robotic procedure.
2.3 Potential advantages of robotics in knee replacement surgery
- More precise implant placement: Through millimeter-accurate planning and implementation, the implant can be ideally aligned.
- Reduced risk of complications: Precise cuts lead to less tissue trauma and lower infection rates.
- Less blood loss and less soft tissue damage: Gentler surgical methods mean faster healing.
- Faster rehabilitation and better long-term results: Patients regain their mobility more quickly.
3. Why will robotics be standard in the future?
3.1 Advances in medical technology
- Improved sensor technologies enable precise navigation during the procedure.
- Artificial intelligence supports the surgeon with real-time analyses.
- Optimized planning methods ensure individual patient adjustments.
3.2 Potential long-term benefits for patients
- Longer implant lifespan: Less wear and tear due to precise placement.
- Fewer revision surgeries required: Lower error rate reduces the need for follow-up operations.
- Increased patient satisfaction: Improved functionality and a natural feeling of movement.
3.3 Cost efficiency in the long term
Although the initial costs for robots are high, the reduction of complications and faster healing leads to lower healthcare costs in the long run.
4. Challenges and limitations of knee robots
4.1 High acquisition costs for hospitals
- Investment in expensive robot technology.
- The need for dedicated operating rooms and maintenance costs.
4.2 Need for specialized surgeons
- Longer training periods for surgeons.
- Ongoing training is required.
4.3 Technical Risks
- Possible system failures or software problems.
- The need for a backup strategy for emergencies.
5. Future outlook: Where is robotics headed in endoprosthetics?
5.1 Development of autonomous robot systems
- Self-learning algorithms for maximum precision.
- Real-time corrections to optimize surgical outcomes.
5.2 Combination with other technologies
- Augmented Reality for improved visualization.
- 3D printing for individually customized implants.
5.3 Individualized patient treatment
- Motion analysis for optimal implant selection.
- Patient-specific surgical planning for a perfect fit.
6. Conclusion: Robots for knee replacement (total knee arthroplasty) will become commonplace in the future
Robot-assisted total knee replacement (TKR) will become the standard in the future due to its superior precision, lower complication rate, and improved long-term outcomes. While challenges still exist, the long-term benefits for both patients and the healthcare system are undeniable. With further advances in medical technology, robotics will become an indispensable method in knee surgery.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .