Arthrofibrosis of the knee – no further surgery!
Why surgery usually doesn't help with arthrofibrosis
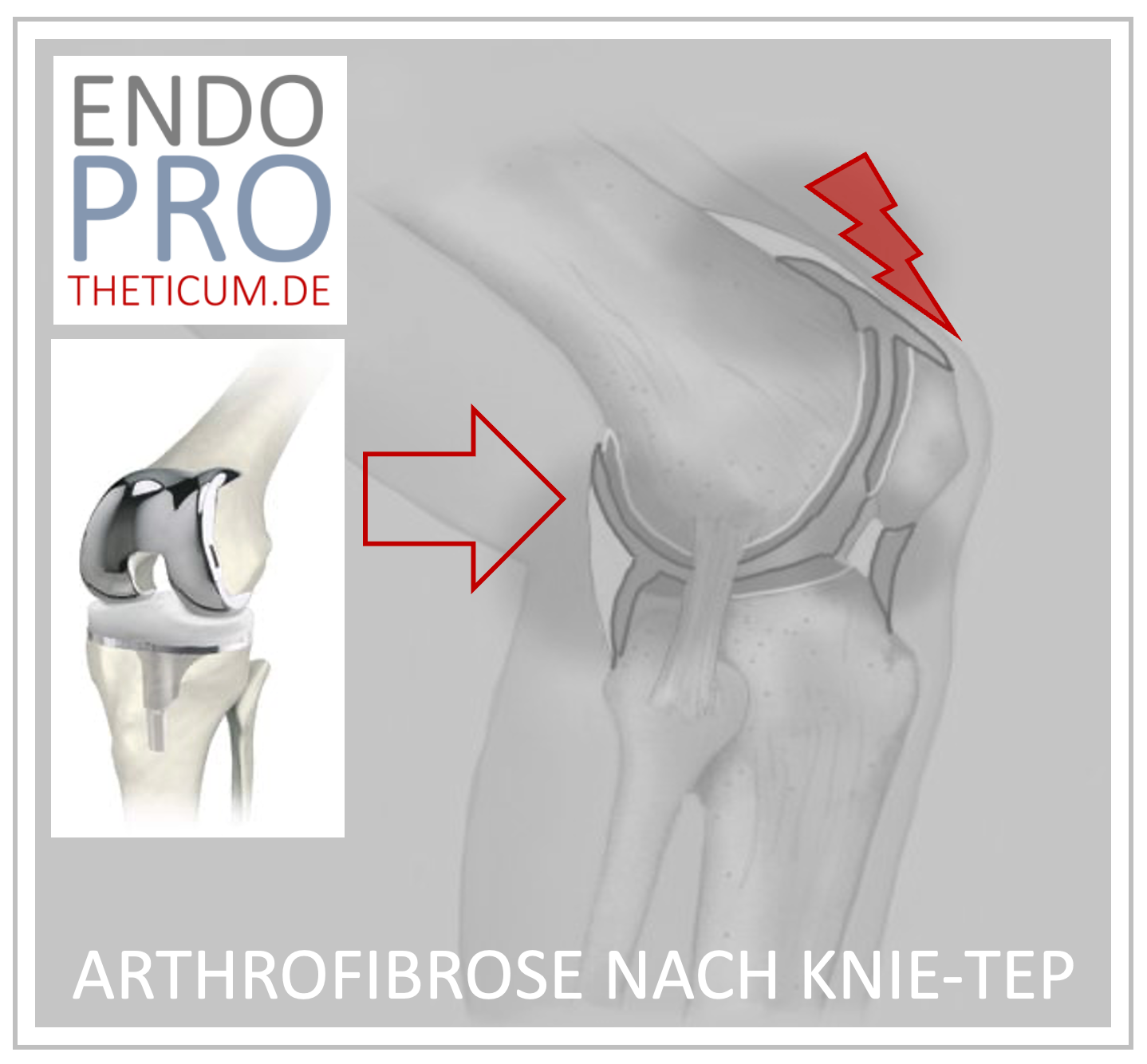
Arthrofibrosis is one of the most feared complications following knee surgeries such as total knee replacement or cruciate ligament reconstruction. The condition is characterized by the formation of excessive scar tissue in the knee, leading to significant restriction of movement, swelling, and often considerable pain. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and, in particular, effective treatment options for arthrofibrosis of the knee – with special consideration of alternative approaches and treatment regimens.
What is arthrofibrosis?
Arthrofibrosis describes an abnormal, excessive formation of scar tissue in the knee joint following surgical procedures or injuries. This disrupts the normal healing process of the tissue, leading to an increase in collagenous scar tissue. This causes a narrowing of the joint space and restricted movement of the knee joint.
Causes and risk factors of arthrofibrosis
Surgical procedures as the main cause
Arthrofibrosis often occurs after procedures such as knee replacements, cruciate ligament reconstructions, or arthroscopic surgeries.
Risk factors
- Multiple operations
- Overextension of mobilization after surgery
- Joint infections
- Genetic predisposition to scarring
- Inadequate postoperative physiotherapy
Symptoms of arthrofibrosis
- Limited mobility: Typical features include extension deficits and a limited flexion angle.
- Pain: Dull pain or a feeling of tension are characteristic.
- Swelling: Affected individuals often report persistent "swollen knees".
- Stiff feeling: Many patients feel as if their knee is "blocked".
Why further operations are often not effective
Surgical removal of scar tissue remains a common treatment option for arthrofibrosis. However, this carries significant risks:
Risk of renewed scarring
Arthrofibrosis often recurs after revision surgery because the surgical stimulus further promotes scar formation.
Lack of long-term results
Studies show that the success of further surgery only lasts in the short term, while the symptoms often worsen again after a few months.
Mobilization under anesthesia
Forced movement under anesthesia can cause microtrauma, exacerbating the problem rather than resolving it. Therefore, mobilization under anesthesia should be viewed very critically and carefully considered today.
Alternative treatment options
Instead of aggressive surgical interventions (poor results), modern treatment approaches rely on conservative and holistic measures.
Therapy regimen to suppress the scar formation stimulus
Special multimodal concepts have been developed that rely on minimally invasive and conservative techniques to effectively treat arthrofibrosis:
- Manual lymphatic drainage: Swelling is reduced to improve mobility.
- Heat and cold therapy: Alternating applications have an anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effect.
- Gentle movement exercises: The aim is to gradually restore mobility without introducing new stimuli.
- Physiotherapeutic measures: Gentle manipulation of the tissue reduces adhesions.
Drug therapy for arthrofibrosis
Medications play an important role in the conservative treatment of arthrofibrosis. The following active ingredients are frequently used:
Prednisolone
Prednisolone is a glucocorticoid with anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects. It inhibits the production of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators that contribute to scarring. However, its use should be short-term to avoid side effects such as osteoporosis or immunosuppression.
Propranolol
Propranolol is a beta-blocker typically used to treat cardiovascular diseases. Studies suggest that propranolol reduces fibroblast activity, thereby inhibiting the formation of scar tissue. It may also help reduce chronic pain associated with arthrofibrosis.
Pregabalin (Lyrica)
Pregabalin is an anticonvulsant frequently used to treat neuropathic pain. In arthrofibrosis, it can help modulate pain sensations and thus improve patients' quality of life. Its effect is mediated by the inhibition of calcium channels in nerve cells.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or diclofenac are often used to relieve inflammation and pain. They inhibit the cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2), thus reducing the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for the pain and inflammatory response.
Long-term forecast and recommendations
With a consistently implemented, conservative treatment plan, many affected individuals have a good chance of regaining their mobility and quality of life. The most important recommendations are:
- Early diagnosis: Rapid detection of arthrofibrosis and immediate initiation of appropriate therapy is crucial.
- Individual therapy plans: No two knees are alike – treatment must be adapted to individual needs.
- Patience and consistency: The therapy requires commitment and perseverance.
Conclusion: Conservative therapy instead of repeat surgery
Arthrofibrosis is a complex complication that presents patients with significant challenges. Surgical approaches are often not a sustainable solution. Alternative methods that rely on conservative measures to control scarring in the long term and restore quality of life are more promising. Here, minimizing manipulation and irritation is often crucial. Forced exercises are frequently detrimental. Early and targeted treatment is the key to success.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT?
You are welcome to make an appointment either by phone or online .