Dislocation of the hip prosthesis – short stem prostheses offer greater safety
How the "anterior tilt" in short-stem prostheses protects against hip dislocations
Dislocation, or the slippage of a hip prosthesis (total hip arthroplasty), is one of the most feared complications after hip replacement surgery. However, modern implant technologies such as short-stem prostheses have significantly contributed to reducing the risk of dislocation. This article explores the reasons for the reduced risk of dislocation with short-stem prostheses and explains why they have become the optimal solution for patients in many cases.
Why dislocations can occur with hip replacements (total hip arthroplasty)
Dislocation of a hip prosthesis can have various causes:
- Suboptimal reconstruction of hip anatomy: If the original anatomy of the hip is not precisely restored, the risk of instability increases.
- Soft tissue tension: Incorrect tension of the surrounding muscles and ligaments can promote dislocation.
- Movement patterns: Risky movements such as strong bending or rotations can dislodge the prosthesis from its position.
The type of prosthesis and the surgical technique play a central role in minimizing these risks.
The advantage of the short-stem prosthesis in anatomical reconstruction
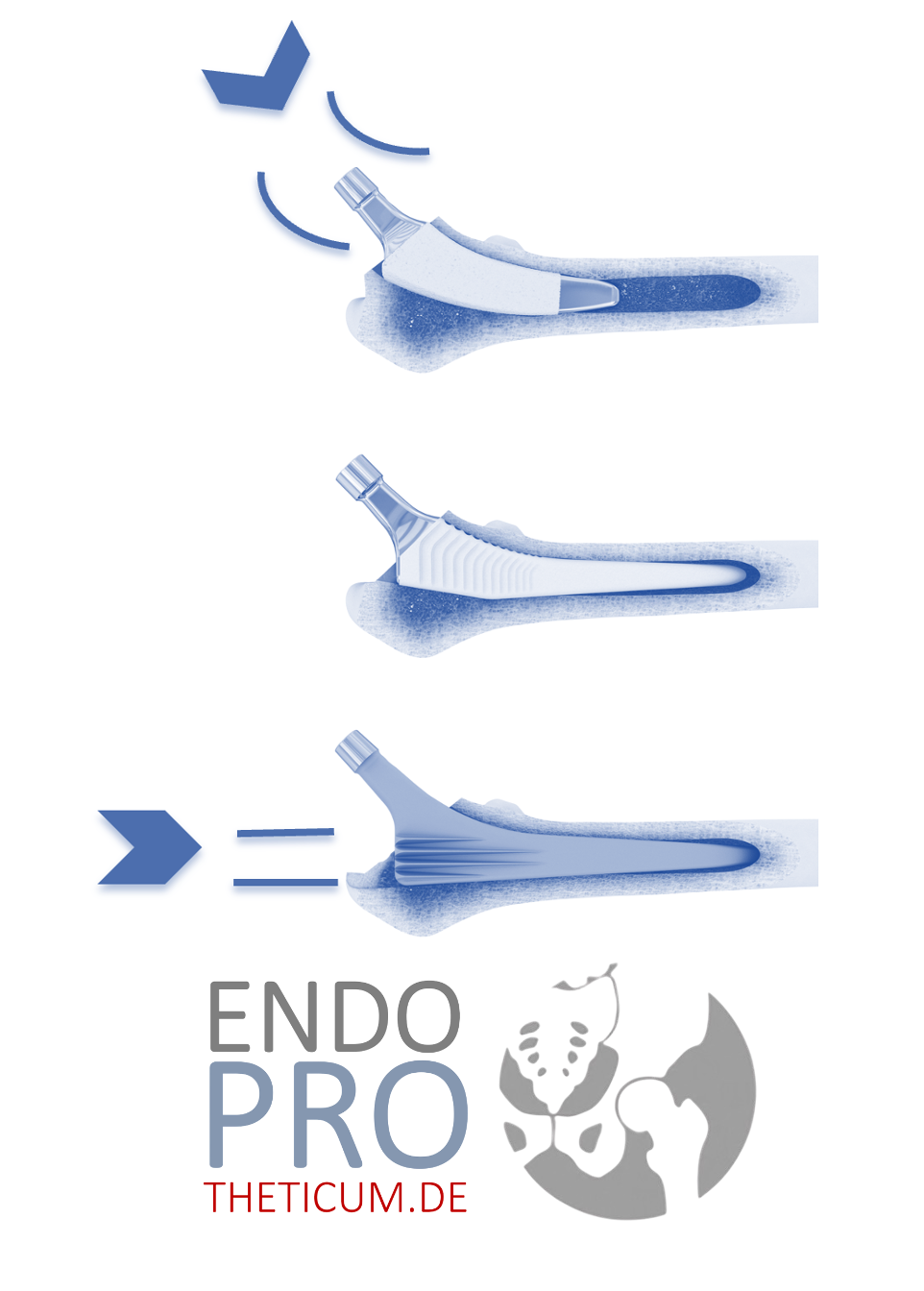
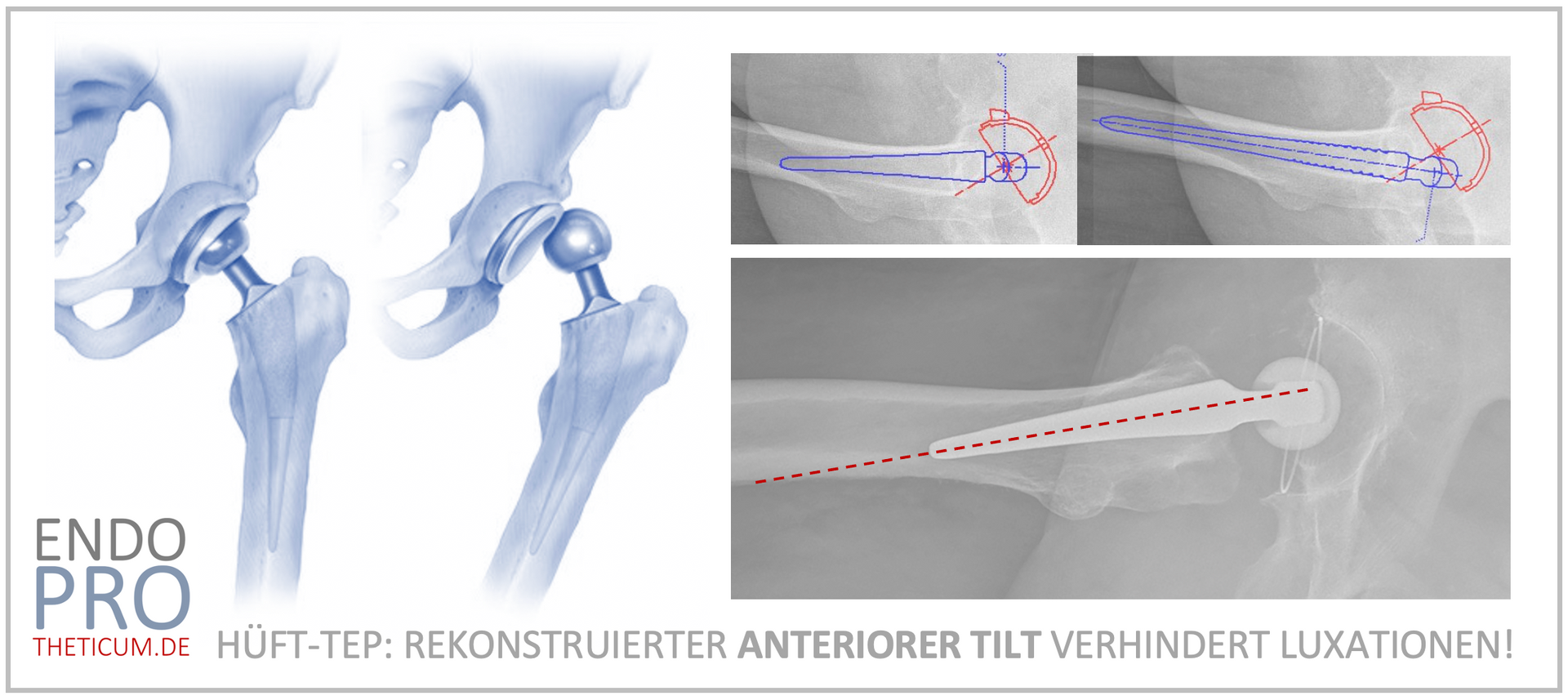
The short-stem prosthesis differs significantly from longer, traditional straight-stem prostheses. Its design allows for a lifelike reconstruction of the individual hip anatomy, particularly by taking into account the so-called anterior tilt .
(see also: " Short stem prosthesis: advantages, challenges and success factors ")
What is anterior tilt?
Anterior tilt describes the natural, forward-facing slope of the femoral neck in the region of the hip joint. This angle ensures biomechanically optimal load distribution and stability in the joint.
With a long stem that is anchored in the diaphysis of the femur, the possibility of precisely replicating this anatomical angle is limited. The diaphysis, i.e., the central tubular part of the femur, forces an alignment along its natural axis, which often does not correspond to the individual inclination of the femoral neck.
Why short stem prostheses support anterior tilt
The short-stem prosthesis is primarily anchored in the upper part of the femur, the so-called metaphysis. This point of attachment allows for a more precise adaptation to the natural inclination of the femoral neck. Due to its shorter stem length, a short stem is less likely to fracture through the bone wall, the cortex, despite this inclination. This results in:
- A biomechanically optimal reconstruction of the anatomy is guaranteed.
- greater stability of the hip joint , as the natural axis of movement is maintained.
- The risk of dislocation is minimized because the femoral head is in the correct position relative to the hip socket.
Straight shaft vs. short shaft: Why the difference matters
Longer, straight shafts require anchoring in the diaphysis. This has several disadvantages:
- Biomechanical conflict: The rigid alignment of the shaft often contradicts the natural inclination of the femoral neck.
- Increased risk of dislocation: The non-anatomical alignment creates instability in the joint.
- More soft tissue damage: When implanting a long stem, more bone and soft tissue often have to be removed, which makes healing more difficult.
In contrast, short-stem prostheses preserve the individual geometry and ensure a functional reconstruction of the hip.
Short stem prostheses: Less invasive, more safety
The shorter length of the short-stem prosthesis allows not only for a better anatomical fit, but also for a less invasive surgical technique. This results in:
- The surrounding tissue and muscles are spared, which accelerates postoperative mobility.
- The bone structure is preserved: This facilitates later revisions, if necessary.
(See also: " Only 90 degrees of flexion after hip replacement: Is that really necessary? ")
Minimizing dislocations in hip replacements – Conclusion
Short-stem hip prostheses have proven to be particularly safe and effective in hip surgery, especially when it comes to reducing the risk of dislocation. Their ability to accommodate anterior tilt and precisely replicate hip anatomy sets new standards in endoprosthetics. Patients benefit from greater stability, fewer complications, and faster recovery. This type of prosthesis can be optimally implanted in specialized centers that utilize state-of-the-art surgical techniques such as AMIS or ALMIS.
For many patients, the use of short stem prostheses brings a significant improvement in quality of life – with maximum safety and a new freedom of movement without pain.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .