Hip-Tep: When cement-free, when cemented?
What criteria apply to the choice of cement-free or cemented hip prosthesis (hip-tep)?
The implantation of an artificial hip joint, also referred to as a hip totalendoprosthesis (hip-tep), is one of the most successful operations in modern orthopedics. Various methods for anchoring the prosthesis are available: the cemented and cement -free fixation. Both techniques have specific advantages and disadvantages that should be weighed down depending on the individual patient conditions.
In this article, the two procedures are presented comprehensively, their respective areas of application are discussed and important decision criteria are explained. The aim is to offer a well -founded basis for decision -making for patients and doctors.
2. Anatomical basics of the hip joint
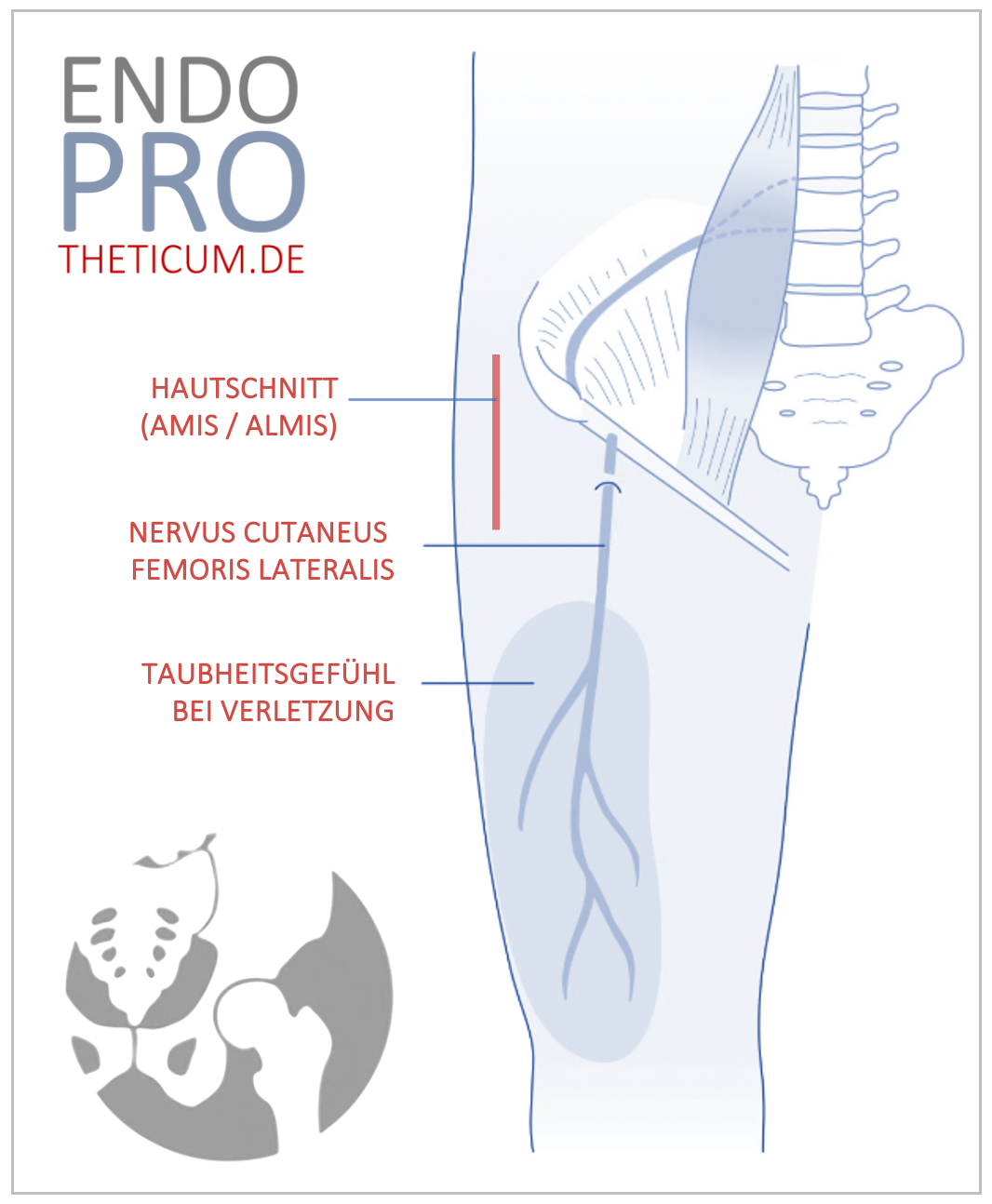
The hip joint is one of the largest and most stressed joints in the human body. It consists of the spherical thigh head (Caput femoris) and the pan (acetabulum) in the pool. A complex interplay of cartilage, ligaments, muscles and articular fluid ensures stability and smooth movement.
Turnover symptoms such as osteoarthritis lead to pain, restrictions on movement and ultimately to the need for a joint replacement.
3. History and development of the hip-Tep
Modern hip prosthetics has had a long development. The first attempts with artificial joints go back to the early 20th century. In the 1960s, Sir John Charnley revolutionized the endoprosthetics with the introduction of the cemented prosthesis. Cement -free models were later developed that enable biological integration of the implant in the bones.
Today the latest materials and techniques are available that have significantly improved the durability and functionality of the prostheses.
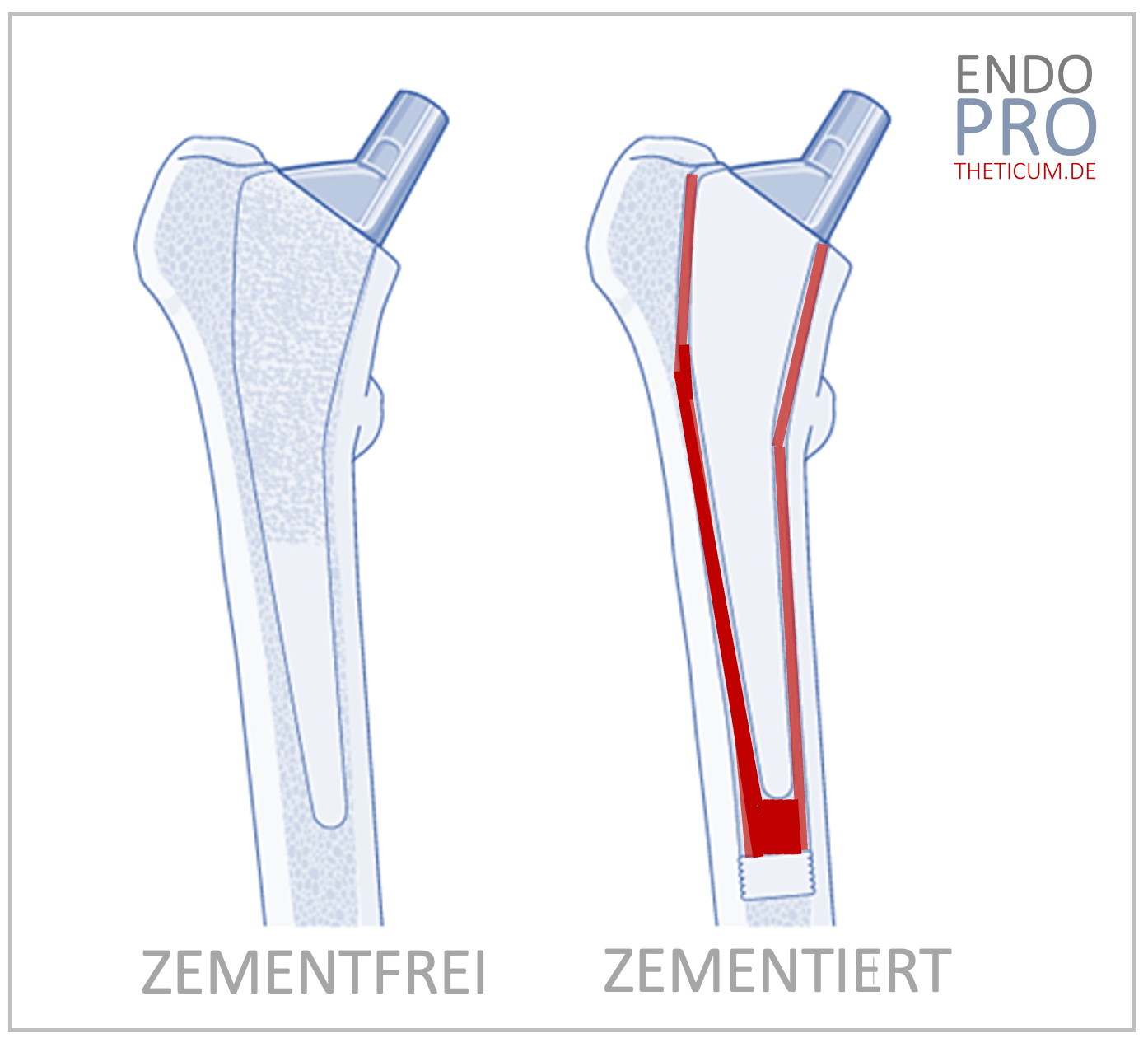
4. cemented hip-Tep
4.1 Process and technology
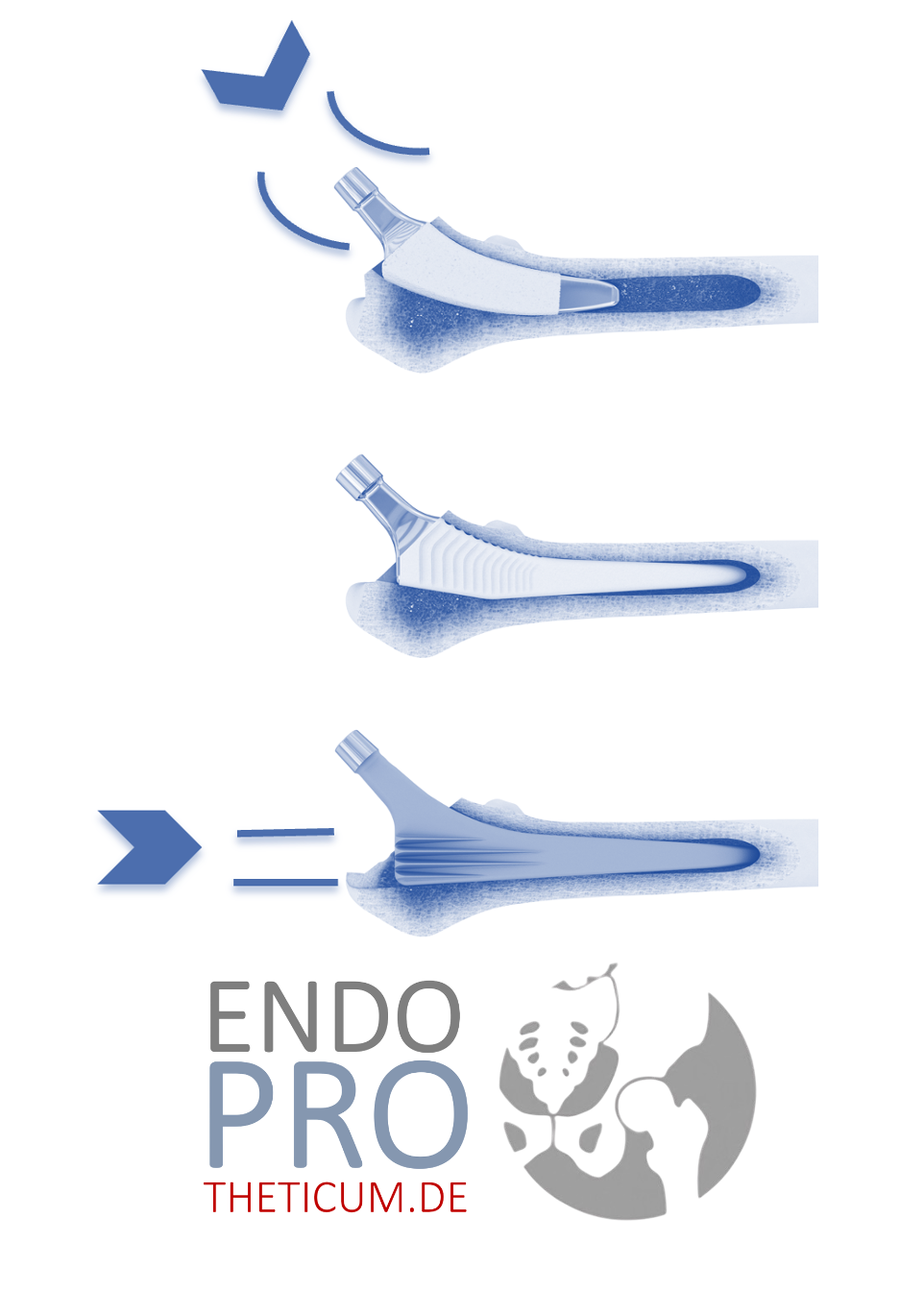
In the cemented hip-TEP, the prosthesis is fixed with a bone cement in the thigh bone. The cement (polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA) hardens within minutes and creates an immediately resilient connection between the implant and bone.
4.2 Advantages of the cemented hip prosthesis
- Immediate resilience: The prosthesis can be loaded fully after the operation.
- Suitable for osteoporosis: With soft or porous bones, the cement fixation offers stable anchoring.
- Less fracture risk: No need to press the implant firmly in the bones, which can avoid fractures.
4.3 Disadvantages of the cemented hip prosthesis
- Revisions are more difficult: removing a cemented prosthesis is complex and can cause bone loss.
- Possible cement reactions: In rare cases, cement allergies or cement embolism can occur.
4.4 Indications of the cemented hip prosthesis
- Older patients with reduced bone quality
- Patients with osteoporosis
- People with restricted mobility
5. Cement-free hip-Tep
5.1 Process and technology
In the case of cement -free technology, the implant is connected to the bone by a specially coated surface. This porous structure promotes the growth of the bone and ensures stable, biological fixation.
5.2 Advantages of the cement -free hip prosthesis
- Longer shelf life: Biological integration can offer more stable long -term anchoring.
- Simpler change surgery: no cement that needs to be removed.
- No cement complications: no risk of broken cement or embolism.
5.3 Disadvantages of the cement -free hip prosthesis
- Delayed resilience: The full resilience is only reached after a few weeks.
- Higher risk of fracture during the operation: pressing in the implant can weaken the bones.
5.4 Indications of the cement -free hip prosthesis
- Younger, active patients
- Good bone quality
- Patients with high physical stress
6. Hybrid technology
A combination of both methods is the so-called hybrid technique. For example, the hip pan is cement -free and the shaft is implanted. This technology can combine advantages of both methods.
7. Decision criteria: when cement -free, when cemented?
The choice between cemented and cement-free hip-free depends on several factors:
- Age: younger patients often receive cement -free prostheses.
- Bone quality: osteoporosis speaks more for a cemented prosthesis.
- Activity level: sporty people often benefit from cement -free models.
- Diseases: Certain previous illnesses may require cemented fixation.
8. Rehabilitation and aftercare
The right post -treatment plays a crucial role in the success of the prosthesis. Physiotherapy, targeted strengthening exercises and a gradual increase in the load are essential for an optimal function of the new joint.
9. Conclusion: The choice of a cement-free or cemented hip-TEP is individual!
Both methods are justified and should be individually coordinated with the patient. The cemented fixation offers immediate stability, while the cement -free variant enables long -term biological integration. Detailed advice from the treating hip specialist is essential to make the best decision.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .