Top 20 questions and answers about short-stem hip replacements

1️⃣ What is a short-stem hip prosthesis and how does it differ from a normal hip prosthesis?
A short-stem prosthesis is a modern type of artificial hip joint that preserves natural bone structure as much as possible. Unlike a traditional hip replacement, the short-stem version only replaces the upper part of the femur – the femoral neck is partially preserved. This allows more of the body's own bone to remain, which is a significant advantage, especially for younger or active patients.
Short-stem prostheses are usually implanted without cement and integrate biologically with the bone. The anatomically adapted shape results in a very natural feeling of movement. Many patients report being able to stand and walk confidently again shortly after surgery.
Modern short-stem systems such as Metha®, Fitmore®, and Optimys® have been clinically proven for many years and are considered just as reliable as conventional prostheses – only more bone-conserving.
2️⃣ Why do doctors or patients choose a short-stem prosthesis instead of a standard prosthesis?
The most important reason is the
preservation of valuable bone substance . With a short-stem prosthesis, less bone needs to be removed, which is particularly crucial for younger or athletically active individuals. Should a revision surgery become necessary later, sufficient stable bone structures will still be available.
The shorter stem length offers biomechanical advantages: the force transmission more closely resembles the natural movement pattern, which many patients find more comfortable. Furthermore, short-stem prostheses can often be implanted via
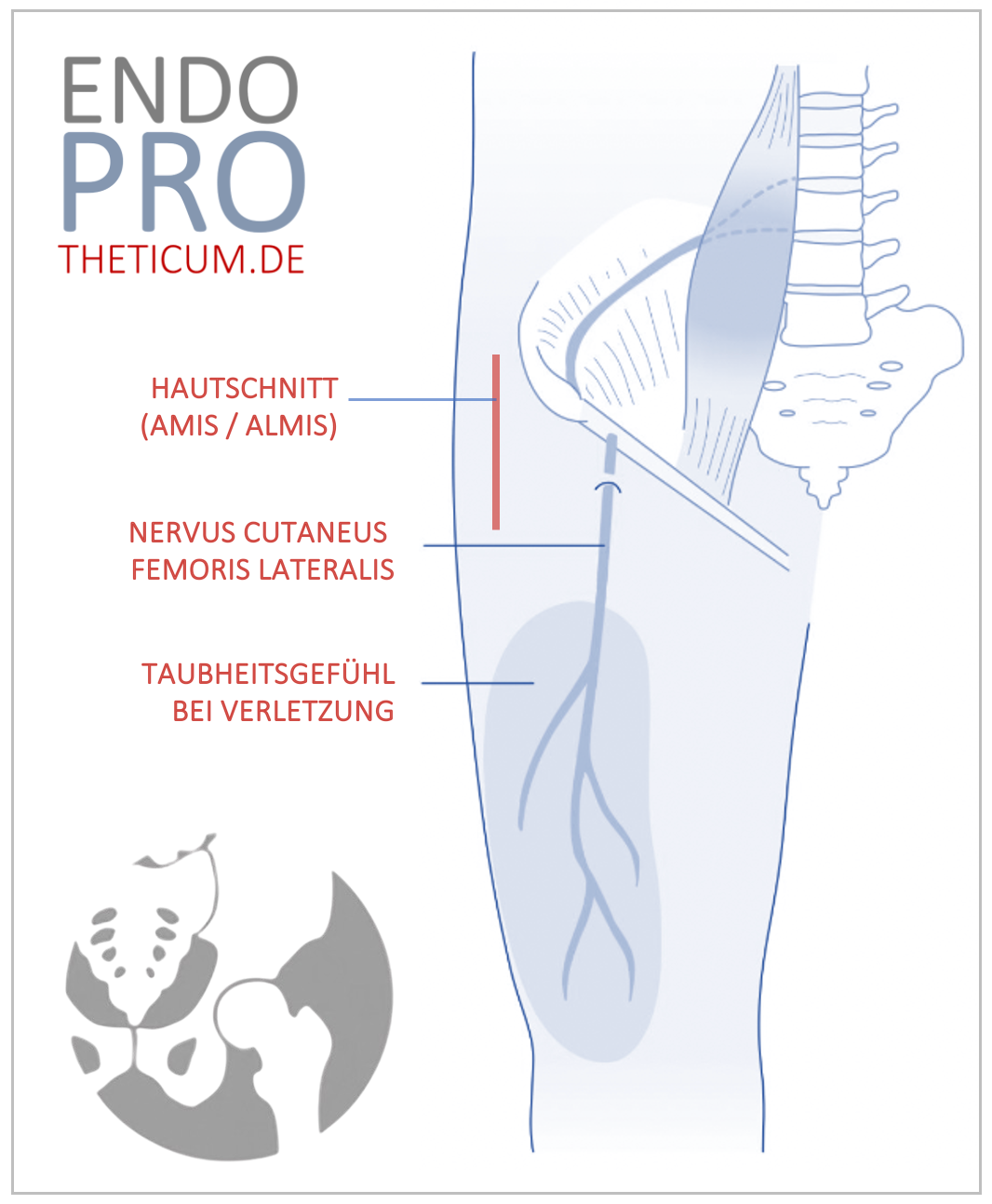
minimally invasive approaches – this means smaller incisions, less blood loss, and faster recovery.
In experienced hands, such as those of specialists like Prof. Dr. Karl Philipp Kutzner at the Endoprostheticum Rhein-Main , excellent results can be achieved with this technique – both functionally and cosmetically.
3️⃣ How does the short stem prosthesis work in the bone?
Short-stem prostheses are generally
anchored without cement . This means the surgeon precisely inserts the stem into the upper part of the femur, where it fits snugly. The rough titanium surface is usually
coated with a microporous material , allowing the body's own bone tissue to grow directly into it.
After a few weeks, the implant is biologically fused – similar to a natural connection between bone and prosthesis. This physiological load transfer continues to stimulate the bone, preventing bone loss.
This cementless approach is considered particularly durable and, if necessary, also allows for a later prosthesis revision with relatively little effort. However, it is important that the exact placement and selection of the prosthesis model be carried out by an experienced hip specialist.
4️⃣ Is the short stem prosthesis a “new” or established method?
While short-stem prostheses represent a modern advancement, they are by no means experimental. Initial concepts emerged as early as the 1980s, but the decisive progress came with titanium alloys and new coatings from the 2000s onward.
Today, long-term results for the most well-known short-stem systems span 10 to 15 years , with survival rates exceeding 95%. This makes them
just as durable as standard prostheses when correctly indicated and implanted.
The technique is routinely used,
particularly in specialized centers like the Endoprostheticum Rhein-Main a proven, safe, and future-oriented alternative – especially for patients who value bone preservation, mobility, and natural function.
5️⃣ For whom is a short stem prosthesis particularly suitable?
Short-stem hip replacements are particularly suitable for
active, young, or young-at-heart with good bone quality. They are frequently used in patients between approximately 40 and 70 years of age whose hip joint is damaged by osteoarthritis, malalignment, or wear and tear.
Athletically active individuals also benefit from this type of implant, as it maintains a very natural range of motion. A prerequisite is that the upper part of the femur (metaphysis) is stable to ensure secure implant anchorage.
Short-stem replacements are not suitable in cases of severe bone loss (osteoporosis) or complex malalignments. In all other cases, however, they offer an excellent option for a long-lasting, bone-conserving, and functional hip replacement .
6️⃣ Is it possible to get a short-stem prosthesis at an older age?
Yes, in principle, this is possible – however, it depends on
bone quality . If the femur is stable enough, a short-stem prosthesis can be a sensible option even for older patients.
The advantage is that less bone is removed, making the procedure less invasive Rehabilitation can also
be faster because the muscles are often better preserved.
bone density, overall health, and desired level of activity are decisive . Many patients over 70 also benefit from this technique – provided it is used in the right setting.
7️⃣ When is a short stem prosthesis not advisable?
A short-stem prosthesis is less suitable if the bone structure in the upper thigh is severely damaged, for example, by osteoporosis, previous fractures, or large cysts. The stability of a short stem may also be insufficient in cases of severe anatomical deformities or after certain prior surgeries (e.g., osteotomies).
In such cases, a standard prosthesis with a longer stem used to ensure maximum stability.
individualized planning using X-rays or 3D imaging is crucial. An experienced arthroplasty surgeon can determine when a short-stem prosthesis is optimal – and when other solutions are safer.
8️⃣ Is the short stem prosthesis also suitable for athletically active people?
Yes – especially for athletically active people, the short-stem prosthesis is often an excellent choice.
Thanks to its anatomically adapted shape and bone-preserving fixation, the natural force transmission in the thigh is largely maintained. This leads to a very harmonious feeling of movement.
Many patients report that they can cycle, hike, or swim again just a few weeks after the operation. Sports with a low impact or jumping component are also generally possible without any problems.
The prerequisites are good bone quality and
expert implantation by an experienced surgeon . Specialists like Prof. Dr. Karl Philipp Kutzner at the Endoprostheticum Rhein-Main provide individual consultations to determine which activities are possible again after the operation.
9️⃣ What materials are used in short stem prostheses?
Modern short-stem prostheses are almost always made of
high-purity titanium or titanium alloys .
Titanium is lightweight, strong, highly biocompatible, and provides excellent conditions for bone ingrowth. The bearing surfaces—that is, the components forming the femoral head and acetabulum—are usually made of ceramic-on-ceramic or
ceramic-on-polyethylene .
This combination minimizes friction and wear and ensures extremely smooth movement.
Furthermore, titanium alloys are corrosion-resistant and biologically inert—the body does not recognize them as foreign material.
The result: long-lasting durability , excellent biocompatibility, and optimal mobility.
🔟 What does "cement-free" mean in the context of a short stem prosthesis?
"Cementless" means that the prosthesis
is not fixed with bone cement , but is inserted directly into the bone.
The surface of the stem is specially coated (usually with titanium or hydroxyapatite structures) so that bone tissue grows into the implant surface .
This biological integration makes the connection particularly stable and durable.
Another advantage: Should a replacement be necessary in 20 or 30 years, a cementless implant can be removed much more easily without significant bone loss.
Cementless short-stem prostheses are currently the gold standard for younger and active patients .
1️⃣1️⃣ How is it ensured that the short stem prosthesis is firmly embedded in the bone?
The stability of the prosthesis is achieved through a combination of a
precise fit, optimal size, and biological integration .
Before the operation, the bone is measured with millimeter precision – often using 3D planning or digital X-ray analysis.
During the procedure, the stem is then inserted precisely into the prepared bone until it fits snugly and securely.
In the first few weeks after the operation, the bone grows directly into the titanium surface.
After about six to eight weeks, the connection is biologically stable.
This combination of mechanics and biology ensures that the short-stem prosthesis permanently anchored and provides a very natural walking sensation.
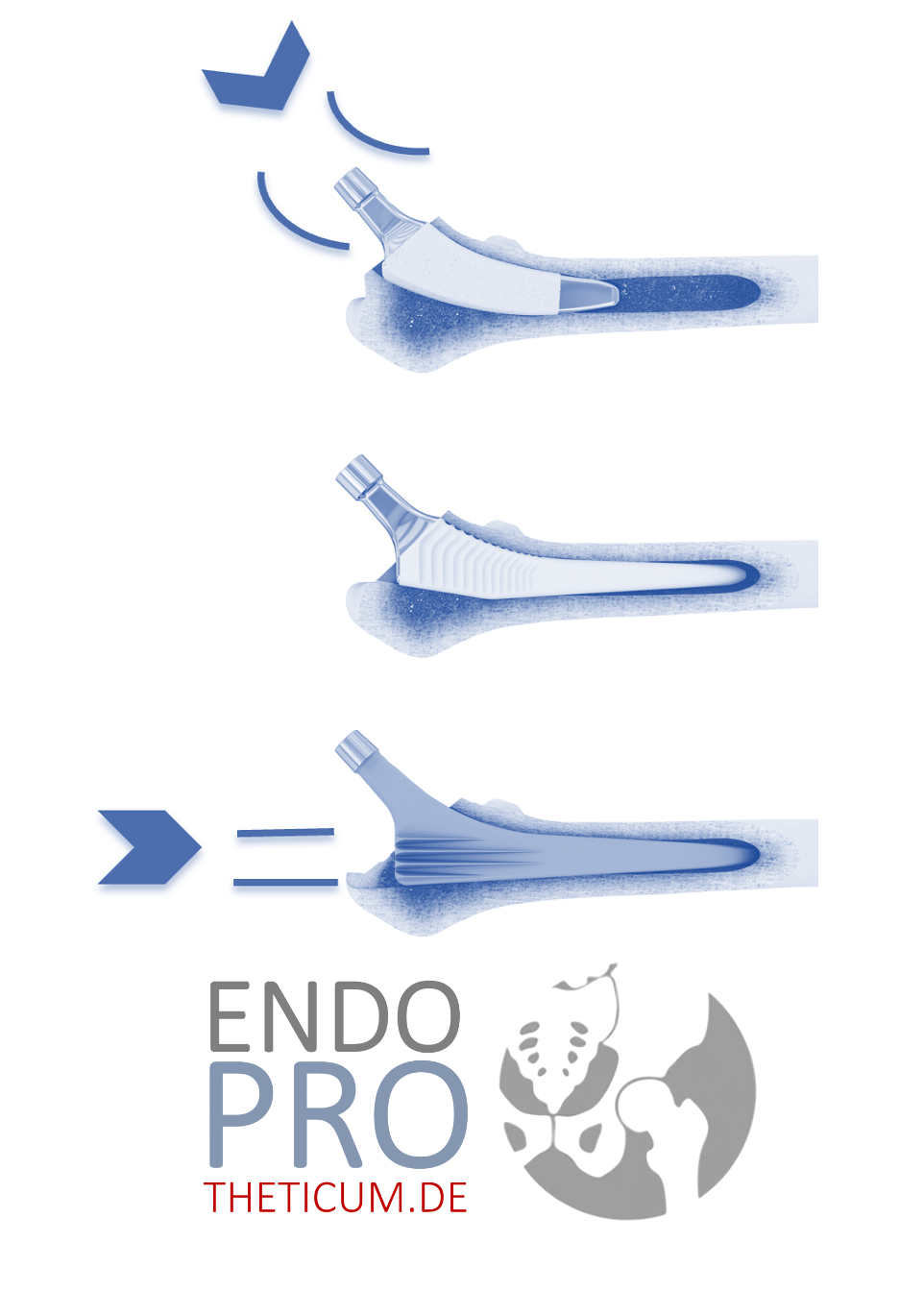
12 What are the differences between different short-stem models (e.g., Metha®, Fitmore®, Optimys®)?
There are various short stem systems that differ slightly in shape, length and anchoring principle:
- Metha® shaft : a proven classic with an anatomically curved shape, particularly suitable for standardized bone conditions.
- Fitmore® stem : has a rather straight shape, which allows for very stable metaphyseal anchoring.
- Optimys® stem : combines a short design with physiological power transmission – ideal for young, active people.
All stems share the goal of preserving bone, protecting muscles, and allowing natural stress .
The selection is always individualized – depending on bone shape, age, activity level, and the surgeon's experience. - Prof. Dr. med. Karl Philipp Kutzner is a proven expert for the Optimys® shaft .
13 How is the operation for a short stem prosthesis performed?
The operation is performed under general or regional anesthesia and usually lasts
between 60 and 90 minutes .
Through a small, muscle-sparing incision, the femoral head is removed, and the femur is prepared so that the short stem can be inserted precisely.
The femoral head and acetabulum are then fitted with the new bearing surfaces.
Because the procedure is minimally invasive, muscles and tendons are largely spared – resulting in less pain and a faster recovery.
Patients can get up and walk under the guidance of a physiotherapist as early as the first day after surgery.
14 How long does the operation take and how long will I stay in the hospital?
The actual surgery itself usually takes about an hour.
The average hospital stay is 5 to 7 days .
During this time, pain management, mobilization, and initial gait training take place.
This is generally followed by outpatient or inpatient rehabilitation to specifically build muscle strength and mobility.
Many patients report that they are able to walk independently again, climb stairs, and perform simple everyday activities after just a few weeks.
15 When can I walk, drive, or work again after the operation?
Walking with crutches is possible as early as the first or second day after surgery.
After about two weeks, short distances be covered without assistance.
Driving is generally permitted again after four to six weeks – depending on the individual healing process.
Light office work is possible after two to four weeks, while physically demanding activities can be resumed after about two to three months.
Regular physiotherapy supports recovery and ensures that the hip quickly feels stable.
16 How long does rehabilitation take after a short stem prosthesis?
Rehabilitation usually begins immediately after discharge from the hospital and lasts an average of
three to four weeks .
The goal is to rebuild muscle strength, balance, and coordination.
Because the procedure is bone-sparing, rehabilitation is generally faster than with standard prostheses .
Many patients report that they are largely mobile again after about six weeks and can easily climb stairs, take walks, or cycle.
In most cases, full weight-bearing capacity is achieved after three months.
17 How natural does walking with a short-stem prosthesis feel?
One of the biggest advantages of a short-stem prosthesis is the
natural gait .
Because force transmission through the bone remains physiological and less material "replaces" the femur, movement and balance usually feel very harmonious.
Many patients report that after a short adjustment period, they hardly notice any difference from their natural gait.
Most even forget in everyday life that they are wearing an artificial joint – especially if the implant has been positioned with anatomical precision.
1️⃣8️⃣ Is it permissible to play sports with a short stem prosthesis – and if so, which ones?
Yes, exercise is expressly encouraged!
Joint-friendly sports such as cycling, swimming, hiking, Nordic walking, cross-country skiing, or moderate strength training .
High-intensity sports involving jumping or twisting movements (e.g., soccer, squash, jogging) should be discussed individually with your doctor.
Generally speaking, those who were physically active before surgery will usually be able to resume their activities afterward with a short-stem prosthesis – often even pain-free and with a significantly improved quality of life.
19 How long does a short stem prosthesis last on average?
Current studies show that modern short-stem prostheses achieve well
over 95% durability after 10–15 years – and the trend indicates that they are likely to be just as long-lasting as traditional hip replacements.
Because more bone is preserved, subsequent revision surgeries are simpler and less risky.
Crucial for longevity are precise implantation, good bone quality, and appropriate weight-bearing .
With regular checkups and a healthy lifestyle, a short-stem prosthesis can easily 30 years or more .
20 What happens when a short stem prosthesis needs to be replaced at some point?
A prosthesis revision is usually only necessary if the implant loosens, wears down, or the bone structure changes.
Thanks to the bone-preserving design, revision of a short-stem prosthesis is significantly easier , as more healthy bone is retained.
In many cases, a short stem can even be used again, or a longer stem if required.
In experienced hands – such as at the Endoprostheticum Rhein-Main under Prof. Dr. Karl Philipp Kutzner – such revision surgeries are performed routinely and with excellent results.
💡 Conclusion: The Endoprotheticum Rhein-Main as a leading institution for short-stem hip prostheses
If you are suffering from hip pain or would like to know whether a short-stem prosthesis is suitable for you, you should contact a specialized center.
At the Endoprotheticum Rhein-Main, under the direction of
Prof. Dr. Karl Philipp Kutzner, you will find one of Germany's leading centers for modern, bone-conserving hip replacement surgery – offering personalized consultation, experience, and innovative technology.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .