Hip pain in equestrian sports — what helps?
When the hip joint fails: Riding with hip pain
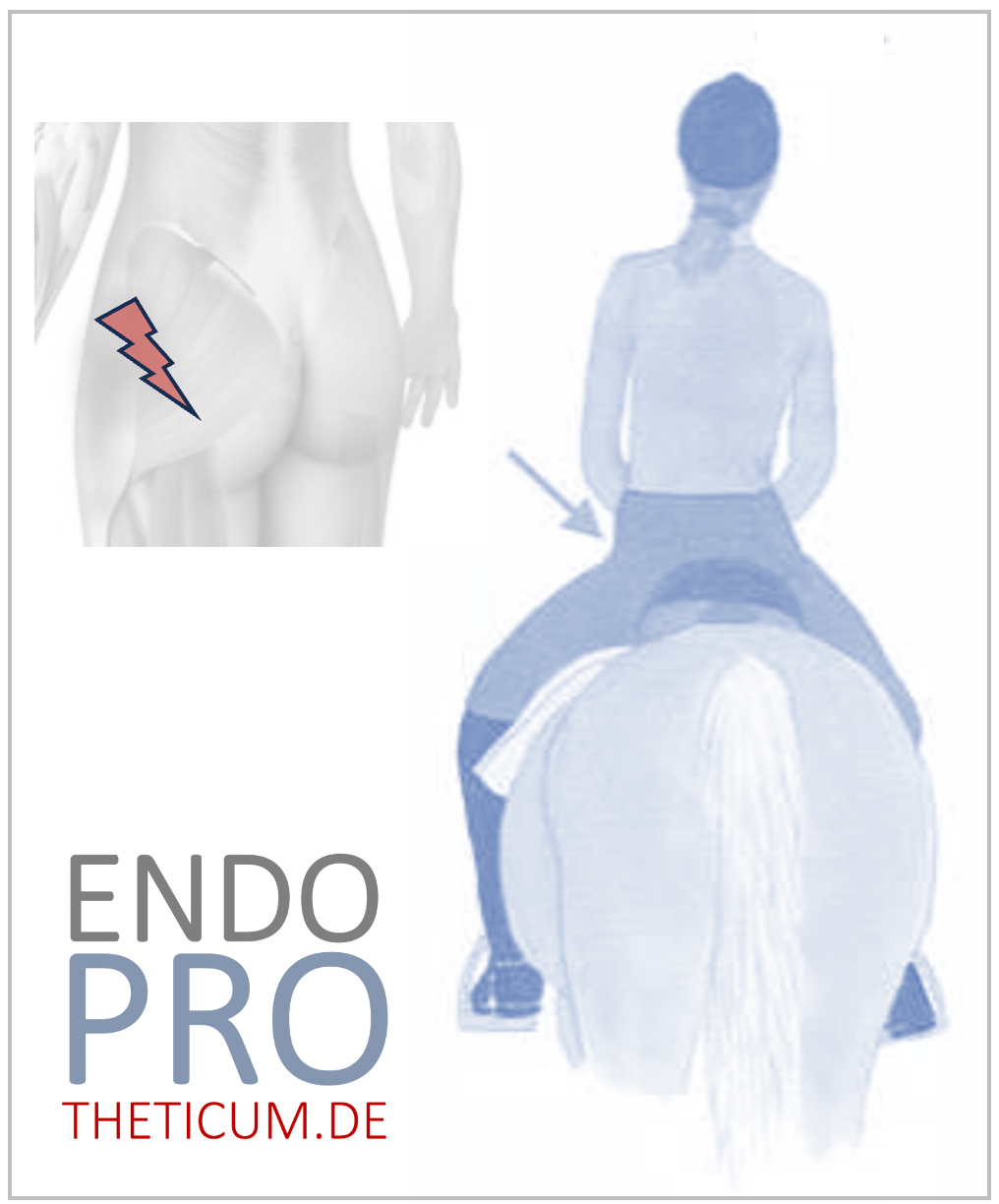
Riding is a way of life for many people. The close connection to the horse, the feeling of freedom in the terrain or the concentration on fine aids in dressage: All this makes riding unique. But when the hip no longer cooperates, joy quickly turns to frustration. Hip pain is one of the most common problems in equestrian sports. It can change the seat, make communication with the horse more difficult and in the worst case lead to riding being abandoned altogether.
Why hip pain when riding is so stressful
The hip is one of the most important joints in the human body. It connects the upper body to the legs, bears our entire body weight, and enables movements such as walking, sitting, and climbing stairs. When riding, the hip takes on an even greater role:
- It is the "control center" for the seat.
- We control the horse with subtle movements of the pelvis.
- A stable, relaxed seat is only possible with healthy hip joints.
When the hip hurts, not only the rider suffers, but also the horse. A tense seat leads to unclear signals. Many horses react nervously, rebelliously, or show behavioral changes.
Therefore, hip pain is not just a physical problem, but affects the entire rider-horse team.
Typical complaints with hip pain in equestrian sports
Hip problems can manifest in very different ways. Especially in equestrian sports, typical patterns often occur:
- Groin pain when sitting in the saddle: Riders often experience a pulling or stabbing sensation in the groin, especially during long riding sessions.
- Pain when trotting or galloping: Dynamic movements put more strain on the hip, complaints occur particularly often here.
- Restricted mobility: Some affected individuals notice that they can no longer tilt their pelvis loosely or that their legs no longer fall freely outward.
- Asymmetric Seat: To avoid pain, the weight is shifted – the horse receives one-sided aids.
- Radiation into the leg or buttocks: Hip problems can irritate nerves, leading to pain in the thigh or buttocks.
- Problems when mounting or dismounting: Sometimes it's not the riding itself that's the problem, but the way in and out of the saddle.
Many riders identify with these symptoms. It is important: These complaints should be taken seriously.
Causes of hip pain when riding
The causes are diverse – it's not always immediately due to osteoarthritis.
1. Muscular problems
- Adductors (inner thigh) are heavily stressed when riding. They can become tense or shortened.
- Iliopsoas muscle (hip flexor) tends to become overloaded, especially when sitting in the saddle for a long time.
2. Incorrect seat or saddle problems
An ill-fitting saddle or an uneven seat lead to incorrect stress. Even small asymmetries can have major effects.
3. Hip joint diseases
- Impingement (FAI): A bony constriction in the hip joint leads to pain during certain movements.
- Labral tears: The labrum can tear and cause pain in the groin.
- Osteoarthritis (Coxarthrosis): Joint wear, often occurring at an advanced age or after previous injuries.
4. Trauma
Falls from the horse or direct blows to the hip can cause long-lasting problems.
5. Problems in the pelvis or sacroiliac joint
Not all "hip pain" actually comes from the hip joint. The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) can also cause discomfort.
How the diagnosis is made
An orthopedist or sports medicine specialist proceeds in a structured manner:
- Conversation (Anamnesis): When does the pain occur? Only while riding or also in everyday life? Are there any pre-existing conditions or falls?
- Physical examination: Mobility, special tests (e.g., impingement test), muscle status.
- Imaging:
- X-ray shows bone changes and osteoarthritis.
- MRI makes cartilage, labrum and muscles visible.
- Ultrasound is suitable for tendons and bursae.
Functional Analysis: Some doctors observe the rider's seat or use video analysis.
This way, the cause of hip pain can usually be clearly identified.
Treatment without surgery – what really helps
Many hip problems can initially be treated conservatively. Especially for riders, there are some sensible approaches:
1. Riding training and saddle check
An incorrectly adjusted or unsuitable saddle is often the root of the problem. A riding instructor or a seat trainer can help correct the seat.
2. Physiotherapy and Training
- Mobilization exercises for hip and pelvis.
- Stretching of the adductors and hip flexors.
- Strengthening the core muscles
3. Manual therapy / Osteopathy
Blockages in the pelvis or ISG can be resolved.
4. Pain medication or injections
Temporarily, anti-inflammatory medications or targeted injections can help.
5. Load adjustment
Often, temporarily reducing training helps:
- More walk, less canter.
- Shorter units.
- Complementary sports such as swimming or cycling.
Training tips for riders with hip pain
Here are some simple exercises you can do on your own:
- Pelvic tilt: While sitting or lying down, slowly move your pelvis forward and backward.
- Adductor stretch: While sitting, bring the soles of your feet together and let your knees fall outward.
- Plank (Forearm support): Strengthens the core muscles.
- Balance exercises on the gym ball: Promotes sitting stability.
Important: These exercises do not replace physiotherapy, but can support the healing process.
When hip surgery or hip replacement is useful
If pain persists and limits quality of life, surgery may be necessary. Reasons include:
- Advanced osteoarthritis.
- Labrum tears or FAI
- Severe movement restrictions.
Hip replacement (Total Hip Endoprosthesis)
A hip TEP is an artificial hip joint used when the natural joint is too damaged. Goal: Freedom from pain and restoration of mobility.
Many patients can ride again after a hip replacement - usually after a rehabilitation period of several months. Studies show that recreational riding is possible after a prosthesis, but intensive tournament riding should be discussed individually.
Riding after a hip replacement
The most common questions are: "Can I ride again after surgery?" and "How long does it take?"
- First rehabilitation phase: Physiotherapy begins on the first day after surgery.
- After 6–12 weeks
- After 3–6 months: A cautious return to riding can be successful – depending on the healing process, muscle mass, and type of sport.
- Long-term
Risks such as falls or extreme stress should be considered. Consultation with the surgeon is mandatory.
Case studies
- Recreational rider, 45 years old: Hip pain in the groin, cause: adductor tension. Therapy: physiotherapy + seat training. After 2 months, symptom-free again.
- Show jumper, 32 years: Diagnosis: Hip impingement. After unsuccessful conservative therapy, arthroscopic surgery. Back in tournament competition after 6 months.
- Rider, 65 years old: Advanced osteoarthritis, severe pain also in everyday life. Solution: hip replacement. After rehabilitation, regular recreational riding in the terrain is possible again.
Conclusion: What to do with hip pain in equestrian sports?
- Hip pain is a common problem among riders.
- Causes range from muscular tension to osteoarthritis.
- A thorough diagnosis is crucial.
- Conservative measures such as seat training, physiotherapy, and training help many affected individuals.
- If necessary, a hip surgery or hip replacement can restore quality of life.
- Riding is possible again in many cases after a hip TEP – with patience and targeted rehabilitation.
Recommendation: Consultation at Endoprotheticum Rhein-Main
If you suffer from hip pain that affects your riding, you should seek specialized help.
At Endoprotheticum Rhein-Main in Mainz you will find:
- with Prof. Kutzner, an experienced specialist for hip diseases,
- State-of-the-art diagnostics,
- and comprehensive care – from conservative therapy to hip replacement surgery.
Here, your sporting goals are taken into account. Because the goal is not only freedom from pain in everyday life, but also a return to the saddle.
Make an Appointment?
You can easily make an appointment both by phoneand online .



























