Endoprosthetics and obesity (adiposity) - Joint replacement with risks
Challenges in endoprosthetics in obese patients (overweight)
Obesity, medically termed adiposity (overweight), is on the rise worldwide. According to current studies, over 25% of the population in Germany is obese. At the same time, the demand for hip and knee replacement surgery is increasing due to the aging population. However, joint replacement poses a particular challenge, especially in obese patients. The combination of obesity and joint replacement is complex, as it affects both the risk of perioperative complications and long-term outcomes.
This article highlights the risks, the optimal preparation of obese patients for joint replacement, and the importance of a healthy metabolism for the success of the operation.
Epidemiology: Obesity (overweight, overweight) and joint replacement in numbers
- Rising numbers: With increasing obesity prevalence, the number of patients requiring joint replacement is also rising. Around 50% of endoprosthetics patients have an elevated body mass index (BMI) of over 30 and are therefore overweight.
- Increased risk of osteoarthritis: Obesity (overweight, adiposity) increases the risk of osteoarthritis many times over, especially in the area of weight-bearing joints such as the hip and knee.
Why obese patients have a higher risk in endoprosthetics
Increased risk of infection
Patients with obesity (overweight) have a significantly higher risk of postoperative infections. The reasons for this are:
- Impaired wound healing: The reduced blood flow to the fatty tissue delays healing.
- Increased skin surface exposure: The risk of skin lesions and infections in the surgical area increases.
- Elevated blood sugar levels: Many obese patients suffer from diabetes or insulin-resistant metabolic disorders, which further increases susceptibility to infection.
Technical challenges during the operation
- Limited visibility: The thick layers of soft tissue make surgical access and optimal placement of the endoprosthesis difficult.
- Longer operating times: Studies show that operations on obese patients often take longer, which increases the risk of perioperative complications.
Mechanical stress on the prosthesis
Obesity leads to excessive mechanical stress on the prosthesis, which:
- Easing of restrictions
- Early implant wear
- may result in an increased revision rate
Preparing obese patients for joint replacement
Optimal preparation is crucial to minimize risks and maximize the chances of success for the operation.
1. Weight loss before surgery
Significant weight loss before surgery can:
- Reduce the mechanical stress on the prosthesis,
- Reduce the risk of infection,
- Improve overall fitness and thus enable faster rehabilitation.
2. Benefits of weight loss
- Mechanical advantages: Reduced pressure on the joints also relieves the prosthesis.
- Improved wound healing: A lower BMI leads to better blood circulation and optimizes the body's healing ability.
- Reduction of systemic inflammation: Weight loss can reduce inflammatory processes in the body that could negatively affect the success of surgery.
3. Preparation through physiotherapy
- Strengthening of the surrounding muscles
- Optimizing mobility before the procedure
4. Metabolic Management
A recently published study shows that obese patients in a catabolic metabolic state also have an increased risk of complications during surgery. This underscores the importance of a stable nutritional and metabolic status before the procedure. Consequently, excessively rapid weight loss prior to joint replacement surgery could also be detrimental.
Surgical considerations for obese patients
The implantation of a joint replacement in cases of obesity (overweight) requires specialized surgical techniques to avoid complications.
Minimally invasive techniques
These can be advantageous for obese patients, as they make access gentler and minimize the risk of wound infections.
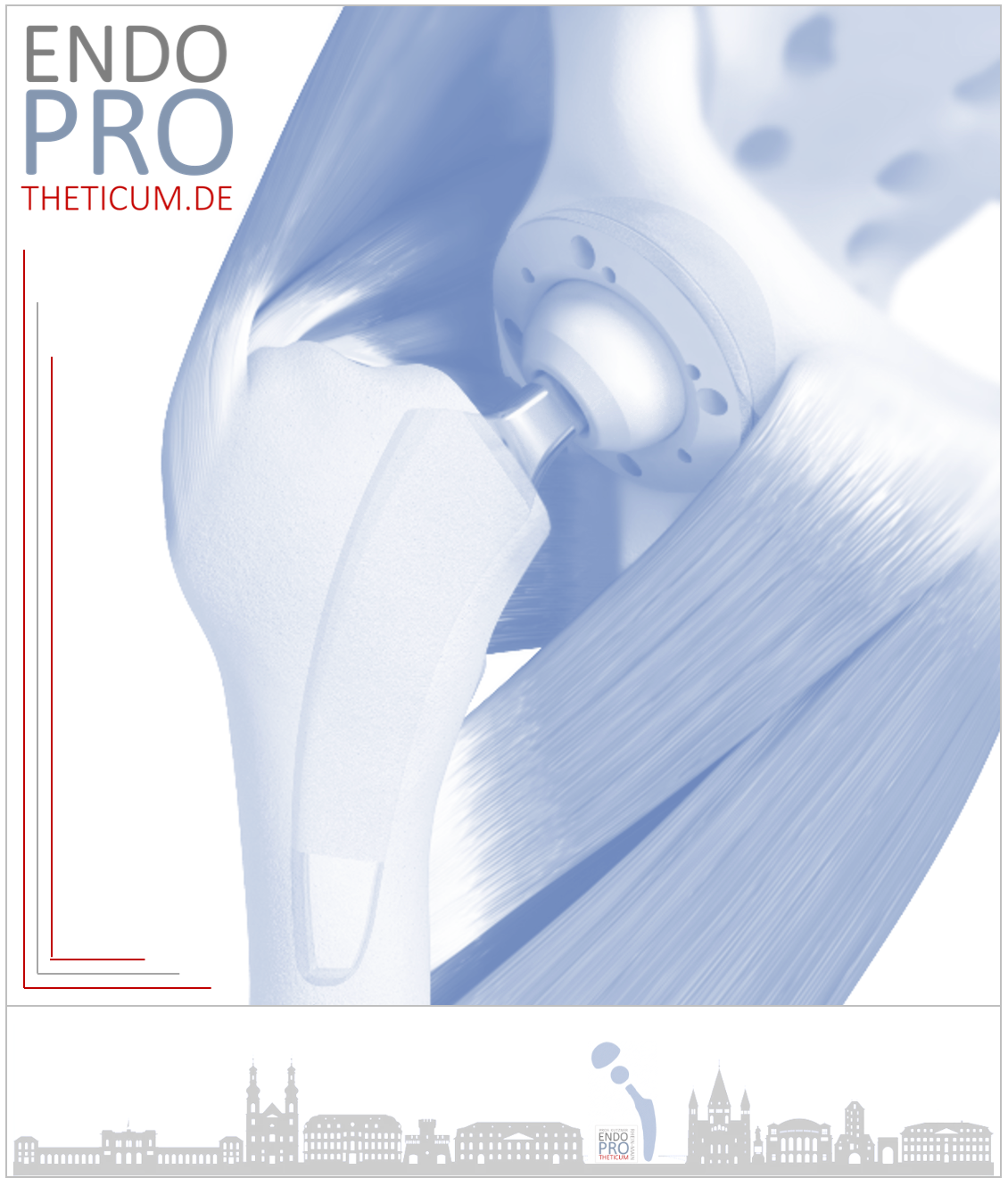
Special implants
In overweight patients, particularly robust implants must be used, as well as ideal bearing pairs that can withstand increased mechanical stress.
Aftercare and rehabilitation
Individual rehabilitation plans
Obese patients require adapted plans that:
- Promoting sustainable mobility,
- Address the stress placed on the new prosthesis,
- Support the gradual development of muscle mass.
Nutrition and Lifestyle
Sustainable weight loss remains crucial even after surgery.
Future prospects in endoprosthetics for obesity (overweight, overweight)
New technologies
- Robotics and navigation systems: Open up more precise implantation possibilities.
Conclusion
Joint replacement in obese patients undoubtedly carries specific risks, but can be successfully managed through comprehensive preparation, specialized surgical techniques, and sustained aftercare. The benefits of weight loss before and after the procedure are undeniable. However, a catabolic metabolic state around the time of surgery should be avoided. The combination of modern medicine and patient-centered care offers obese patients the opportunity to sustainably improve their quality of life.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .