Coxarthrosis: Recognize symptoms early and treat effectively
Symptoms and treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip

introduction
Coxarthrosis, also known as hip osteoarthritis, is a degenerative disease of the hip joint that can lead to significant pain and restricted movement. It is one of the most common forms of osteoarthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide, particularly older adults. Early detection of symptoms and effective treatment are crucial to improving the quality of life for those affected and slowing the progression of the disease. In this comprehensive blog post, we will examine the symptoms of coxarthrosis in detail, how to recognize it early, and what modern treatment methods are available.
What is coxarthrosis?
Coxarthrosis is a form of osteoarthritis that affects the hip joint. It develops due to the progressive breakdown of articular cartilage, which protects the ends of the bones and allows for smooth movement. As the cartilage deteriorates, the bones rub directly against each other, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. The condition can affect one or both hips and has various causes, including genetic predisposition, obesity, injuries, and inflammatory diseases.
Causes of coxarthrosis
The development of osteoarthritis of the hip can be influenced by a variety of factors. The most common causes include:
Genetic predisposition
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of osteoarthritis of the hip. A family history of osteoarthritis can increase the risk of developing the disease. Certain genetic markers can increase susceptibility to the degeneration of articular cartilage.
Overweight and obesity
Obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of osteoarthritis of the hip. Overweight individuals exert additional pressure on their hip joints, which accelerates cartilage degeneration. Studies show that weight loss can significantly reduce the risk and symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip.
Injuries and trauma
Injuries to the hip joint, such as fractures or severe contusions, can damage the cartilage and lead to the development of osteoarthritis. Sports injuries, especially among elite athletes, also increase the risk.
Inflammatory diseases
Chronic inflammation, such as that occurring in rheumatoid arthritis, can break down joint cartilage and lead to osteoarthritis. Inflammatory processes in the body can directly damage cartilage and impair joint health.
Old
The risk of osteoarthritis of the hip increases with age. The articular cartilage is subject to a natural wear and tear process, which is accelerated by aging.
Gender
Women are more frequently affected by osteoarthritis of the hip than men, which is attributed to hormonal differences. After menopause, the risk increases significantly for women, due to the decline in protective estrogen levels.
Early symptoms of coxarthrosis
Early detection of osteoarthritis of the hip is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment measures in a timely manner. Early symptoms include:
hip pain
The first signs of osteoarthritis of the hip are often pain in the hip, which initially only occurs during activity. The pain can radiate into the groin, thigh, or buttocks and improves after periods of rest. Initially, this pain is often misinterpreted as muscular discomfort.
stiffness
Another early symptom is stiffness in the hip joint, especially in the morning or after prolonged periods of inactivity. The stiffness can last from a few minutes to several hours and restrict movement.
Movement restrictions
In the early stages of osteoarthritis of the hip, those affected may have difficulty performing certain movements, such as putting on shoes or bending over. These limitations are often subtle but can increase over time.
Advanced symptoms of coxarthrosis
In advanced stages of osteoarthritis of the hip, symptoms worsen and can significantly impair quality of life. The most common advanced symptoms include:
Chronic pain
The pain can become chronic and also occur during periods of rest or at night, which can disrupt sleep. This chronic pain often leads to a significant impairment of daily life and mobility.
Hip joint deformity
In advanced stages, visible deformities of the hip joint can occur. These changes can be seen on X-rays and lead to a functional leg length discrepancy.
Walking disability
Hip mobility is severely restricted, making walking, climbing stairs, and other everyday activities difficult. Many patients develop a limping gait to minimize pain, which, however, can lead to further muscular imbalances and discomfort.
Muscle atrophy
The protective posture and reduced activity can lead to atrophy of the muscles around the hip joint. This results in further instability of the joint and exacerbates the symptoms.
Secondary symptoms
The altered stress patterns and compensatory postures can lead to secondary problems such as back pain or pain in other joints. These problems are often the result of improper stress and muscular imbalances.
Diagnosis of coxarthrosis
Coxarthrosis is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging procedures. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for planning the correct treatment strategy.
Medical history
The doctor will take a detailed medical history to understand the patient's medical background. Important information includes the duration and nature of the pain, previous injuries, family history, and other medical conditions.
Physical examination
During the physical examination, the doctor will test the mobility of the hip joint and look for points of pain. Tests such as the Faber test or the Trendelenburg test can help assess the function of the hip joint.
Imaging procedures
Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans are crucial for diagnosing osteoarthritis of the hip. X-rays show typical changes such as joint space narrowing, osteophyte formation, and subchondral sclerosis. An MRI can provide detailed images of early cartilage damage and soft tissue changes.
Laboratory tests
Laboratory tests are generally not specific for diagnosing osteoarthritis of the hip, but they can help rule out inflammatory diseases. Tests for rheumatoid factors or other markers of inflammatory processes can be performed to consider rheumatic diseases in the differential diagnosis.
Modern treatment methods for coxarthrosis
The treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip aims to relieve pain, improve joint function, and slow the progression of the disease. Treatment may include conservative, invasive, and surgical measures.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment is often sufficient in the early stages of coxarthrosis and includes:
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is one of the most effective treatments for osteoarthritis of the hip. It includes specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint, improve mobility, and relieve pain. Therapists may use manual techniques, electrotherapy, and ultrasound to alleviate symptoms.
Drug therapy
Pain relievers such as paracetamol and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain and inflammation. In severe cases, stronger pain relievers such as opioids or injections of corticosteroids into the joint may also be considered.
Weight loss
Weight reduction is an important aspect of conservative treatment, especially in overweight patients. Reducing body weight can decrease pressure on the hip joint and alleviate symptoms.
Orthopedic aids
The use of orthopedic aids such as walking sticks or orthopedic shoes can reduce the strain on the hip joint and improve mobility. Special seat cushions and ergonomic furniture can also alleviate symptoms.
Invasive treatment
If conservative measures are insufficient, more invasive treatments can be considered:
Injection therapy
Injections of corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid into the hip joint can reduce inflammation and improve joint function. These injections are usually effective in the short term and can be administered repeatedly.
Minimally invasive surgery
Arthroscopic procedures can be used to clean the joint and remove damaged tissue. These procedures are less invasive than open surgery and have shorter recovery times.
Surgical treatment
In advanced cases of coxarthrosis, when conservative and invasive measures are no longer sufficient, surgery may be necessary:
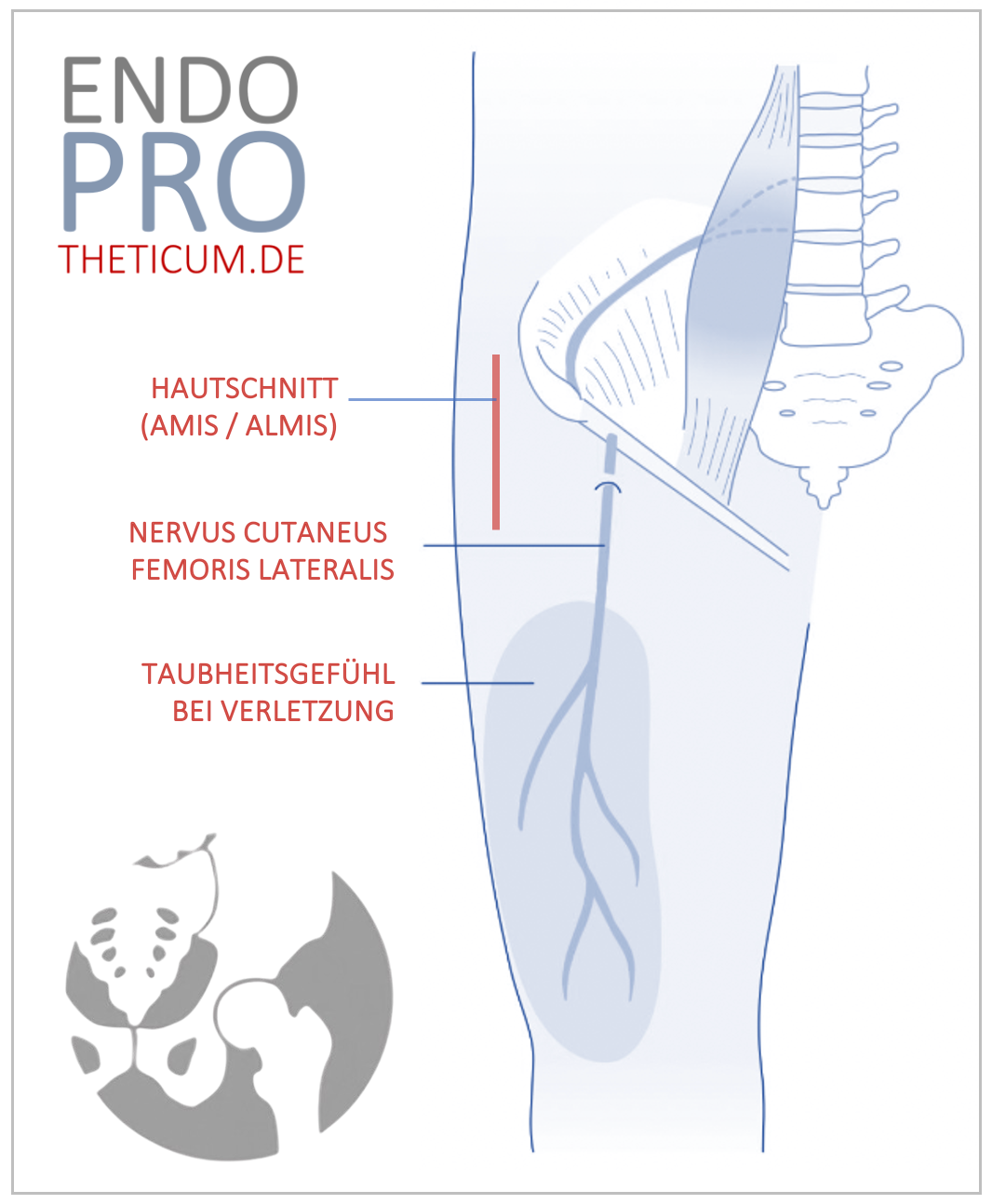
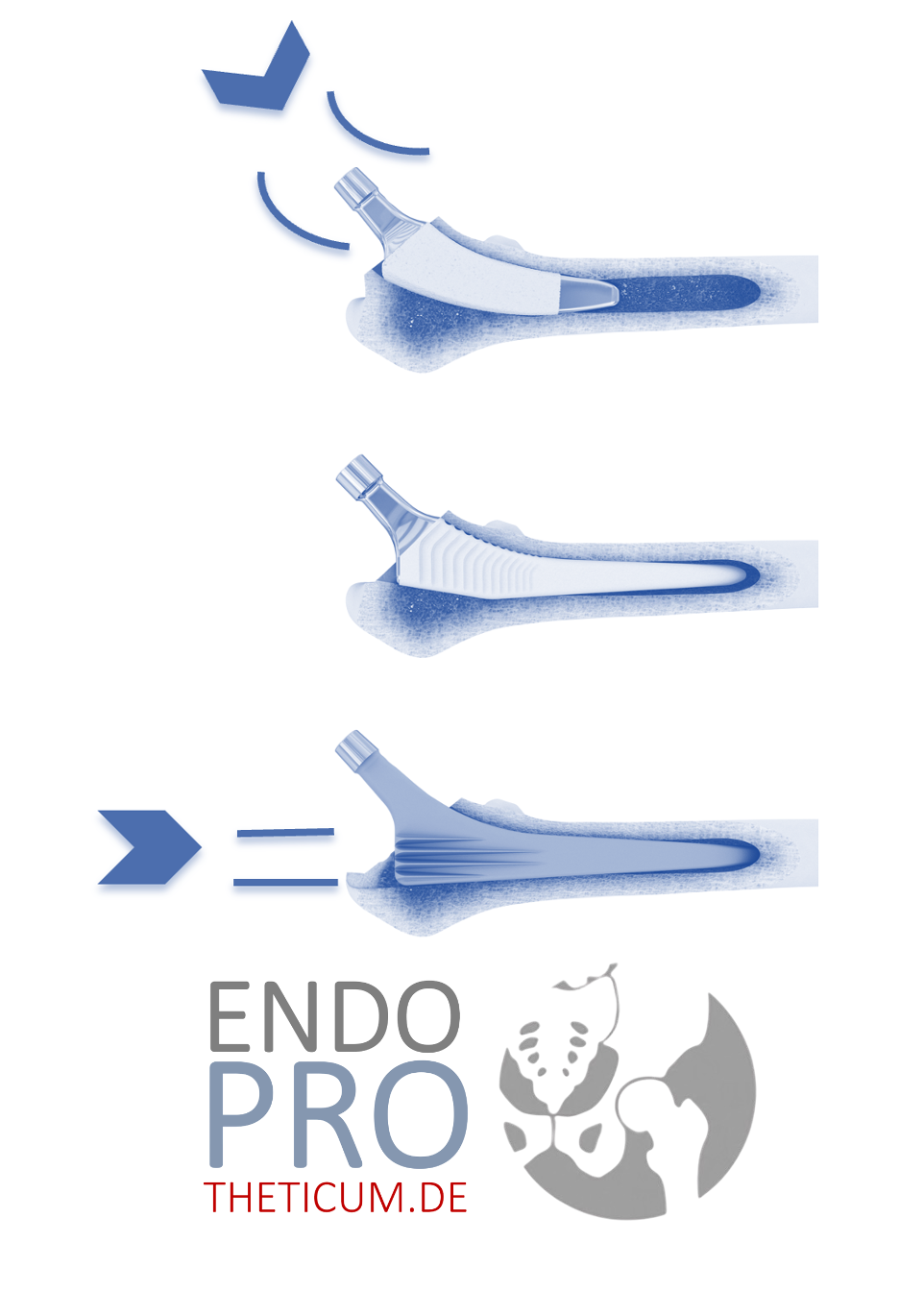
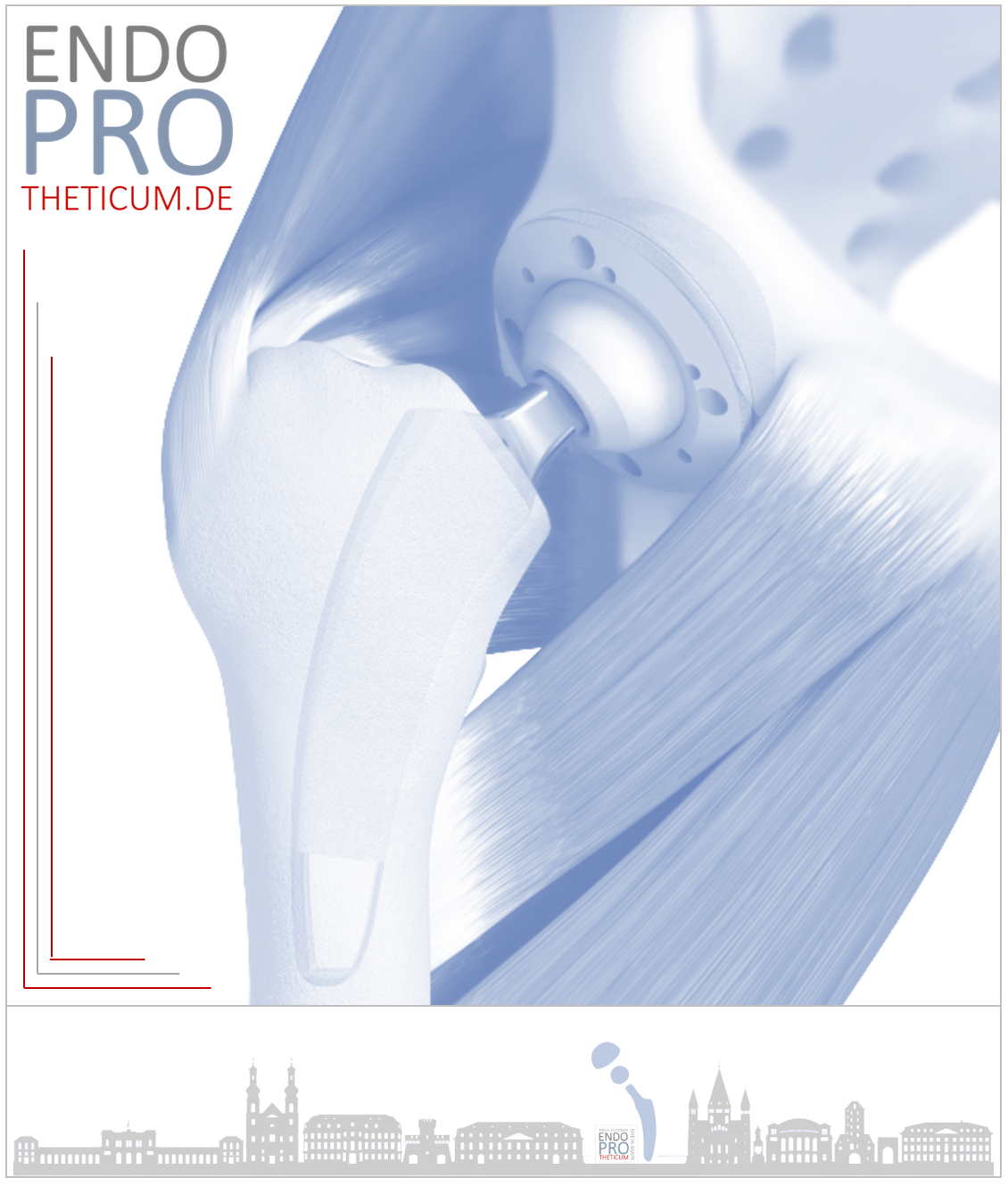
Total endoprosthesis (TEP)
Total hip replacement surgery is the most common surgical treatment for osteoarthritis of the hip. In this procedure, the damaged joint is replaced with an artificial hip. Modern prostheses have a high success rate and can significantly improve quality of life.
Osteotomy
In younger patients or those with specific anatomical problems, an osteotomy may be considered. This involves realigning the bone around the hip joint to better distribute the load and slow down cartilage degeneration.
Hip joint fusion
In rare cases, when other measures are unsuccessful, hip fusion (arthrodesis) may be considered. This procedure permanently fuses the hip joint to relieve pain.
Prevention of coxarthrosis
Prevention of osteoarthritis of the hip includes measures to reduce risk factors and promote joint health:
Healthy eating
A balanced diet can help maintain a healthy weight and support joint health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins can have anti-inflammatory effects and protect cartilage.
Regular exercise
Regular, joint-friendly exercise is crucial for preventing osteoarthritis of the hip. Activities such as swimming, cycling, and Nordic walking promote joint health without putting excessive strain on the joints.
Injury prevention
Avoiding injuries and properly treating joint injuries can reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis of the hip. Athletes should pay attention to good technique and appropriate training to avoid injuries.
Weight control
Maintaining a healthy weight is an important preventative factor. Overweight individuals should take steps to lose weight in order to reduce the strain on their hip joints.
Rehabilitation after hip surgery
After hip surgery, comprehensive rehabilitation is crucial for the success of the treatment:
physical therapy
After the operation, rehabilitation begins with intensive physiotherapy to improve mobility and strengthen muscles. An individually tailored exercise program is crucial for restoring function.
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapists help patients resume everyday activities and offer support in adapting their home environment. This can include the use of assistive devices and furniture modifications.
Pain management
Effective pain management is crucial for recovery after surgery. This includes the use of pain medication, physical therapy methods, and alternative therapies such as acupuncture.
Psychological support
Psychological support can help cope with the emotional and mental challenges following hip surgery. This can be provided through counseling, self-help groups, and relaxation techniques.
Future prospects in the treatment of coxarthrosis
Treatment options for osteoarthritis of the hip are constantly evolving. Future developments could further improve patients' quality of life
Biological therapies
Research into biological therapies, such as stem cell therapy and genetic approaches, offers promising perspectives. These therapies aim to restore cartilage and maintain joint function in the long term.
Technological innovations
Technological advances, such as the development of new materials for endoprostheses and minimally invasive surgical techniques, could further improve treatment outcomes and shorten recovery times.
Precision medicine
Precision medicine, which is tailored to the individual genetic and biological characteristics of the patient, could enable personalized treatment of coxarthrosis in the future.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis of the hip (coxarthrosis) is a widespread and debilitating condition, but it can be effectively managed with the right measures and treatments. Early detection of symptoms and comprehensive treatment are crucial to improving the quality of life for those affected and slowing the progression of the disease. From conservative measures and innovative therapies to surgical interventions, numerous options are available to alleviate symptoms and preserve hip joint function. Through a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and supportive measures, those affected can actively contribute to improving their situation. The future of osteoarthritis treatment is promising, with continuous advances in medical research and technological innovations offering new hope for patients.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .