ALMIS Method and Short Stem - Perfect Combination for the Hip
Minimally invasive approach to the hip: ALMIS method and short stem prosthesis
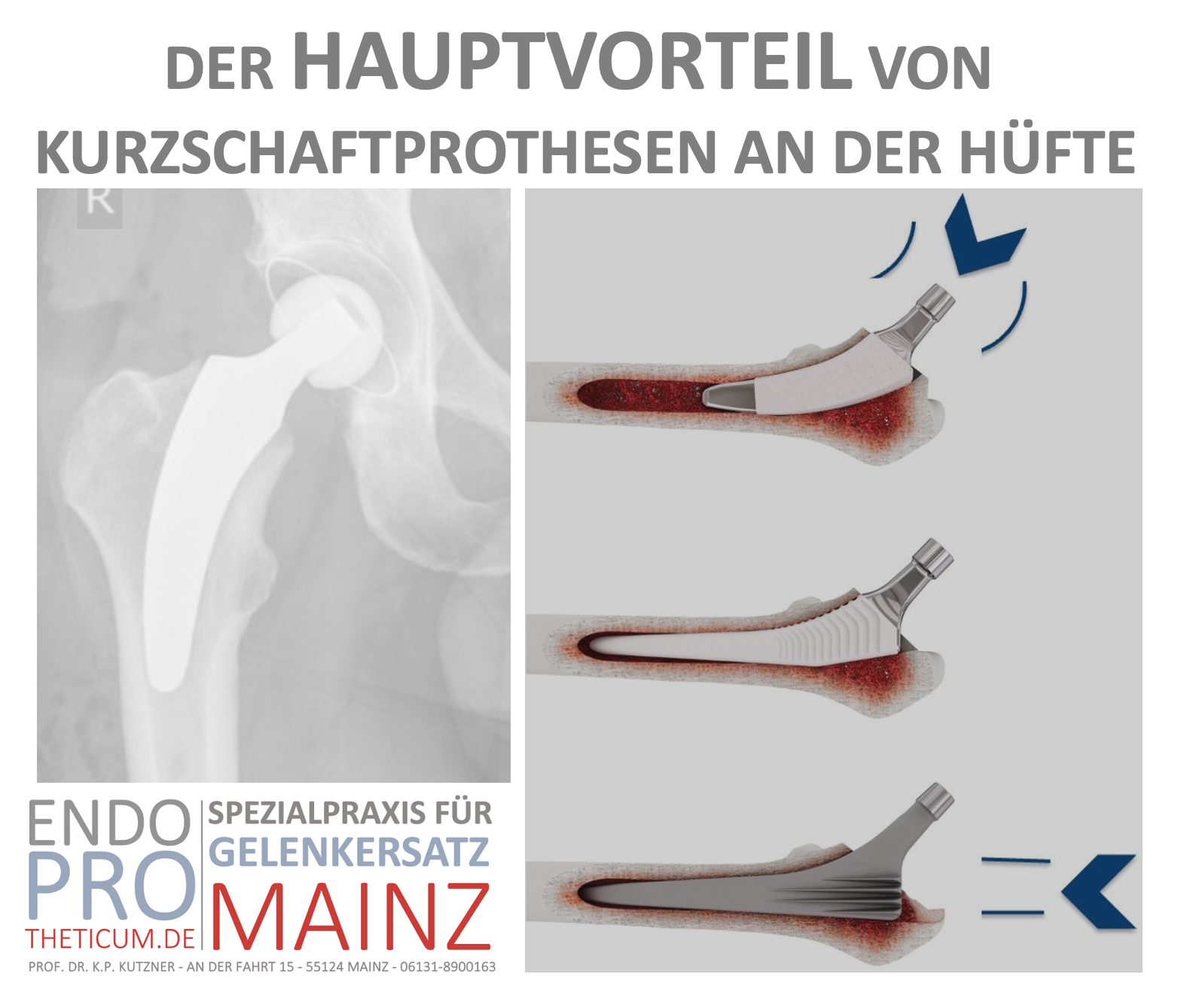
Modern endoprosthetics has advanced significantly over the past few decades. One of the latest innovations is the ALMIS method (Anterolateral Minimally Invasive Approach), which, in combination with short-stem prostheses, has developed into a proven technique. This combination offers an optimal solution for patients undergoing hip joint surgery. In this article, you will learn everything about the ALMIS method, the benefits of short-stem prostheses, and why this approach is considered the future of hip endoprosthetics.
What is the ALMIS method?
The ALMIS method represents a minimally invasive approach to the hip via the anterolateral approach. This surgical approach does not require detachment of muscles or tendons, reducing postoperative pain and accelerating rehabilitation.
Benefits of the ALMIS method
Geringere Gewebeschädigung: Der Muskel bleibt intakt, wodurch weniger Komplikationen auftreten.
Faster mobilization: Patients can often get up on the same day.
Shorter hospital stays: The minimally invasive approach shortens the healing period.
Improved stability: The joint remains stable because muscle function is preserved.
What is the ALMIS approach?
The ALMIS approach is a surgical intervention that takes place via an anterolateral incision. This approach has been specifically developed to spare muscle structures such as the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus, thereby ensuring faster recovery and better functionality after hip surgery.
Unlike traditional surgical approaches, the ALMIS approach enables precise placement of the prosthesis without extensive severing of muscles or tendons. This is particularly advantageous when implanting a short stem prosthesis.
Technique of the ALMIS approach
Incision: An incision is made at an angle of about 10–12 cm along the front of the thigh, near the hip.
Muscle preservation: The anterolateral position ensures that no important muscles are directly severed. Instead, the access is between the muscles (intermuscular) or along their fibers (interfascial).
Preservation of nerve structures: The technique minimizes the risk of damage to sensitive nerves such as the femoral nerve or the superior gluteal nerve.
Precise implantation: With the ALMIS approach, the prosthesis is precisely positioned, reducing the risk of complications such as dislocations.
Benefits of the ALMIS approach
Shorter operation time and faster recovery:
Thanks to the minimally invasive nature, the ALMIS approach enables rapid postoperative mobilization. Many patients can get up and walk within a few hours after surgery.
Muscle and tissue preservation:
The avoidance of extensive muscle dissection leads to less pain and better muscle preservation, which is particularly important for athletic or younger patients.
Reduction of complications:
With the ALMIS approach, the risk of postoperative instability or dislocation is reduced, as important soft tissue structures remain intact.
Improved aesthetics:
The smaller incision leaves a minimally visible scar, which is cosmetically advantageous for many patients.
Areas of application of the ALMIS approach
Short stem prostheses: The ALMIS approach is ideally suited for the implantation of short stem prostheses, which are particularly used in younger, more active patients with high bone density.
Revision operations: Even in demanding interventions, such as the replacement or revision of hip prostheses, the ALMIS approach offers clear advantages.
Early arthrosis or joint-preserving interventions: This method is also optimally suited for patients with less advanced arthrosis.
Limitations and challenges
Despite its numerous advantages, the ALMIS approach is not always the method of choice. Patients with severe deformities, significant overweight, or limited mobility of the hip joint may benefit from other approaches. The surgeon decides individually.
The ALMIS approach revolutionizes hip arthroplasty with its minimally invasive, tissue-sparing approach. Especially in combination with a short stem prosthesis, this method opens up entirely new dimensions in patient care. Rapid rehabilitation, improved functionality, and fewer postoperative complaints make it one of the most advanced approaches in modern orthopedics.
What is a short stem prosthesis?
A short stem prosthesis is an innovative variant of hip joint prosthesis, specifically developed for younger and active patients. Unlike conventional prostheses, it requires less bone material for anchoring.
Characteristics of the short stem prosthesis
Less invasiveness: Minimal bone cut.
Optimal bone integration: Specifically designed for long-term stability.
Flexibility: Adaptable to various anatomical conditions.
Indications
Younger patients with high activity level.
Good bone quality.
Patients with high demands on functionality.
Benefits of combining ALMIS and short stem
The combination of the ALMIS method and short stem prostheses offers many benefits to patients.
1. Less postoperative pain
Due to the muscle-sparing approach of the ALMIS method and the minimally invasive technique of the short stem prosthesis, patients report less pain.
2. Faster rehabilitation
Patients can be mobilized earlier, which accelerates the healing phase.
3. Natural range of motion
The bone-preserving approach enables a faster restoration of natural mobility.
4. Longer-Lasting Results
Long-term prognoses show that short-stem prostheses in combination with the ALMIS method achieve higher patient satisfaction.
Anatomy of the Hip and the Importance of Short Stem Prostheses
To understand the benefits of the ALMIS method and short stem prosthesis, it is essential to be familiar with the anatomy of the hip.
Anatomy of the hip
The hip consists of the femur and the acetabulum. In diseases such as osteoarthritis, the articular cartilage is destroyed, leading to pain and limited mobility.
Why short stem prostheses are optimal here
Preservation of the femoral bone structure.
Adaptation to the natural anatomy.
Improvement of load distribution in the joint.
Postoperative rehabilitation with the ALMIS method
Rehabilitation begins immediately after surgery.
Phase 1: First days after surgery
Early mobilization: Getting up on the first day.
Pain management: Use of pain medication as needed.
Phase 2: Weeks 1-6
Physiotherapy: Focus on mobility exercises.
Avoiding incorrect loading: Correct gait technique with walking aids.
Phase 3: Months 2-6
Increasing the load.
Gradual return to normal activities.
Why the combination of ALMIS and short stem is the future
The ALMIS method, combined with short stem prostheses, offers numerous benefits and has established itself as one of the best techniques. The innovative technology, muscle-sparing approach, and excellent rehabilitation options make it the first choice for many patients.
Conclusion
The combination of ALMIS and short stem is a revolution in endoprosthetics. It offers patients a safe, effective, and sustainable solution for hip diseases. With correct indication and implementation, this method is undoubtedly one of the best options for hip surgery.
Make an Appointment?
You can easily make an appointment both by phoneand online .



























