The hip offset - why is accurate reconstruction using hip replacement so important?
Why the offset during hip replacement implantation should not be too small or too large
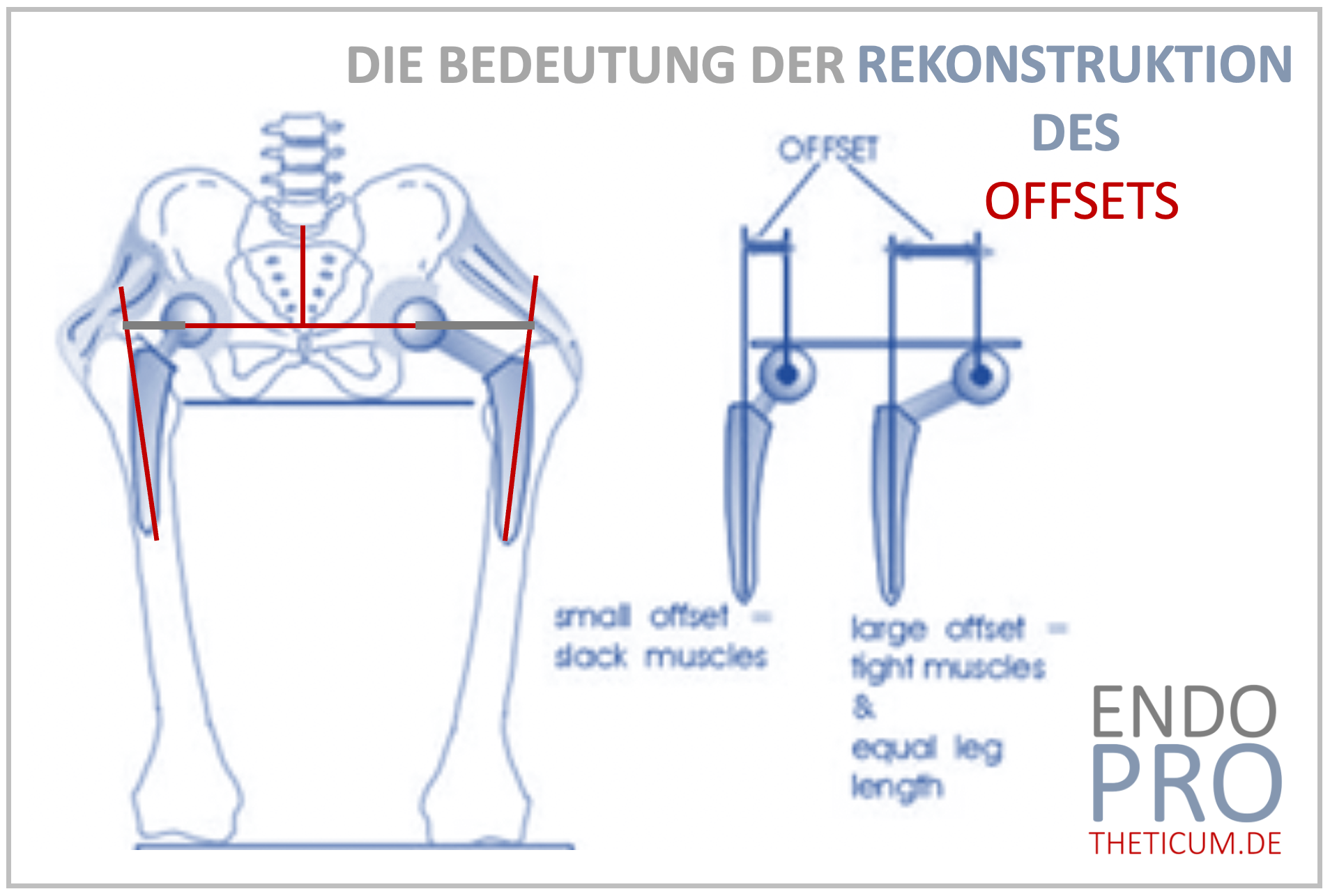
The offset of the hip plays a crucial role in the biomechanical function of the hip joint. Especially during the implantation of an artificial hip (total hip replacement), an exact reconstruction of the offset is necessary to ensure optimal force distribution, joint stability, and muscle function. If the offset is not restored correctly, various complications such as instability, muscle weakness, or even chronic pain can occur. This article explains in detail the anatomy, the different types of offset, the strategies for reconstruction, and the consequences of incorrect offset restoration.
Anatomy of hip offset: what is offset?
The hip offset describes the lateral distance between the center of the femoral head and the midline of the femur. It affects the tension of the surrounding musculature, particularly the gluteus medius muscle, and contributes to the stability of the hip joint. There are three main types of offset:
- Acetabular offset: Refers to the distance between the center of the acetabulum and the pelvis. Incorrect reconstruction can lead to poor force distribution.
- Femoral offset: The lateral distance of the femoral shaft from the femur. An increased femoral offset can alter muscle tension.
- Total offset: The combination of acetabular and femoral offset, which describes the overall lateral displacement of the hip.
Strategies for offset reconstruction in total hip arthroplasty
During the implantation of a hip prosthesis, there are various possibilities for correctly restoring the offset:
- Individual adjustment of the acetabular position: By optimally placing the acetabulum, the acetabular offset can be exactly reconstructed.
- Selection of the appropriate stem design: Different stem models offer various offset variants to enable the best possible reconstruction.
- Modular prosthesis components: Allow for finer adjustment of the offset through the use of different neck lengths and angles.
Medialization of the acetabulum and compensatory enlargement of the femoral offset
The medialization of the socket means that the prosthetic socket is positioned slightly inward (toward the pelvis). This reduces the lateral displacement of the joint center and allows for a better load distribution in the pelvic area. To maintain the overall offset, the shaft offset is correspondingly increased. This combination results in an optimized lever arm of the hip musculature and improves the stability of the joint.
Biomechanically, this results in higher efficiency of the gluteus medius muscle, minimizing postoperative muscle weakness and improving gait.
Consequences of incorrect offset reconstruction
Offset loss
A reduced offset can lead to a shortening of the lever arm of the abductors, resulting in a decrease in muscle strength. This can manifest as gait disturbances, instability, and an increased risk of dislocation. Additionally, a lower offset reconstruction can lead to uneven loading of the prosthesis, promoting wear.
Offset increase
An offset that is too large leads to overstretching of the musculature. This can cause chronic pain, muscular imbalances, and increased stress on the trochanteric bursa, potentially resulting in bursitis (inflammation of the bursa). Patients with excessive offset enlargement often report persistent lateral hip pain due to the soft tissues being subjected to unnatural tension. Additionally, this can lead to limited mobility and long-term impairment of muscle function.
Conclusion: Offset reconstruction in the hip is crucial!
The exact reconstruction of the offset is crucial for the success of a hip replacement. Incorrect restoration, whether due to offset loss or offset increase, can have significant negative consequences, including instability, muscle weakness, and chronic pain. Modern prostheses and surgical techniques now enable more precise adjustment of the offset, allowing patients to expect optimal function and longevity of their hip prosthesis. Therefore, offset reconstruction should always be carefully planned and individually adapted to avoid possible complications.
Make an Appointment?
You can easily make an appointment both by phoneand online .


























