HIP: SHORT STEM PROSTHESIS BY THE EXPERT
The short stem prosthesis is a modern form of artificial hip joint, which is anchored in a bone-sparing manner in the upper thigh. It enables anatomically close force transmission and preserves more natural bone substance than classical hip prostheses. It is particularly suitable for active patients with good bone quality. Modern studies show very good durability and stable integration. By preserving bone, it can offer long-term benefits, especially in possible later revisions.



Why the short stem prosthesis plays a central role today
The implantation of an artificial hip joint is one of the most successful operations in modern medicine. At the same time, a fundamental change has taken place over the past decades: patients are operated on at a younger age, remain active for longer and increasingly have a desire for a natural joint function.
This development has led to the further development of classical concepts of hip arthroplasty. One of the most important innovations in this context is the so-called short-stem prosthesis.
While conventional hip prostheses are deeply anchored in the femoral bone, the short-stem prosthesis follows a different principle: it specifically utilizes the stable upper region of the bone and preserves as much natural substance as possible. The goal is not only to replace the damaged joint but also to maintain the biomechanical function in the long term.
Today, the short-stem prosthesis is considered a modern, bone-preserving alternative to the classical standard stem – provided it is used correctly.
What exactly is a short-stem prosthesis?
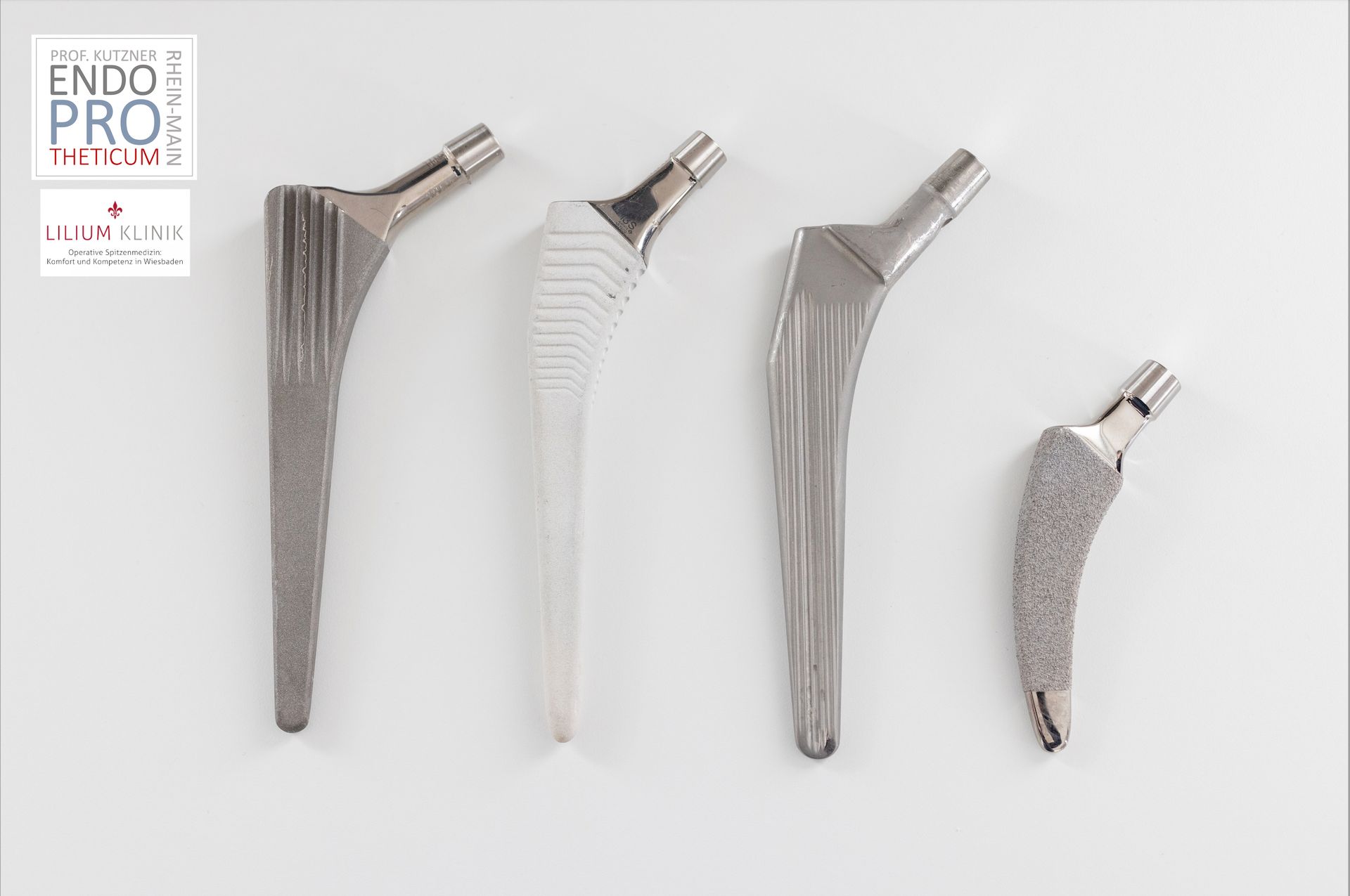
The short-stem prosthesis is a special form of artificial hip joint in which the prosthesis stem is deliberately designed to be shorter than in traditional implants.
The decisive difference lies in the anchoring:
Instead of being seated deep in the medullary cavity of the femur, the short-stem prosthesis stabilizes mainly in the upper, anatomically supporting area of the femur.
This area is biomechanically particularly relevant because the natural force lines of the body run here. Through proximal fixation, the load can be transferred more physiologically.
The consequence is:
- less bone loss
- more anatomical force distribution
- long-term better conditions for possible revisions
The short-stem prosthesis thus not only replaces the joint - it respects the structure of the bone.
Historical Development: From Long Stem to Bone-Sparing Solution
The classic hip prosthesis was originally developed for older patients. In this group, maximum stability was more important than long-term bone preservation.
Over time, however, the requirements changed:
- younger patients with osteoarthritis
- higher activity levels
- longer life expectancy
- increasing need for revision capability
This led to a rethink in implant development.
The question increasingly was:
How can an artificial joint be implanted without sacrificing unnecessarily much bone?
The answer was the development of bone-sparing implants – and finally the short stem prosthesis.
Biomechanical principles of the short stem prosthesis
A hip joint transmits enormous forces. When walking, a multiple of the body weight acts on the joint.
The natural hip distributes these forces via:
- the femoral neck
- the calcar region
- the cortical bone structure
The short stem prosthesis attempts to utilize exactly these physiological load paths.
Instead of dissipating forces deep into the medullary space, stabilization occurs via:
- proximal bone contact surfaces
- metaphyseal anchoring
- calcar-guided load transmission
The goal is a load on the bone that is as natural as possible.
This can help reduce the so-called stress shielding – i.e., bone resorption due to lack of loading.
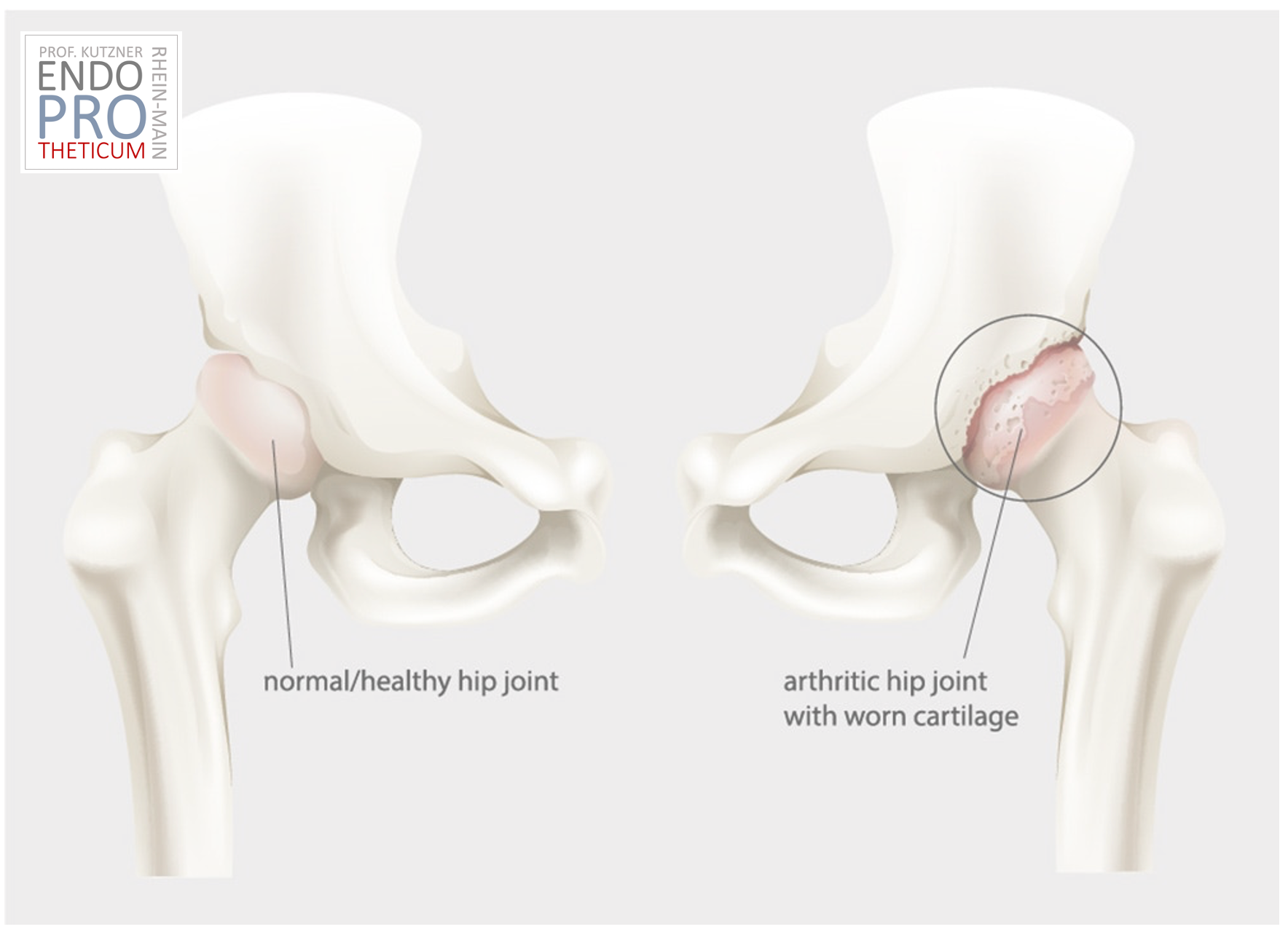

Why bone preservation is so important
Preserving bone is not an end in itself. It has concrete long-term benefits:
- More stable natural load transmission
- lower risk of bone loss
- better conditions for later revision surgeries
- more anatomical reconstruction of the hip
Especially in younger patients, this aspect plays a major role.
The short stem prosthesis is therefore often understood as a strategic solution - not just for the current situation, but also for the future.
Difference to the classic standard stem
The short stem prosthesis differs from the standard stem primarily by:
- shorter length
- proximal anchoring
- bone-sparing implantation
- more physiological force transmission
While a standard stem uses diaphyseal stability, the short stem prosthesis relies on metaphyseal fixation.
Both systems have their justification - the right selection is crucial.
For whom is a short stem prosthesis suitable?
Not every patient automatically benefits from a short stem implant.
Typical prerequisites are:
- good bone quality
- primary osteoarthritis
- stable anatomical conditions
- active lifestyle
It is less suitable for:
- severe osteoporosis
- complex revisions
- massive deformities
Here, a standard shaft may be the better option.
Durability of the short stem prosthesis
Modern studies show:
Short stem prostheses achieve very good long-term results, provided:
- the indication was correctly determined
- the implantation was performed precisely
- the postoperative load is adjusted
Long-term data show survival rates comparable to those of classical stems.
The role of surgical experience
The implantation of a short stem prosthesis requires:
- precise planning
- understanding of the anatomy
- experience with metaphyseal fixation
In contrast to the standard stem, positioning is less tolerant of errors.
Therefore, specialization is crucial.
Specialized short stem endoprosthetics in Mainz
Patients seeking information on modern short stem prostheses can find a specialized facility in
ENDOPROTHETICUM
focusing on modern hip endoprosthetics.
Under the direction of
Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner
, there is a special focus on calcar-guided short stem systems.
Many patients are specifically seeking a second opinion on the question:
👉 Short stem or standard stem?
Conclusion
The short stem prosthesis represents a modern, bone-preserving further development of hip arthroplasty. It enables a more anatomical force transmission and offers long-term benefits - provided it is used correctly.


Indication and decision criteria - When is a short stem prosthesis useful?
The short stem prosthesis is not a universal solution for every hip arthrosis. Its success depends largely on whether it is used in the right patients. Therefore, a careful indication is the first step in every decision.
The goal is not to simply select an implant, but to find the individually suitable solution.
Typical prerequisites for a short stem prosthesis are:
- good bone quality
- stable anatomical conditions
- primary osteoarthritis without complex deformities
- an active lifestyle
- the desire for the most bone-sparing care possible
Especially in younger or physically active patients, the short stem prosthesis can be an attractive option because it preserves more bone in the long term.
It is less suitable, however, for:
- severe osteoporosis
- complex revision surgeries
- massive malalignments
- significant structural damage to the proximal femur
In such situations, a standard stem can provide a more stable solution.
Decisive is:
The choice of implant should never be made dogmatically, but always based on the individual anatomy and life situation.
Minimally invasive implantation – Why short stem and access fit well together
Another advantage of the short stem prosthesis is that it can be particularly well combined with minimally invasive surgical concepts.
Since the implantation area remains limited to the upper femur, it is often possible:
- the surgical access can be kept smaller
- the musculature is better preserved
- postoperative mobilisation occurs more quickly
Minimally invasive does not automatically mean 'small incision', but above all:
👉 minimal impairment of soft tissues
If muscles and tendons are spared, this can lead to:
- Less pain
- faster resilience
- earlier return to everyday life
lead.
However, it remains important:
The access must never compromise the implant position.
Long-term stability is more important than cosmetic aspects.


Short stem prosthesis and sport – Return to activity
One of the most common questions is:
👉 'Can I do sports again after a short stem prosthesis?'
In many cases, the answer is: Yes – with limitations.
The more physiological force transmission can support functional movements. Frequently possible are:
- Cycling
- Hiking
- Swimming
- Golf
- moderate strength training
Sports with high impact stress should be discussed individually.
However, the short stem prosthesis can help lead an active life – especially compared to highly altered biomechanical situations.
Revision and future security – The strategic advantage
A crucial aspect of modern endoprosthetics is long-term planning.
Since the short stem prosthesis:
- removes less bone
- largely preserves the medullary space
better conditions remain for possible revision surgeries.
Should an implant revision be necessary later, there is:
👉 more bone available
👉 a more stable initial situation
This makes the short stem prosthesis particularly interesting for:
- younger patients
- long-term care strategies
Biomechanical reconstruction – Restoration of the natural hip
A central goal of the short stem prosthesis is not only pain reduction but:
👉 functional reconstruction
This means:
- Restoration of leg length
- Reconstruction of the offset
- physiological load transfer
Through proximal anchoring, the natural force line can be better preserved.
This can have long-term effects:
- support muscle balance
- improve joint sensation
- Distribute load more naturally
Post-treatment and rehabilitation with short stem prosthesis
Rehabilitation after short stem implantation follows modern concepts:
- early mobilization
- targeted muscle building
- Gait training
- Load control
Many patients can already:
- mobilize without walking aids
- resume daily activities
- become independently active
However, structured aftercare remains crucial.


Decision: Short stem or standard stem?
In the end, it's not about:
👉 Which implant is better?
but:
👉 Which implant fits better?
The decision is based on:
- Bone quality
- Anatomy
- Activity level
- Age
- individual expectations
In specialized centers, this decision is made with differentiation.
Short stem endoprosthetics in the Rhine-Main region
Patients seeking advice on short stem prosthesis can find a facility focused on modern hip endoprosthetics at
ENDOPROTHETICUM
.
Under the direction of
Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner
, a focus lies on calcar-guided short stem systems.
Many seek a second opinion on the question:
👉 Short stem or standard stem?
Short stem prosthesis as a modern option
The short stem prosthesis enables a bone-preserving, biomechanically oriented care of the hip.
It offers:
- anatomically close force transmission
- long-term revision options
- high functionality
Prerequisite remains:
- correct indication
- precise implantation
- operative experience

Study situation and scientific evidence on short stem prosthesis
Die Kurzschaftprothese hat sich in den letzten Jahren von einer innovativen Idee zu einer wissenschaftlich gut untersuchten Implantatlösung entwickelt. Während frühe Generationen von Hüftprothesen vor allem auf maximale Stabilität ausgelegt waren, liegt der Fokus moderner Entwicklungen zunehmend auf funktioneller Rekonstruktion und Knochenerhalt.
International registry data and clinical studies show that modern short stem systems:
- exhibit very good healing rates
- enable stable metaphyseal fixation
- support a more physiological load transmission
Long-term observations show that the survival rates of modern short stem prostheses can be comparable to classical stems – provided the indication is correctly made.
Important is:
Not every short stem prosthesis is the same.
Implant design, anchoring principle and surgical technique play a crucial role.
The scientific discussion has therefore shifted from the question
„Does short stem work?“
to the question:
„For whom does short stem work best?“
Minimally invasive approaches and their significance in short stem prostheses
Short stem implants can be particularly well combined with muscle- and soft tissue-sparing surgical approaches.
It's not primarily about the size of the skin incision, but about:
👉 Preservation of muscular function
👉 Protection of stabilizing structures
👉 Rapid postoperative activation
Anterior or anterolateral approaches can enable:
- Avoiding muscle detachment
- Supporting joint stability
- Accelerating rehabilitation
The combination of:
✔ Bone-sparing implant
✔ Soft tissue-sparing approach
can create a functionally favorable initial situation.
However, the decisive factor remains:
The precision of the implant position is more important than the approach.
Daily life after short stem prosthesis
After successful implantation, many questions arise:
- When can I walk again?
- When am I allowed to work?
- When am I allowed to travel?
The early phase is characterized by:
- Mobilization
- Load buildup
- Muscle activation
Many patients achieve stable walking ability early on.
In everyday life, this often means:
- Independent getting up
- climbing stairs
- Longer walking distances
The complete functional integration of the joint occurs gradually, however.
Exercise and Sports
An important motivation for many patients is the desire for activity.
The short stem prosthesis can provide a good foundation for:
- Joint-friendly sports
- Functional movements
- Long-term mobility
Create.
Typically possible are:
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Hiking
- Golf
Impact-loading sports should be evaluated individually.
Quality of life after short stem prosthesis
The success of a hip prosthesis is not solely measured by X-rays.
Decisive are:
- Pain freedom
- Mobility
- Everyday suitability
- Independence
Many patients report after successful implantation about:
- improved gait pattern
- greater freedom of movement
- increased quality of life
The combination of functional reconstruction and bone preservation can contribute to long-term satisfaction.
Long-term perspective
Since more bone is preserved, the short stem prosthesis can offer strategic advantages.
In the event of a later revision:
👉 better initial conditions
👉 more bone structure
👉 more stable prerequisites
at your disposal.
This makes it particularly interesting for:
- younger patients
- long-term treatment strategies

Short stem prosthesis in a specialized context
Patients who want to learn more about modern short stem implants will find a specialized center for hip arthroplasty at
ENDOPROTHETICUM
.
Under the direction of
Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner
, a special focus is placed on calcar-guided concepts.
Many patients are specifically seeking a second opinion on the question:
👉 Short stem or standard stem?
Short stem prosthesis as a modern solution
The short stem prosthesis represents a further development in hip arthroplasty.
It enables:
- bone-preserving care
- more physiological load transfer
- long-term perspectives
Prerequisite remains:
✔ correct indication
✔ precise implantation
✔ surgical experience
Frequently Asked Questions about Short Stem Prosthesis
What is the difference between a short stem prosthesis and a normal hip prosthesis?
The short stem prosthesis is mainly anchored in the upper part of the femur and preserves more natural bone substance. Classical hip prostheses extend deeper into the bone. The aim of the short stem prosthesis is a more physiological force transmission and long-term bone preservation.
How long does a short-stem hip prosthesis last?
Modern short stem prostheses show very good durability, which can be comparable to classical hip prostheses. Decisive factors are the correct indication, precise implantation, and good bone quality.
For whom is a short stem prosthesis suitable?
It is particularly suitable for:
- active female and male patients
- good bone quality
- primary osteoarthritis
- stable anatomical conditions
Not optimal for severe osteoporosis or complex revision surgeries.
Is a short stem prosthesis stable enough?
Yes – with correct indication, it offers a stable metaphyseal anchorage. Stability is achieved through bony contact in the upper femur and physiological load transmission.
Can I do sports again after a short stem prosthesis?
In many cases, joint-friendly sports such as cycling, swimming or hiking are possible. However, individual stress tolerance should be medically coordinated.
Can a short stem prosthesis be replaced later?
Yes. Since less bone is removed, there are often better conditions for later revision surgeries.
Is a short stem prosthesis minimally invasive?
It can be well combined with muscle and soft tissue-sparing approaches. However, the decisive factor is not the incision, but the precise implantation.


Short stem prosthesis in Mainz
Anyone interested in a short stem prosthesis will find a particularly specialized care at the highest level in Mainz. At ENDOPROTHETICUM , there is a clear focus on modern, bone-sparing hip arthroplasty with short stem systems. Under the direction of Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner, one of the leading specialists in calcar-guided short stem prostheses, patients benefit from comprehensive experience, precise indication setting, and individual implant selection. The combination of scientifically based expertise, structured planning, and surgical specialization enables excellent short stem care – with the goal of preserving natural biomechanics, conserving bone, and achieving long-term functional results. This is precisely why many patients from Mainz and the entire Rhine-Main region consciously choose to consult with a certified short stem specialist.
What makes Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner a leading specialist in short stem prostheses?
The short stem prosthesis is one of the more demanding concepts in modern hip arthroplasty. Its successful use requires not only surgical experience but also a deep understanding of the biomechanics of the hip joint and individual anatomy.
Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner is considered one of the leading specialists in this field because he has been intensively involved in the development, application, and scientific evaluation of short stem systems for many years.
A particular focus of his work is on the so-called calcar-guided short stem arthroplasty. The focus is not only on joint replacement but also on the most physiological reconstruction of the hip possible while preserving valuable bone substance. This approach requires precise indication setting and differentiated surgical technique.
In addition to his clinical work, Prof. Kutzner has published numerous scientific papers on short-stem prostheses and has intensively examined their biomechanical properties and long-term results. Through this combination of surgical practice and scientific analysis, he contributes to answering open questions about the function and stability of modern short-stem implants.
Another aspect of his specialization lies in differentiated decision-making. Not every hip situation is suitable for a short-stem prosthesis. The selection of the appropriate implant is therefore made individually, taking into account bone quality, anatomy, and functional requirements.
This combination of:
- many years of surgical experience
- scientific expertise
- focus on bone-preserving implant concepts
- individual indication setting
makes Prof. Kutzner one of the leading experts in the field of modern short-stem arthroplasty.



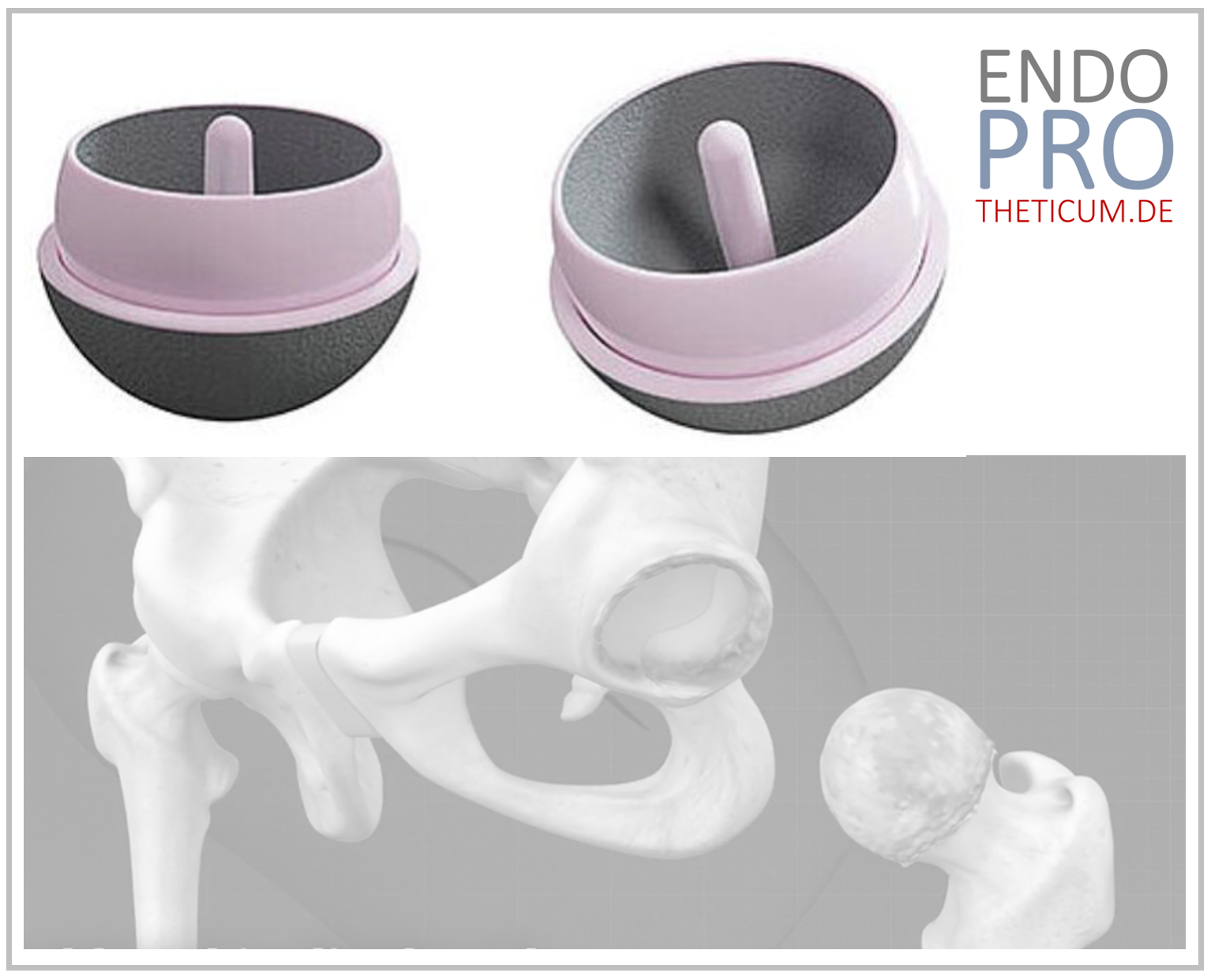
The calcar-guided short-stem prosthesis – Anatomically close reconstruction of the hip
The calcar-guided short stem prosthesis represents a further development of modern hip arthroplasty. It follows the principle of not only replacing the joint, but also reconstructing the natural biomechanics of the hip as accurately as possible.
At the center of this is a special form of anchoring:
👉 the force-transmitting guidance along the calcar.
What does “calcar-guided” mean?
The calcar is a stable bone structure in the upper femur that plays a central role in the natural transmission of forces in the hip.
In the calcar-guided short stem prosthesis, the stabilization of the implant is achieved specifically along this structure.
This means:
- no deep anchoring in the medullary canal
- utilization of the load-bearing proximal bone
- more physiological load transfer
The prosthesis thus follows the natural load paths of the body.
Biomechanical principle
The natural hip transmits forces via:
- the femoral neck
- the calcar
- the cortical bone structure
The calcar-guided short stem prosthesis imitates this principle.
Instead of shifting forces to the shaft area, the load transfer takes place:
👉 proximal
👉 anatomy-friendly
👉 bone-preserving
The goal is a functional reconstruction – not just a replacement.
Advantages of the calcar-guided short stem prosthesis
This form of anchoring can result in several advantages:
- Preservation of natural force lines
- Reduction of stress shielding
- Better adaptation to individual anatomy
- bone-sparing implantation
- Long-term revision options
Particularly relevant is the possibility of individually mapping the CCD angle.
This allows the hip geometry to be:
- more anatomically reconstructed
- functionally adapted
- stably loaded
be.
Individualized implant positioning
A key feature of the calcar-guided short stem prosthesis is its adaptability.
The implant can be:
- varus
- neutral
- valgus
positioned.
This enables a patient-specific reconstruction of the hip.
The position follows the anatomy – not the other way around.
Bone preservation as a strategic advantage
Since the anchoring is predominantly in the proximal femur, more bone is preserved.
This can:
- support long-term stability
- facilitate revisions
- promote physiological loading
This aspect is particularly important for younger patients.
Who is the calcar-guided short stem prosthesissuitable for?
It can be particularly useful for:
- good bone quality
- primary osteoarthritis
- stable anatomy
- active lifestyle
Not every hip condition is suitable.
The decision should be made on an individual basis.
Importance of surgical experience
Calcar-guided implantation requires:
- precise planning
- understanding of bone structure
- experience with metaphyseal fixation
Positioning is less tolerant of deviations than classical stems.
Therefore, specialization is crucial.
Calcar-guided short stem prosthesis in MAINZ
Patients interested in a calcar-guided short stem prosthesis can find a specialized facility at
ENDOPROTHETICUM
.
Under the direction of
Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner
, there is a particular focus on anatomy-oriented short stem concepts.
The calcar-guided short stem prosthesis represents a biomechanically oriented concept that takes into account the natural force transmission of the hip and simultaneously preserves bone substance.
It enables individual reconstruction and can offer long-term benefits - provided it is correctly indicated and precisely implanted.


Bilateral short stem prosthesis in one operation – simultaneous treatment of both hips
In selected cases, it may be useful to treat both hip joints in a single operation with short stem prostheses. This so-called simultaneous bilateral implantation is considered when both hips are similarly severely affected and the patient's general health allows it.
The advantage of bilateral treatment in one operation lies primarily in the overall strategy: instead of undergoing two separate surgeries with their own rehabilitation, the functional reconstruction of both hips occurs in a single treatment step. This can help avoid muscular imbalances and enable a symmetrical restoration of leg length and hip mechanics.
This approach can be particularly interesting when using short-stem prostheses, as the bone-sparing implantation preserves the anatomical structures to a large extent. As a result, both hips can be reconstructed to be functionally comparable.
A simultaneous bilateral treatment can also:
- shorten the overall treatment time
- allow for a single anesthesia
- consolidate rehabilitation
At the same time, this approach requires careful selection of patients. Factors such as overall health status, physical resilience, and individual risks must be carefully assessed in advance.
Whether a bilateral treatment in one operation is useful should therefore always be decided on an individual basis.
When is bilateral treatment useful?
Bilateral hip osteoarthritis often occurs:
- due to age
- influenced by genetics
- due to malalignments
- after previous load-related damage
If both hip joints are symptomatic, treatment of both sides may be necessary – either:
- at different times
- or in certain cases in a single operation
The short stem prosthesis can help preserve bone on both sides.
Benefits of bilateral short stem supply
Due to the bone-preserving implantation, the short stem prosthesis can be particularly useful in bilateral care.
Possible benefits:
- Preservation of natural bone structure
- anatomically close force transmission
- better conditions for long-term stability
- strategic options for later revisions
Especially in bilateral osteoarthritis, long-term bone preservation plays an important role.
Simultaneous or staged surgery?
In bilateral care, the question often arises:
👉 both hips simultaneously or consecutively?
The decision depends on:
- general health status
- Resilience
- individual situation
A staged supply enables gradual rehabilitation.
Simultaneous care can be useful in selected cases.
Biomechanical significance
The hips work as a functional unit.
In bilateral osteoarthritis, symmetrical reconstruction can help:
- improve gait pattern
- to support muscular balance
- to reduce incorrect loading
The short stem prosthesis enables an anatomically oriented reconstruction.
Rehabilitation after bilateral treatment with short stem prosthesis
The follow-up treatment is based on:
- surgical strategy
- individual resilience
Important goals are:
- restoration of mobility
- Muscle building
- gait stability
A structured rehabilitation supports functional integration.
Long-term perspective
In bilateral treatment, bone preservation is particularly relevant.
The short stem prosthesis can:
👉 support long-term stability
👉 preserve future options
This makes it a modern solution for bilateral osteoarthritis.
Conclusion
Bilateral treatment with short stem prostheses can be a bone-preserving and functionally oriented solution with suitable indication.
It enables an anatomically close reconstruction of both hips and can offer long-term perspectives.

Short stem prosthesis or surface replacement (hip cap) – two bone-preserving concepts in comparison
Both the short stem prosthesis and the surface replacement of the hip (often referred to as "hip cap") pursue a similar goal:
👉 to preserve as much bone as possible
👉 to enable natural force transmission
👉 to create long-term perspectives
Nevertheless, both concepts differ fundamentally.
What is a surface replacement (hip cap)?
In surface replacement, the femoral head is not removed, but rather covered with a metal cap. At the same time, a matching acetabular cup is implanted.
The principle:
- maximum bone preservation in the femur
- large joint surface
- anatomically close loading
The procedure was considered an attractive option for young, active patients for a long time.
Biomechanical difference to short stem prosthesis
The short stem prosthesis replaces the femoral head, but uses the proximal femur for stabilization.
The surface replacement, on the other hand, completely preserves the femoral head.
This means:
Short stem prosthesis
→ metaphyseal anchoring
→ calcar-guided force transmission
Hip cap
→ epiphyseal loading
→ direct head loading
Both systems attempt to utilize natural load paths – in different ways.
Benefits of the short stem prosthesis
The short stem prosthesis offers:
- good primary stability
- controllable implant position
- less dependence on the bone quality of the head
- flexible reconstruction of the hip geometry
In addition, there are very good long-term clinical results today.
Challenges of surface replacement
The surface replacement places high demands on:
- Bone quality
- Anatomy
- precise indication
In particular, fractures of the femoral neck and material-related aspects were discussed in the past.
Therefore, the application is now more selective.
Revision – strategic difference
A central point is the revision surgery.
After short stem prosthesis:
👉 often good prerequisites for standard implants
After hip resurfacing:
👉 Revision can be more complex, especially with bone loss
For whom is which concept suitable?
Short stem prosthesis:
- good bone quality
- Desire for bone-preserving care
- broader applicability
Surface replacement:
- very selected patient groups
- stable head structure required
Conclusion
Both concepts pursue bone-preserving strategies.
The short-stem prosthesis offers today a broader applicability and stable clinical results.
The surface replacement remains an option for selected situations.
The decision should be made on an individual basis.
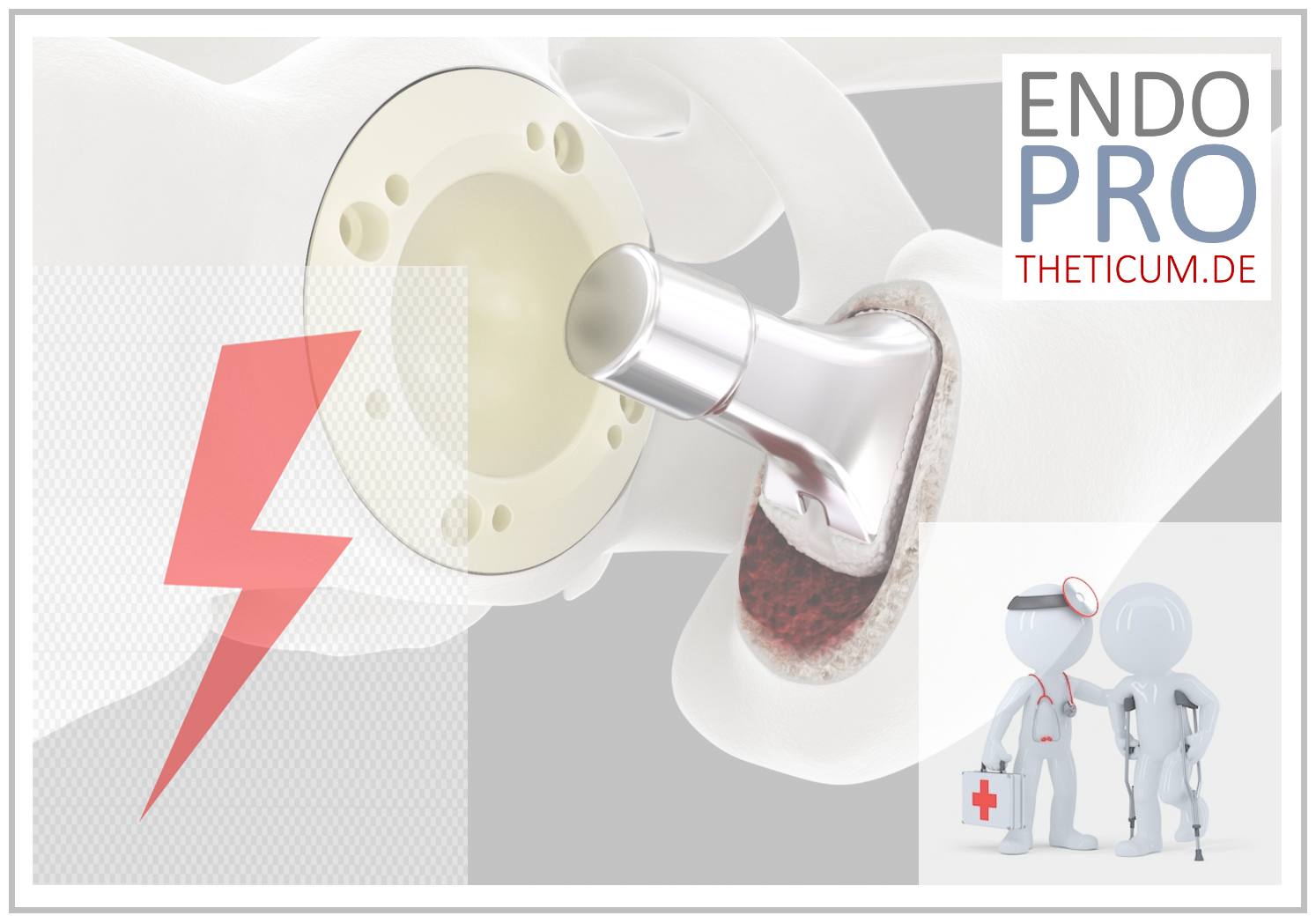
Short-stem prosthesis and longevity –
How long does a modern hip implant last?
One of the most common questions from patients is:
👉 How long does a short-stem prosthesis last?
The answer is nuanced – and depends less on the length of the stem than on several crucial factors.
Modern short-stem prostheses show stable long-term results
Short-stem prostheses were originally developed with the goal of preserving bone and supporting natural force transmission. Today, there is increasing clinical data available that shows:
Modern short-stem systems achieve survival rates that are comparable to those of classical hip prostheses.
The decisive factor is not only the implant itself, but:
- the correct indication
- a precise implantation
- the bone quality
- the individual load
The service life is thus a combination of implant design, surgical technique, and patient-specific factors.
Which factors influence durability?
The service life of a short-stem prosthesis is determined, among other things, by:
- Bone quality
- Implant position
- Activity level
- Body weight
- Load pattern
A well-positioned implant with stable metaphyseal anchoring can function reliably in the long term.
Role of physiological force transmission
A central advantage of the short-stem prosthesis is the anatomically close load transmission.
Since the forces are predominantly introduced proximally, it can:
👉 Stress shielding can be reduced
👉 Bone loss can be reduced
A more physiological load can contribute to long-term stability.
Importance of patient selection
Not every hip is equally suitable.
The durability also depends on whether:
- the bone structure is stable
- the anatomy is suitable
- the indication was correctly determined
The selection of the appropriate implant remains crucial.
Service life and long-term strategy
The short stem prosthesis is often considered a strategic solution.
Since more bone is preserved:
👉 better conditions exist for later revisions
This is particularly relevant for:
- younger patients
- long-term care concepts
Conclusion
The short stem prosthesis can enable long-term stable care.
Its service life depends not only on the implant, but also on:
✔ Indication
✔ Implantation
✔ Bone quality
✔ Load
When used correctly, it offers a modern, bone-saving option with a good long-term perspective.

How can one extend the durability of a short stem prosthesis?
A short stem prosthesis can function stably for many years - provided it is not only implanted correctly, but also loaded sensibly in the long term. In addition to surgical precision, post-operative behavior plays a decisive role in longevity.
The durability of a hip implant is not a static value, but is influenced by several factors that patients can actively influence.
Muscle building and stability
One of the most important measures to extend longevity is targeted muscle building.
Well-trained muscles:
- stabilizes the hip joint
- reduces peak loads
- improves force distribution
Particularly relevant are:
- Gluteal muscles
- Core muscles
- Thigh muscles
A stable muscular guidance relieves the implant in the long term.
Joint-friendly movement
Exercise is important - but the type of load counts.
Favorable are:
- uniform movements
- cyclic loading
- joint-friendly activities
Examples include:
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Walking
These forms of exercise support blood circulation and maintain function without putting excessive strain on the implant.
Avoiding Overload
Short stem prostheses are stable - but not indefinitely resilient.
Unfavorable are:
- abrupt shock loads
- extreme rotational movements
- repeated high-impact activities
Conscious load control can help reduce mechanical stress.
Body weight and load
Body weight directly affects the forces in the hip joint.
Even small weight differences can:
ὄ9 significantly alter the joint load
A stable weight situation can contribute to the protection of the implant.
Regular follow-up checks
Long-term stability also depends on the early detection of possible changes.
Regular checks enable:
- Assessment of implant position
- Detection of load problems
- timely adjustment of activity
This can help to address potential problems early on.
Consciously shaping everyday life
Everyday movements also play a role.
Helpful are:
- ergonomic lifting
- conscious rotational movements
- Avoiding jerky loads
In the long term, this can contribute to relief.
Conclusion
The durability of a short stem prosthesis depends not only on the implant, but also on long-term handling.
Muscle building, joint-sparing movement and adapted stress can help maintain function over many years.



















