Pain after partial knee replacement – what to do?
What to do if pain persists after partial knee replacement surgery?
Partial knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee arthroplasty or partial knee replacement, is a proven and minimally invasive treatment method for osteoarthritis-related knee pain. Despite its advantages and faster recovery compared to total knee replacement, postoperative pain can still occur after partial knee replacement. This comprehensive guide examines the common causes of pain after partial knee replacement and presents effective treatment options. We also address potential long-term complications such as retropatellar osteoarthritis or residual knee joint osteoarthritis.
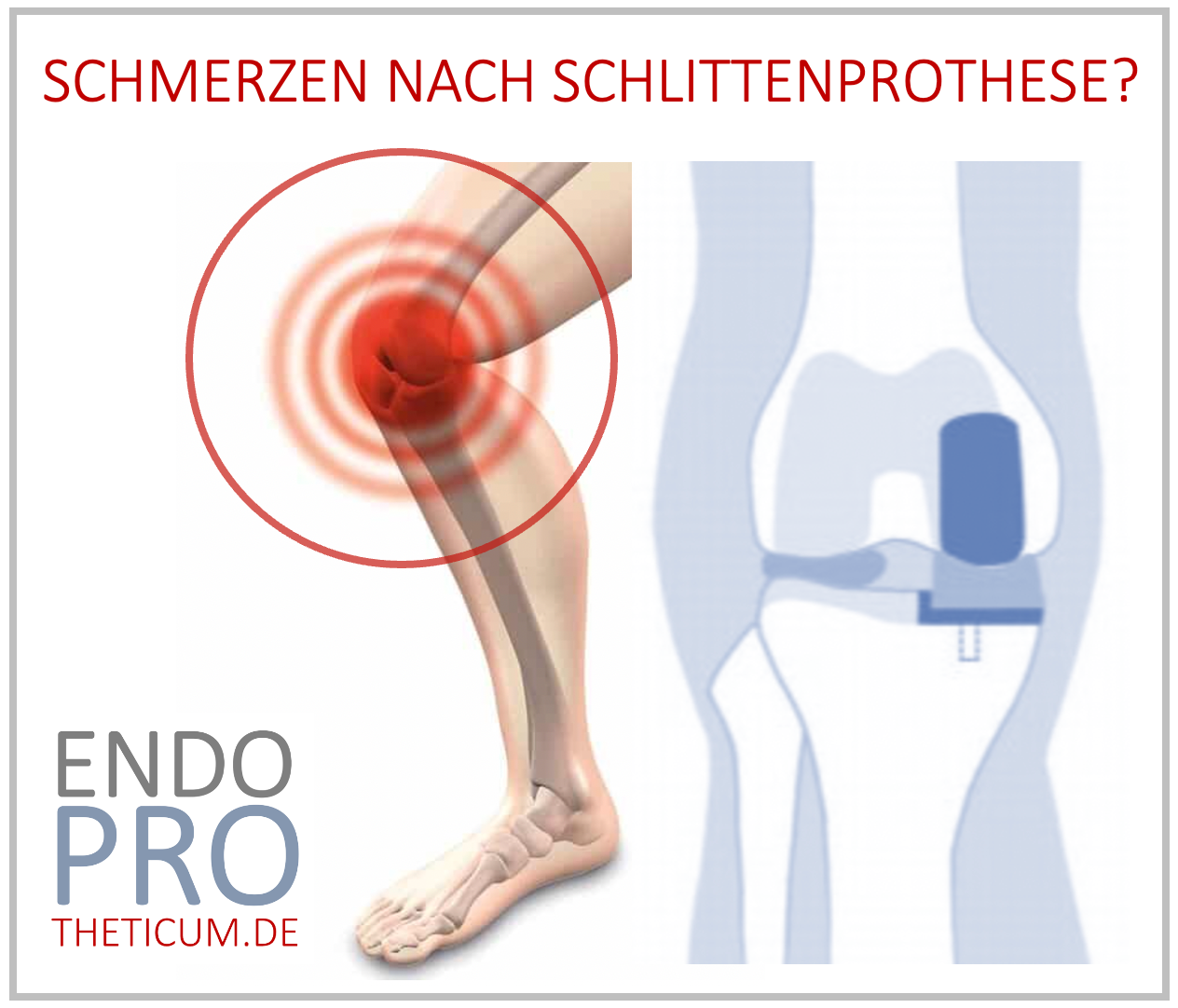
What is a sled prosthesis?
A partial knee replacement is used in cases of advanced osteoarthritis affecting only one side of the knee, most often in the medial compartment or less frequently in the lateral compartment. Unlike a total knee replacement, a partial knee replacement only replaces the affected part of the joint, leaving healthy structures intact.
- Advantages of the partial knee replacement:
- Minimally invasive procedure.
- A more natural feeling of movement.
- Faster healing process.
- Restrictions:
- Not suitable for all patients, e.g., those with inflammatory joint diseases.
Possible causes of pain after a partial knee replacement
1. Postoperative overload
- Description: Immediately after surgery, the knee is sensitive. Pain can occur due to premature or intense strain.
- Therapy: Rest, physiotherapy, use of mild painkillers.
2. Scar pain or skin irritation
- Description: Scarring or nerve irritation in the surgical area can cause discomfort.
- Therapy: Local massages, silicone patches, laser therapy.
3. Instability of the knee joint
- Description: Instability can occur if the ligaments of the knee are overstressed or not optimally balanced after surgery.
- Therapy: Adjustment of rehabilitation, targeted muscle training, possibly surgical correction.
4. Suboptimal prosthesis placement
- Description: Misalignments can cause friction and pain.
- Therapy: Imaging procedures for diagnosis, possibly revision of the prosthesis.
5. Residual knee joint osteoarthritis
- Description: A partial knee replacement only treats part of the joint. Over time, wear and tear can occur in other areas of the joint.
- Special feature: Retropatellar osteoarthritis, in which the cartilage layer behind the kneecap degenerates, is common.
- Therapy: in severe cases, extension to a total endoprosthesis.
Diagnosis of postoperative pain after partial knee replacement
1. Clinical examination
- Palpating the knee to locate the pain.
- Mobility tests to check function.
2. Imaging techniques
- X-ray: Checking the prosthesis placement.
- MRI: Detection of soft tissue changes or remaining cartilage damage.
- CT scan: Detailed analysis in cases of suspected prosthesis malposition.
3. Laboratory tests
- Exclusion of infections through blood tests and joint puncture.
Postoperative treatment approaches
1. Medications
- Painkillers: NSAIDs or paracetamol for pain relief.
- Anti-inflammatories: Cortisone injections for swelling.
2. Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation
- Goal: To improve joint stability, mobility, and muscle strength.
- Measures:
- Manual therapy.
- Electrotherapy.
- Aquatic therapy for joint-friendly strengthening.
3. Operational Options
- Prosthesis revision: In cases of loosening or misalignment.
- Extension to total endoprosthesis: In cases of progressive osteoarthritis in other joint areas.
Long-term problems with a partial knee replacement
1. Progressive joint wear
- Even after successful surgery, wear and tear can occur in the non-prosthetically treated knee area.
2. Retropatellar osteoarthritis
- Those affected complain of pain behind the kneecap.
- Solution: Depending on the severity, adjustment of the therapy or surgical intervention.
3. Loosening of the prosthesis
- Can be caused by material fatigue or insufficient bone substance.
- Treatment options include revision surgery.
Preventive measures to avoid pain
1. Optimal Rehabilitation
- Regular physiotherapy.
- Patient education on the correct way to load the knee.
2. Weight control
- Avoiding excess weight, as this reduces the strain on the knee joint.
3. Adapted sports
- Joint-friendly activities such as swimming or cycling.
Conclusion
Postoperative pain after a partial knee replacement is possible in rare cases and can be triggered by various factors. Precise diagnosis and individually tailored therapy are crucial for effectively treating discomfort and improving quality of life. Despite potential risks, partial knee replacement remains an excellent option for patients with localized knee osteoarthritis, provided the indication is carefully considered.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .